When you purchase through connection on our site , we may garner an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it influence .
tropic cyclone in the Caribbean are make more frequent — and could increase significantly in the coming tenner , grounds find inter deep within the Great Blue Hole suggests .
research worker make a deposit core from the Great Blue Hole swallow hole , situated about 50 miles ( 80 kilometers ) off the coast of Belize , which revealed that tropical cyclones have increased in frequence over the preceding 5,700 years . The scientists depict their findings in a study published March 14 in the journalGeology .

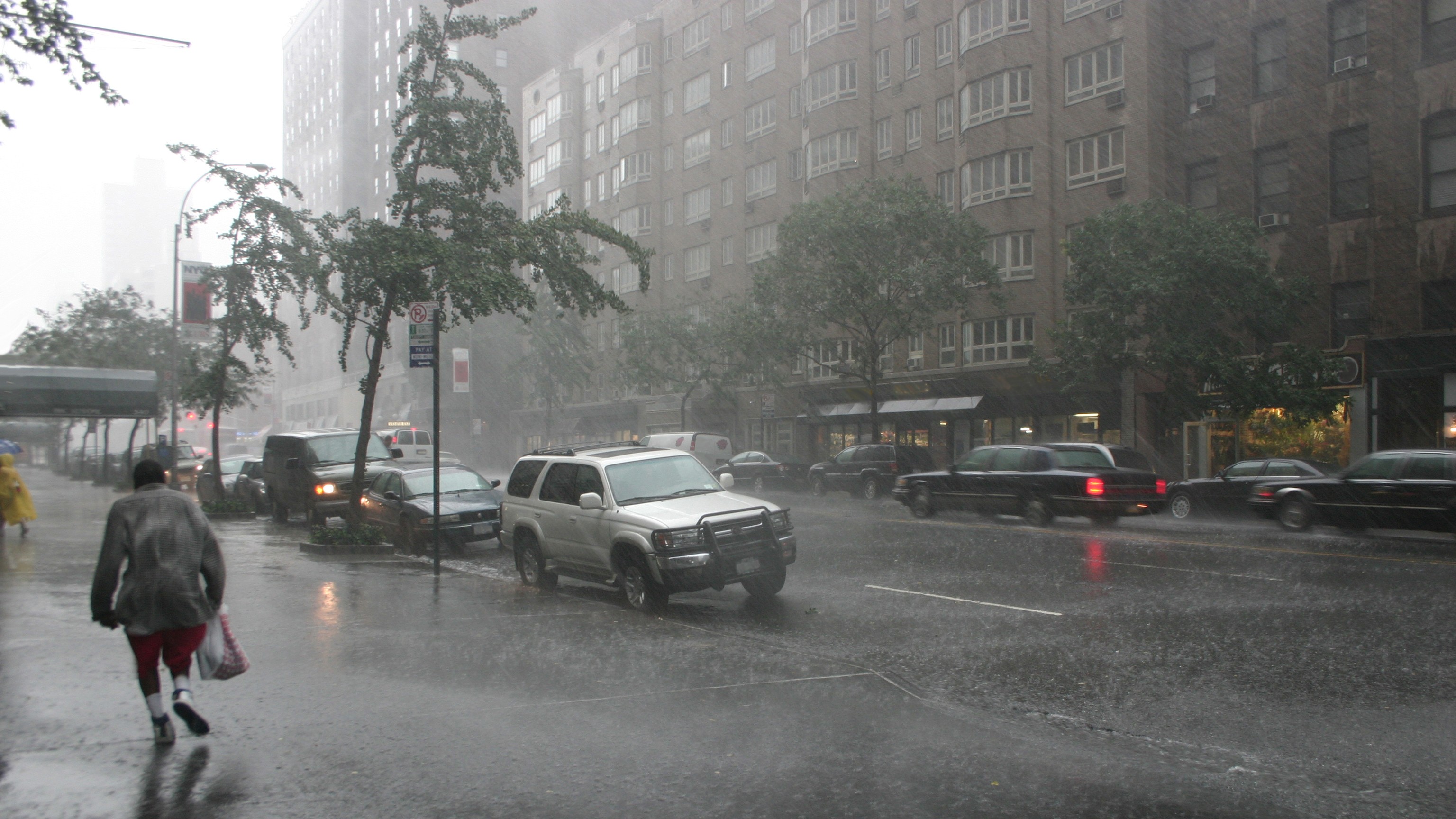
Scientists took a 98-foot core sample from the bottom of the Great Blue Hole off the coast of Belize to uncover patterns of tropical cyclones over the last 5,700 years.
" A fundamental finding of our subject field is that the regional storm frequency has increase continuously since 5,700 years B.P. ( before present tense ) , " study leash authorDominik Schmitt , a researcher at Goethe University Frankfurt ’s Biosedimentology Research Group , told Live Science . " Remarkably , the frequency of storm landfalls in the study area has been much higher in the last two ten than in the last six millennia — a absolved indication of the influence of Modern Global Warming . "
The bottom of the Great Blue Hole
Tropical cyclones are vivid , revolve , small - force per unit area systems that form over fond ocean waters . They transfer rut from the ocean into the upper atmospheric state . Tropical cyclones can be highly destructive , grow strong winds , heavy rainfall and storm surges .
To find out more about these storm over a long period of time , the researchers extracted the sediment core from the bottom of the 410 - foot - deep ( 125 meters ) Great Blue Hole — a massive underwater sinkhole thatformed as ocean levels roseduring thelast ice age , around 10,000 year ago . This sediment core , measuring 98 feet ( 30 m ) long , is the longest continuous book of tropical violent storm in the orbit .
By analyzing the level of sediment in the marrow , the scientist could determine the number of tropical cyclones that had occurred over the past 5,700 years . Two layers of middling - weather deposit are usually lay down every year , enabling the research worker to count back the years like the rings of a tree and equate when violent storm - event sediment layer were deposited .
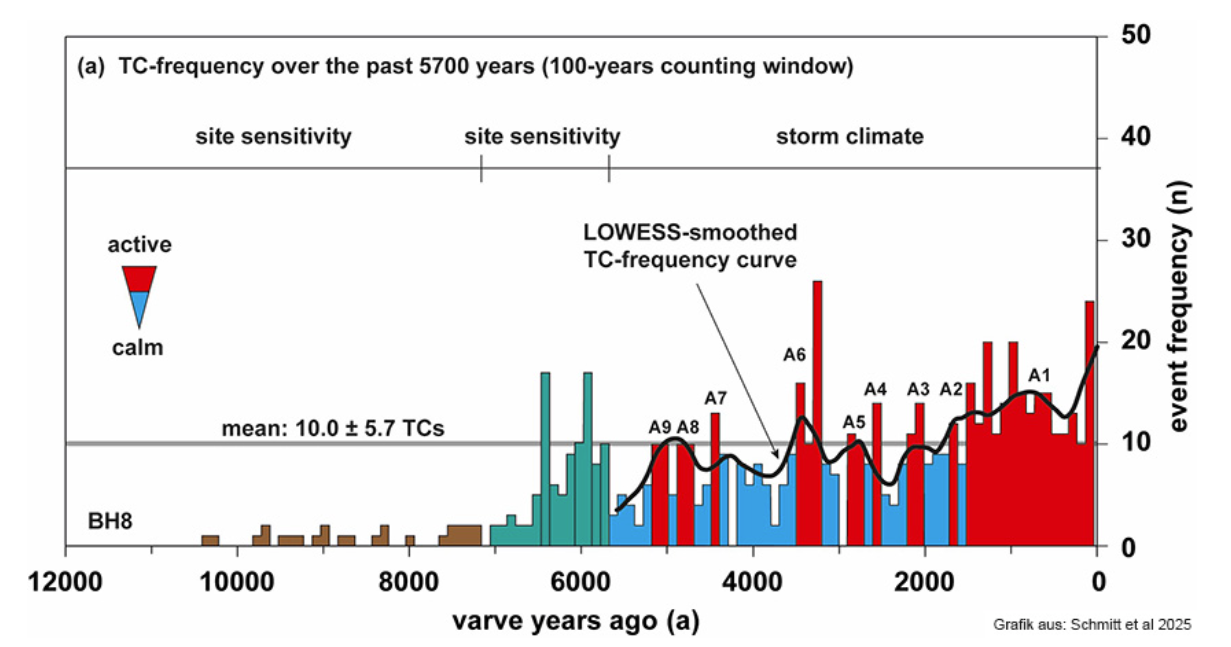
A graph from the study showing the storm frequency in the Great Blue Hole in 100-year counting windows. The black line represents the 5,700-year trend towards increasing storm frequency in the southwestern Caribbean.
The researcher found that tropic cyclones have been get more frequent over the preceding 5,700 years , with a finical increase in frequence since we started burn off fogey fuels during the Industrial Revolution .
" Over the past six millennia , between four and sixteen tropical storms and hurricanes have go past over the Great Blue Hole every hundred , " Schmitt said . In the past 20 years alone , however , the investigator found evidence of nine tropical storms passing over the same part .
There appear to be two factors get the rise in tropic cyclones , the researchers noted . Much of the absolute frequency increase over the retiring few thousand twelvemonth may be due to a southward migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone ( ITCZ ) .

