When you purchase through links on our website , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it run .
mankind have an attuned sense of soupcon that connects us to our surroundings , and now , scientists imagine they ’ve discovered a antecedently strange way that we use this sense .
A young study has revealed that cells within the outer stratum of ourhair follicles , the tiny tube in ourskinthat surround hairsbreadth fiber , can detect touch . In response , these cells relinquish chemicals scream neurotransmitter that trip nearbysensory neurons , which relay information about our environs to thebrain . It was previously thought that touch detectors were found only in nerve endings in the skin and nigh hair follicles — not really within the follicle themselves .
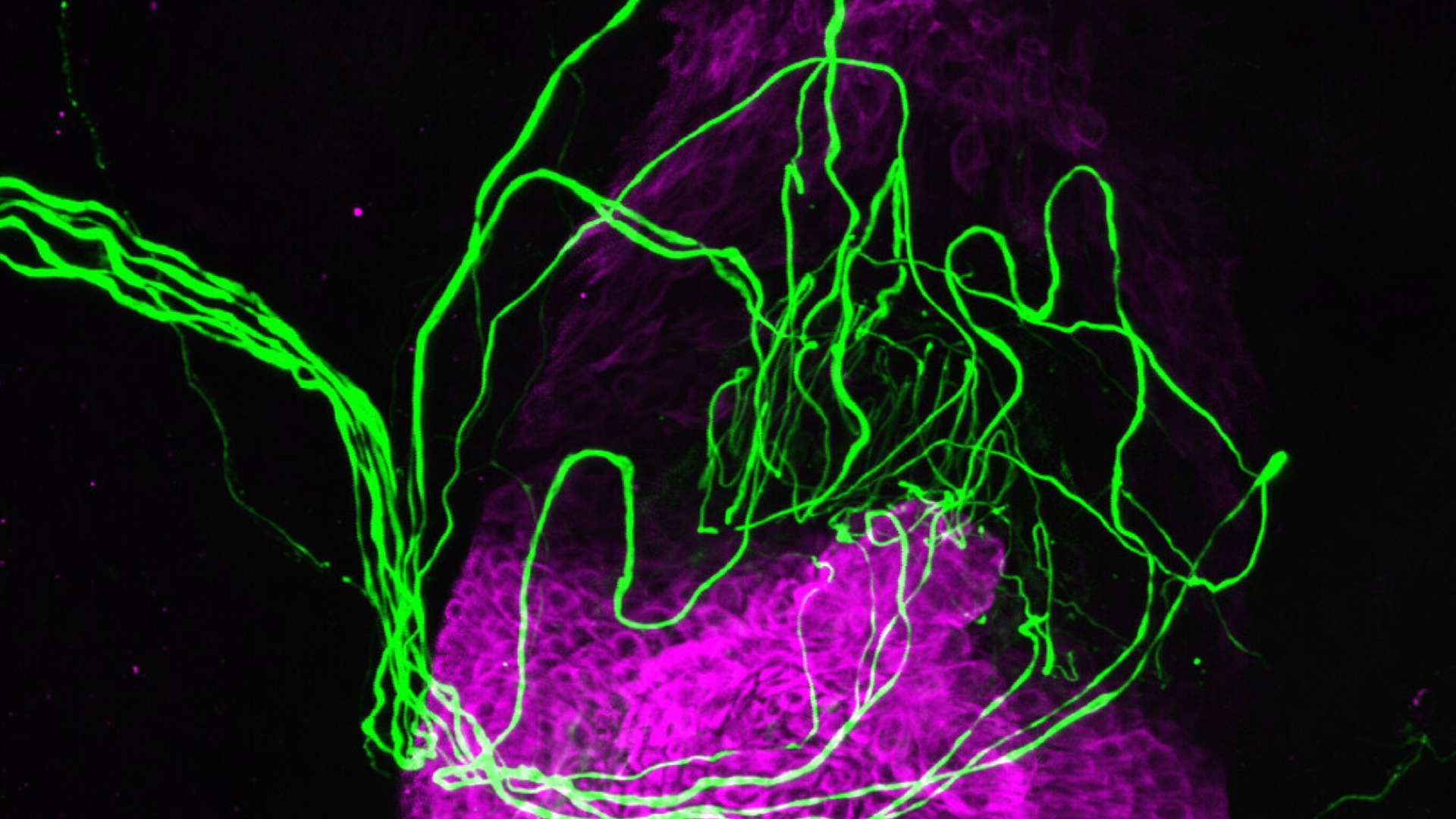
Here, sensory nerves (green) are shown wrapped around a hair follicle (purple). These nerves can be activated by signals from touch receptors within the follicle, a new study shows.
The finding , published Oct. 27 in the journalScience Advances , were drawn from quarantined cellular telephone and have yet to be prove in support organisms . However , if affirm , they may expand the repertoire of known elbow room that humans smell touch , including via the activation of sensory neuron in the skin that notice both touch sensation and the movement of hair’s-breadth .
" The mechanism we have presented is not better , or more sensitive than direct activation of sensorial neurons , which is how we ordinarily process tactual sensation , " co - older study authorClaire Higgins , a tissue paper regeneration researcher at Imperial College London , told Live Science in an e-mail .
" So , we are intrigue to discover what the hair follicle adds to the process of touch sensation and why it has this role , " she said .

bear on : The five ( and more ) human sens
In the new work , the research worker analyzed the factor activity of more than 40,000 cells isolated from human hair follicles and skin . They did this by look atRNAmolecules , which relay instructions for build protein from the cell ’s desoxyribonucleic acid to its protein mental synthesis situation . They found that the hair follicle cell contained three time as many touching - sensitive receptor as the skin cells .
In a separate test , apply tension to human hair follicle electric cell that had been grown in the lab alongside sensory nerve cell head to the activation of the latter .

In another experimentation , the authors discovered that hairsbreadth follicle cells activate the nearby nerve cell by releasing the neurotransmitter serotonin andhistamine , which also triggersinflammation . The cutis cadre also discharge histamine in reaction to touch , but not serotonin , and the authors are queer whether both the cutis cells ' and pilus follicles ' activating could be linked to skin diseases such aseczema . The pelt status is suppose to beexacerbated by histamine - bring about immune cellular telephone called mast cells , but perhaps these two types of touch sensor also act a role .
" Our work is the first to show that pelt cells can also put out histamine , " Higgins said . " While the levels released are much low than that unblock by mast cells , it still suggests a mechanism for skin cells in this disorder , " she said .
This research is still in its early days , but as serotonin and histamine can shape each other’sproduction and releasein many parts of the body , this could defend a new therapeutic avenue .

— How many cells are in the human body ? novel study provides an response .
— New virtual reality cause lets you reach out & touch ' environs '
— Being superfluous - itchy may mean you ’re missing some cells
" We do n’t have sex if this relationship is mirrored in the cutis , but if it is , we can explore ways of modulating serotonin as a way of life to regulate histamine vent , " she enjoin .
Ever wonder whysome people build muscle more easily than othersorwhy freckle amount out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human body make for tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the internet site !












