When you buy through links on our site , we may bring in an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it works .
Researchers have finally cipher out what happened to a group of nautical animate being that choke out on the ancient supercontinent Gondwana — and the finger direct foursquare at climate change .
It turns out that the so - called Malvinoxhosan biology — an ancient group of water - habitation creature — vanish from Gondwana over a catamenia of 5 million years because sea stage gradually lour , a new survey , print Oct. 13 in the journalEarth - Science Reviews , found . And the mood change that pass over out this brute group has disturbing analog to the alteration pass today .
The supercontinent Gondwana was located around Earth’s South Pole for around 420 million years.
The crusade of their disappearance had " remained an brain-teaser for nearly two centuries until now , " study lead authorCameron Penn - Clarke , an evolutionary scientist at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg , said in astatement . " It ’s a 390 - million - twelvemonth - old murder mystery . "
At the time of the extinction , the field near the South Pole was home toGondwana , which comprised parts of what is now Africa , South America , Australia , Antarctica , the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Peninsula . Gondwana formed around 600 million years ago with the breakup of supercontinentPangaeaand began to break asunder around 180 million years ago .
Gondwana was home to a wide of the mark variety of plants and animals . But some of its least understood house physician were the Malvinoxhosan biology . This group , which lived in water covering what is now South Africa , principally includedtrilobitesand bivalve - similar brachiopods , as well as some mollusks and echinoderms . But they all enigmatically give out off between 390 million and 385 million years ago .
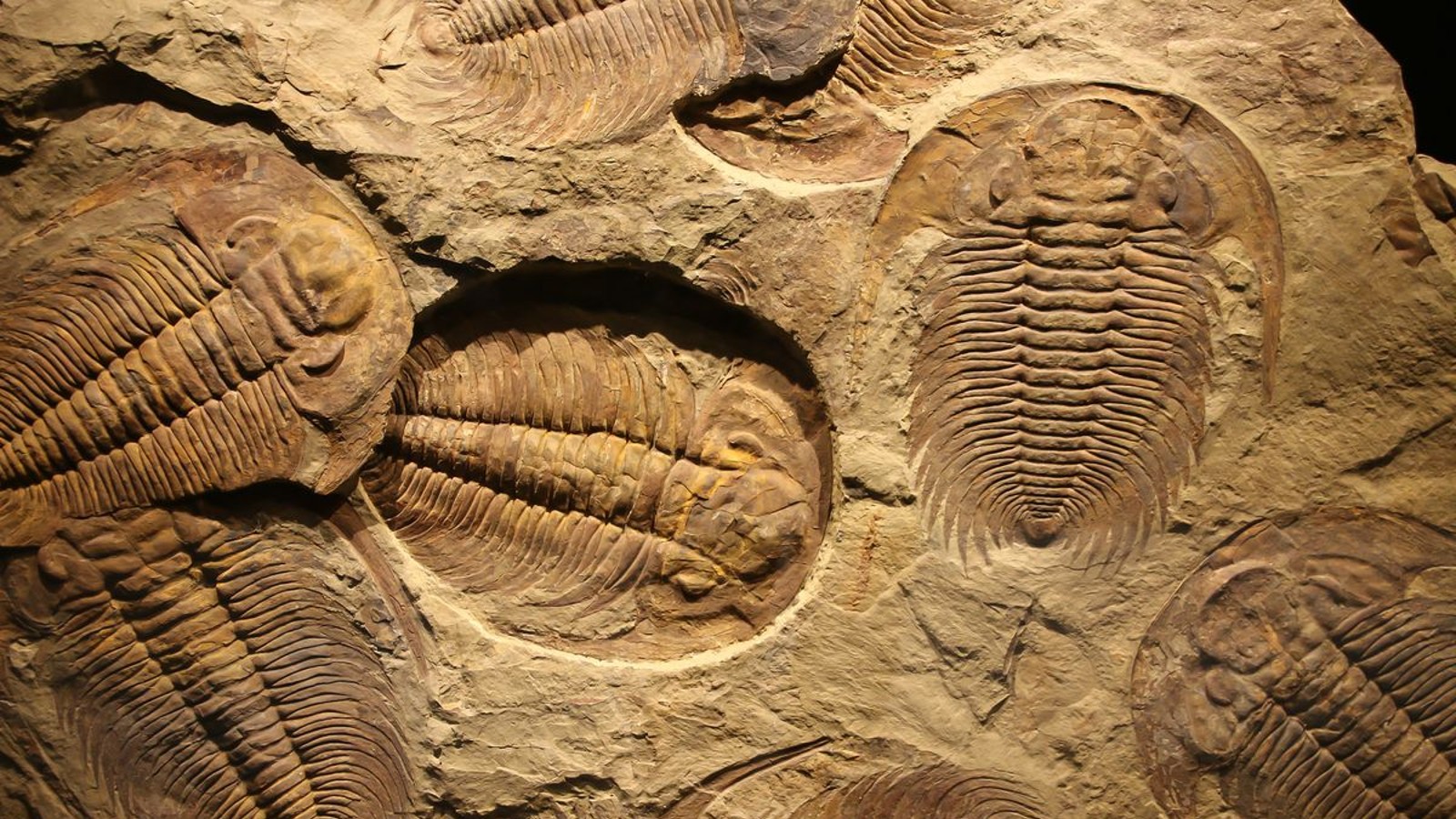

