When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
NASA ’s New Horizons spacecraft has made the most accurate and verbatim mensuration of the total amount of light produce by our population .
The question of just how disconsolate the universe is has vexed astronomers for decades , because from our stretchability of thesolar system , scatter sunshine and interplanetary dust and chalk step in with the measurement of the ambient light bring on by the cosmos ' hundreds of billion of galaxy .

Artist’s illustration of the New Horizons spacecraft flying by the Kuiper Belt object 2014 MU69 on Jan. 1, 2019
Now , more than 18 year after its launch and nine year after mapping the surface of Pluto , the New Horizons spacecraft has produced an reply . float more than 5.4 billion statute mile ( 8.8 billion kilometers ) from Earth in the moth-eaten , dark space of the outer solar system , the space vehicle measured the universe ’s luminousness . The researcher publish their finding Wednesday ( Aug. 28 ) in theThe Astrophysical Journal .
The background knowledge of seeable light add up over the existence ’s lifespan ( call off the cosmic visual desktop or COB ) is important to astronomer because it helps them to cope with the luminance coming from stars and the exteriors of sinister holes with that predicted by theory .
Related : boost ' cocoon of energy ' may power the bright supernovas in the universe

If these two figures delineate up , then our current impression of the universe is mostly right ; but if they misalign , it could mean that there ’s more going on in the universe than we presently jazz . Yet accurately measuring the COB from Earth , or even the interior solar system , is exceedingly difficult .
" People have tried over and over to mensurate it directly , but in our part of the solar organization , there ’s just too much sunlight and reflected interplanetary detritus that scatters the light around into a fuzzy fog that obscures the light-headed light from the distant universe , " co - authorTod Lauer , a New Horizons co - investigator and an uranologist at the National Science Foundation NOIRLab in Tucson , Arizona , said in the statement . " All attempts to evaluate the intensity of the COB from the inner solar organization suffer from large uncertainties . "
To overcome this trouble , the New Horizons space vehicle waitress until it was far aside in the Kuiper Belt , on its room to interstellar distance . Then , it used its dead body to harbour the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager ( LORRI ) from the sun ’s light and indicate itself away from theMilky Way ’s brilliant core group . The spacecraft then snap two - dozen snap of the universe .

— James Webb telescope discovers most distant supernova ever meet — Enormous explosion in ' Cigar Galaxy ' reveal uncommon type of star never seen beyond the milklike Way
— Hubble track farthest and most hefty dissipated radio burst back to ' blob ' of 7 galaxies
After carefully calibrate the sluttish levels watch with those take on in infrared by the Planck satellite to screen out detritus , the researchers get at their estimate for the cosmos ’s seeable Inner Light — a beamy intensiveness 11.16 nanowatts per steradian .
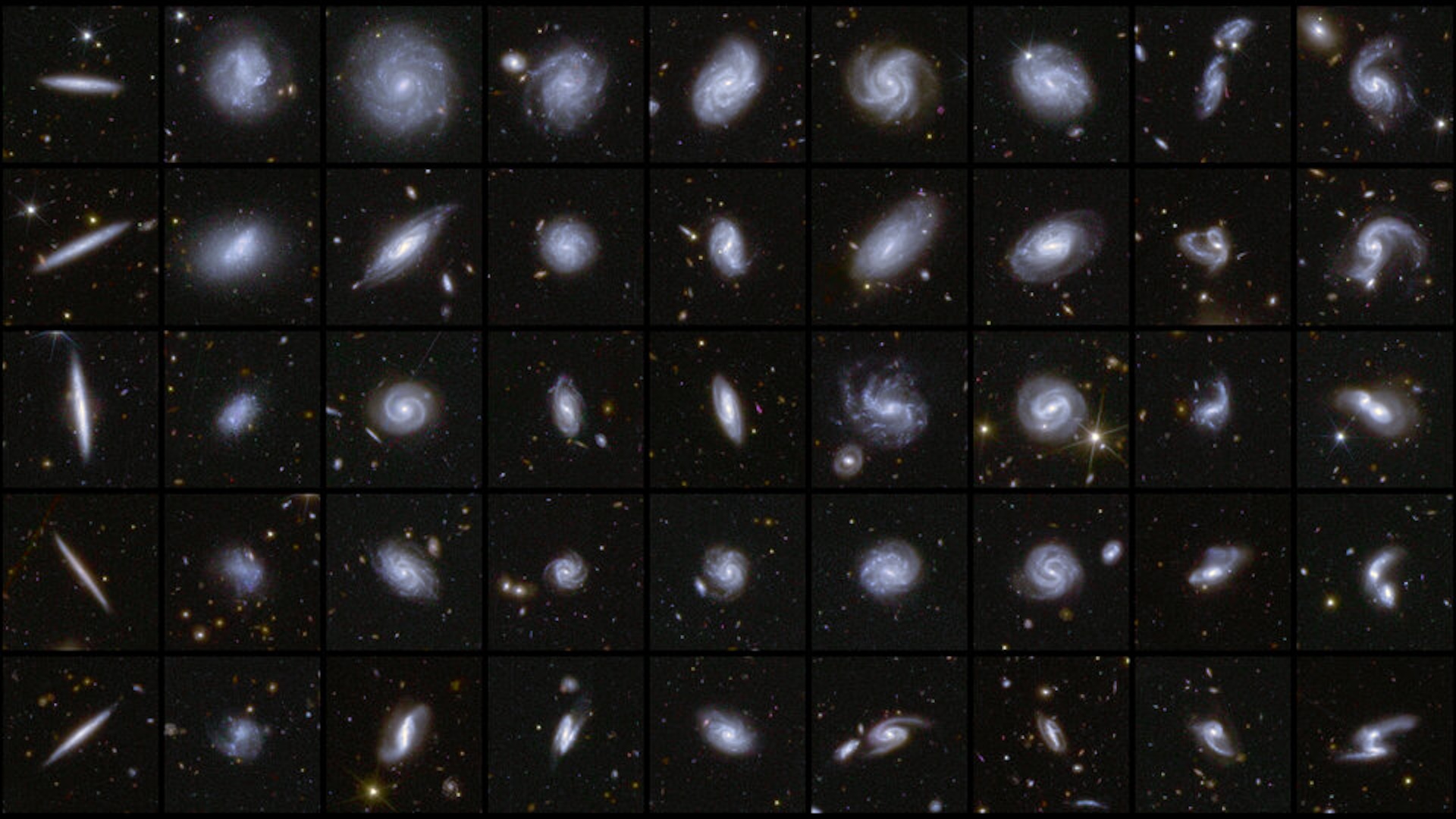

The result was consistent with the light intensity thought to be generated by all galaxies over the preceding 12.6 billion years , meaning that ( at least in thevisible spectrum ) astronomers are unlikely to be missing anything swelled in their models .
" The simplest interpretation is that the COB is completely due to galaxies , " Lauer said . " Looking outside the galaxies , we encounter wickedness there and nothing more . "