The ITCZ is a realm near the equator where the trade wind of the northerly and southerly cerebral hemisphere come together , leave in low atmospheric pressure , high humidness and frequent thunderstorms . Along the northern bound of the ITCZ is the Hurricane Main Development Region ( MDR ) , where most tropical cyclones in the Atlantic form .
The ITCZ usually moves northward in the summer and southwards in the winter as a result of convert ocean surface temperature , but it has also been steadily move southward over the past few thousand years .
This southward migration of the ITCZ " has probably led to a southward shift of the major Atlantic violent storm genesis region , and a shift of the main storm trajectories from formerly higher to now down in the mouth latitudes , " Schmitt explicate .

A surge in storms
Increases in global sea open temperatures as a outcome of human - causedclimate changeare probably responsible for the recent stiletto heel in tropic storms , and will likely leave in even more frequent tropic cyclone in the coming decades , according to the work .
" The nine modern tempest stratum from the last 20 long time argue that extreme atmospheric condition events in this region will become much more frequent in the 21st century , " Schmitt say .
The researchers predict that as many as 45 tropical storm and hurricane could slay the Caribbean before the end of 2100 .

— Deepest blue hole in the world discover , with hidden cave and tunnels trust to be inside
— ' More people are in harm ’s means ' : tornado are shifting east of Tornado Alley , forecasters warn
— Giant , good - perfect swarm band appear in the middle of the Pacific Ocean — Earth from blank space

" This high telephone number is far in overabundance of what has been the case in the past 5,700 years , " Schmitt said . " An explanation for this eminent storm relative frequency is not the natural magnetic variation in climate or solar radiation , but the reformist global warming during the Industrial Age , follow by fast rising sea - Earth’s surface temperature and stronger globalLa Niñaevents , which create optimum conditions for the growth and rapid intensification of storm . "
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to get into your video display name .