When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may make an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it exercise .
For the first clip , scientist have grown 3D mental capacity mannequin using cells from multiple mass .
The new hybrid creation , which researchers have knight " chimeroids , " are a edition ofbrain organoids — flyspeck 3D models made of tissue that mime the structure and subprogram of a full - size brain . These models are more precise to human biological science than 2D cellular models or animals like lab black eye . Because of this , scientist hope that the modelling willaccelerate drug research and development .
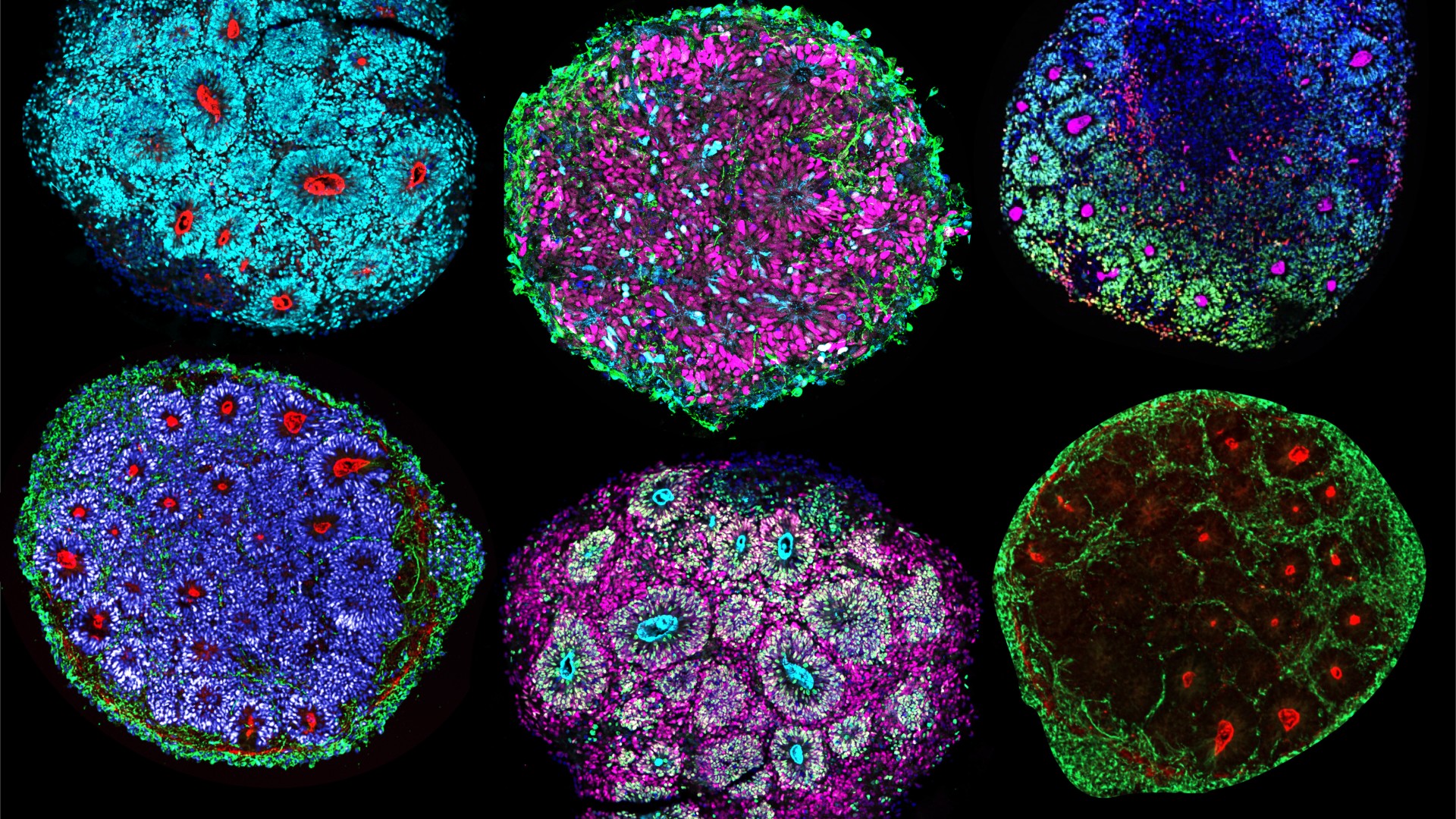
Chimeroids are grown from stem cells from multiple people and contain an array of cell types found in the fetal brain.
Typically , Einstein organoids are develop from cell that are collect from just one donor . This means they ca n’t enamor the genetic unevenness that exists between multitude , which can impact individuals ' mentality development and their reaction to drugs .
Creating chimeroids could overcome this hurdle , according to the scientists behind a new study , issue June 26 in the journalNature . Such a " village in a dish " could be particularly utilitarian in the early stages of drug examination , they said .
Researchers havepreviously grownsheets of brain cells from the radical cells of different people , but this is the first time that 3D models of the brain have been grown this way .

connect : laboratory - develop ' minibrains ' may have just confirmed a leading theory about autism
" Chimeroids are an exciting tool that will be widely sweep up in the field of neurodevelopment , probably with diverse applications,“Aparna Bhaduri , an adjunct professor of biological interpersonal chemistry at the University of California , Los Angeles who was not involved in the research , compose in acommentary of the study .
To make the chimeroids , researchers collect stem cells from five people and then in the lab used growth - inducing chemicals to coax them into growing into brain organoids — each of which had cells from just one person . The scientists then tear the resulting organoids apart and recombined the cells within them to organize chimeroids . This ensured that each chimeroid contained an equal number of cellphone deduct from each person .

After three month , the chimeroids were around 0.12 to 0.2 inches ( 3 to -5 millimeters ) in diam and contained all the same type of cells that are commonly found within thecortex — the outermost layer of the brain — of a foetus .
Separately , the team reveal the chimeroids to two neurotoxic chemicals : ethanol , which is consort withfetal inebriant spectrum disorder , and the antiepileptic drug valproic acid , which canincrease the hazard of birth defects . The team encounter that cells that come from unlike giver responded differently to these drugs , in terminal figure of how extensively the chemicals block their growth , for instance .
— Lab - grown ' minibrains ' help reveal why traumatic genius injury raises dementedness risk

— Mini model of human embryologic brain and spinal electric cord grown in lab
— Could mini blank space - grown organs be our ' cancer moonshot ' ?
If scale up to check cell from even more people , chimeroids could theoretically help determine how patients will respond to drugs before they are tested in a clinical trial , the squad said . They could then be segregate into specific discussion response radical .

" I ’m excited about what the future holds in terms of using organoids , such as the chimeroids , to develop stigma new ways to attain curative innovation for neurologic disease,“Paola Arlotta , co - senior bailiwick author and a prof of base cell and regenerative biology at Harvard University , told Live Science in an electronic mail .
Ever question whysome citizenry build muscle more well than othersorwhy lentigo come out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the capable product line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answer on the website !
Solution to ' cocktail company problem ' could help people with hear red ink

Scientists hijack the human eye to get it to see a brand - raw colour . It ’s shout out ' olo . '
The constant surveillance of modern life could worsen our wit purpose in ways we do n’t fully read , touch study suggest




