When you purchase through link on our web site , we may earn an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
scientist have discovered a new eccentric of cellphone in theliverthat play a vital office in repairing damage .
These " leader cells " are creditworthy for dragging hefty tissue into wounds as they cure after injury , essentially filling the gap and appropriate cellular re-formation to fall out .
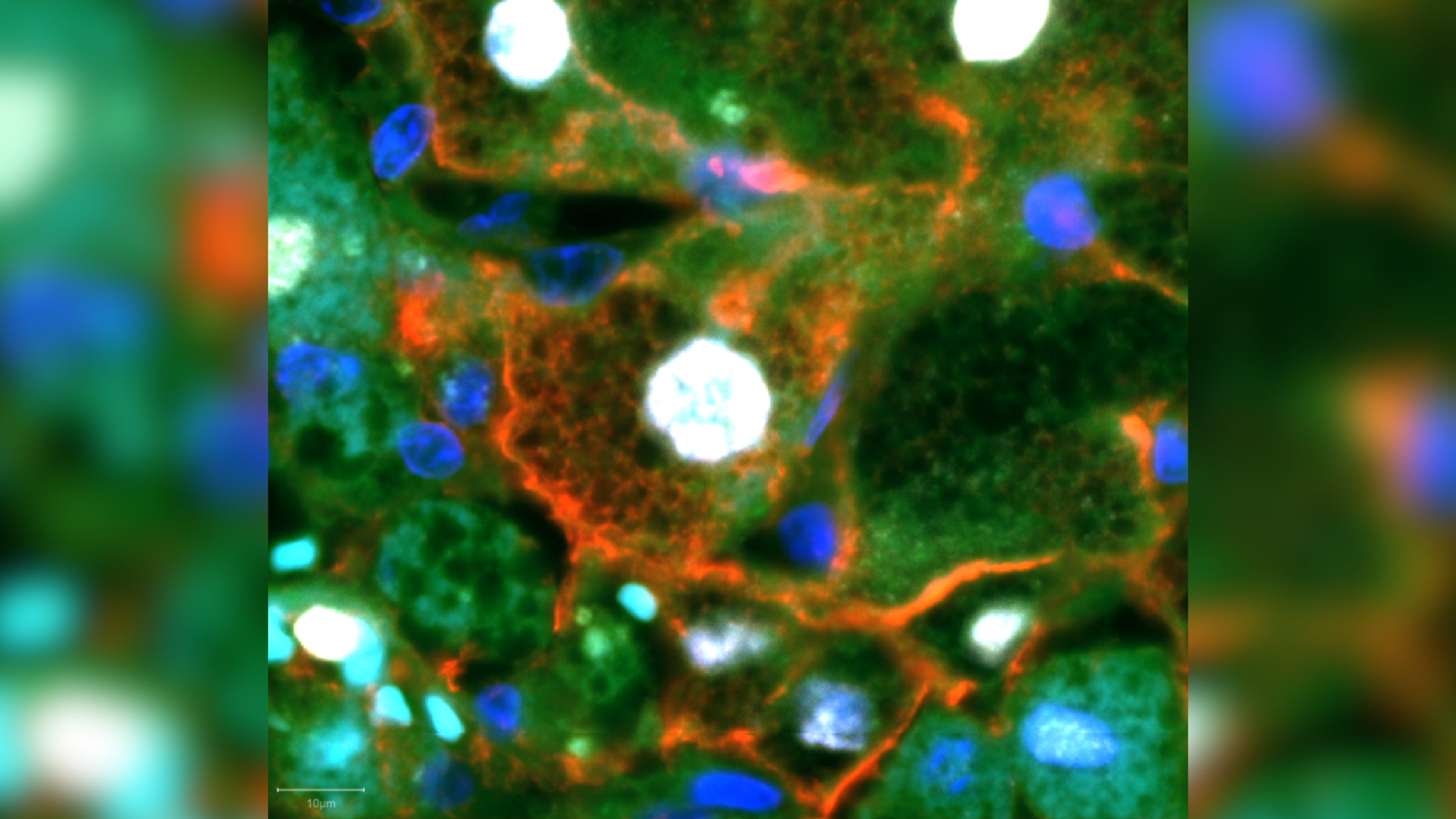
So-called leader cells, pictured under the microscope above, migrate to the edge of a wound, pulling in healthy tissue behind them to close the gap. In this image, the nuclei of these cells can be seen in white and the cell membranes in red
This newfound noesis could be used to create new treatments for liver disease , investigator say . They described their finding in a paper published May 1 in the journalNature .
" thinning - edge technologies have allowed us to study human liver positive feedback in high definition for the first time , facilitate the identification of a cellular telephone type that is critical for liver repair,“Dr . Neil Henderson , co - senior study generator and a professor at the Centre for Inflammation Research at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland , say in astatement . " We hope that our finding will accelerate the find of much - needed Modern treatments for patient with liver disease . "
Related : lashings of unexplained cases of liver disease seen in UK children

The liver helps remove toxins from our ancestry , produces bile to take away waste product of digestion and metabolizes drug . The liver also has the remarkable power to repair itselfafter damage , for illustration due to viral infections such as hepatitis , drug - stimulate injury and alcohol-dependent liver disease .
However , sometimes the liver is so damage that it ca n’t heal quickly enough , leading to acute liver bankruptcy , which affectsmore than 2,000 Americans a yr . The condition can happenwithin 48 hours , potentiallycausing symptomssuch as yellowing of the hide , unreasonable bleeding , brain swelling and multi - organ dysfunction .
reckon on the grounds , some event of acute liver loser , for example thoseinduced by toxic condition , can be reversed with drugs . However , in severe caseful , theonly cureis an emergency liver transplant . There is , therefore , an urgent need for Modern therapy that heighten the liver ’s own natural ability to bring around itself , say the authors of the Modern composition .

To better characterize this healing process , Henderson and colleagues studied liver tissue from patients with acute liver failure who ’d gone on to receive transplants . Although many liver cells from these patients could multiply , their liver still read signs of important legal injury . The team therefore wonder whether repairing the liver required more than just make young cells to interchange the damaged single .
— ruby yeast rice supplements probably damaged this char ’s liver
— Woman ’s liver problem tied to her turmeric supplement

— 5 kid hospitalized with liver unsuccessful person after drink ionized ' Real piss '
So the squad sequenced the genes of every liver cubicle , compare those from affected role with sharp liver failure to ones from healthy individuals . This let them to generate an " atlas " of liver positive feedback , showcasing which cells were fighting and when during the repair process , include the freshly - found drawing card jail cell .
The team also viewed these cells in mouse as they helped resort the liver after acetaminophen - induced injury . They noticed that during wound healing , leader cadre emerge first , to rapidly end the combat injury , before cell proliferation helps further seal the disruption . This suggest that the liver prioritize wound closure before new tissue is made to prevent bacteria get into the organfrom the gutand causingwidespread contagion , the writer wrote in the paper .

Ever wonder whysome citizenry build muscle more well than othersorwhy lentigo total out in the Sunday ? Send us your questions about how the human body do work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your doubtfulness answered on the website !