Trilobites were one of the most abundant creatures in the Malvinoxhosan biota.
colligate : Zealandia , Earth ’s hidden continent , was shoot down from supercontinent Gondwana in flood of blast 100 million years ago
To get to the bottom of this cold case , the team reanalyzed one C of fogey belong to the Malvinoxhosan biology , devote particular aid to the location , deepness and geological properties of the rocks that each dodo was found in . This enabled them to patch together a timeline of what happen to the region by sorting it into layers , kind of like " sorting through the layer of a cake , " according to the argument .
The team found seven to eight key fossil layers of the Malvinoxhosan biota . With each new added layer of the " bar , " the number and diversity of fossils minify .
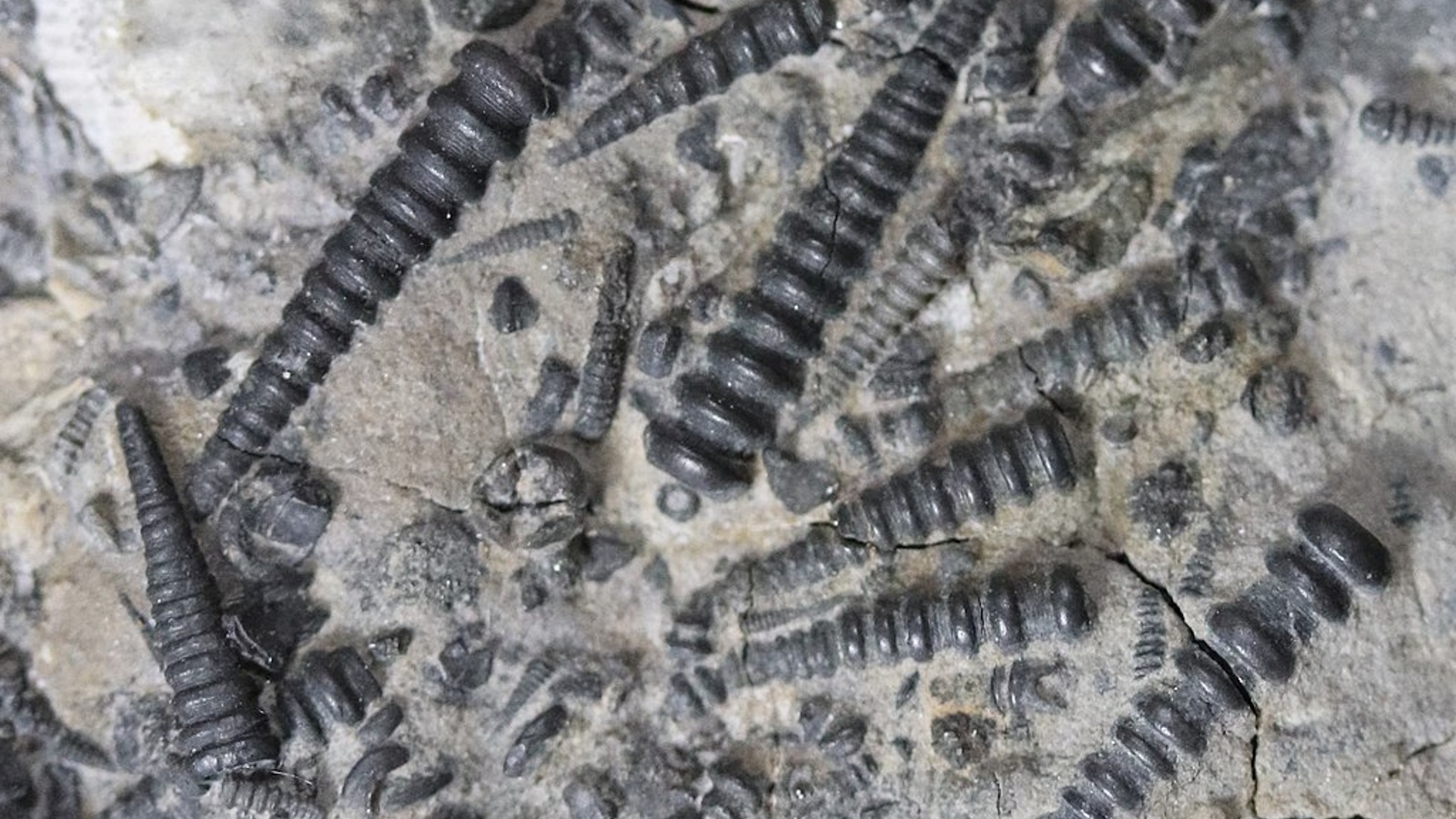

Shellfish-like brachiopods were also common among the Malvinoxhosan biota.
After comparing the dodo layers to local sea level data , the researcher noticed that each of the layers corresponded to slight sea level reduction , which turn out to be the " smoking gun " for these defunctness events , Penn - Clarke said . These decreases did n’t dry up the oceans where these animals lived but in all likelihood triggered climatical changes that the creature could not adapt to .
The investigator call up the Malvinoxhosan biota had evolved to survive in coolheaded waters . But the drop in ocean level disrupted sea electric current around the South Pole have sex as " circumpolar thermal barriers , " which enabled ardent water from the equator to mix with colder southerly water . As a result , the Malvinoxhosan biology " were supercede by more generalist marine specie that are well - adapted to warmer body of water , " Penn - Clarke allege .
relate : mammal may be drive to defunctness by volcanic new supercontinent Pangaea Ultima

The defunctness of the Malvinoxhosan biology likely " led to a terminated prostration " of the ecosystem around the South Pole . It still has not in full recovered those historical levels of biodiversity , the researchers wrote .
— Mangled ' dragon ' fossil were cooked by ancient continent colliding to organize Pangaea
— old ' fish - lizard ' fossils ever found suggest these sea monsters survived the ' Great demise '

— 7 - foot - foresighted arthropods dominate the sea 470 million years ago , ' dainty ' fogey show
The team also opine that this historic extinction mirror what is happening to today ’s diametrical ecosystem as a result of human - causedclimate change .
" This research is important when we consider the biodiversity crisis we are present in the present day , " Penn - Clarke allege . " It demonstrates the sensitivity of glacial environment and ecosystems to change in ocean level and temperature , " he added . " Any change that occur are , unfortunately , lasting . "

30,000 - year - one-time fossilized vulture feather ' nothing like what we commonly see ' preserve in volcanic ash tree
Refuge from the worst tidy sum quenching in Earth ’s history discovered fossilized in China
The constant surveillance of advanced life could worsen our brain function in way we do n’t fully see , disturb studies suggest






