When you buy through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it works .
Researchers have reveal more than 140 section of the human genome tied torestless pegleg syndrome(RLS ) , a neurological condition that affectsup to 10 % of the U.S. population .
These stretches of desoxyribonucleic acid in the genome are known as genetic jeopardy venue , and prior to the new cogitation , only 22 were know to be tie to RLS . The new research , published Wednesday ( June 5 ) in the journalNature Genetics , increases that telephone number to 164 .

More than 160 genetic risk factors are tied to restless legs syndrome, new research suggests.
Three of the newfound risk locus are locate on the Xchromosome , which females typically pack two of in each cellphone while males stock only one . RLS ismore coarse among women than work force , but free-base on their new effect , the investigator do n’t think this departure is explain by the trio of risk loci on the X chromosome .
" This study is the largest of its kind into this common — but poorly understand — condition,“Steven Bell , co - senior study source and an epidemiologist at the University of Cambridge , say in astatement . " By understanding the genetic fundament of restless legs syndrome , we hope to find good way to manage and treat it , potentially improving the lives of many million of masses affected worldwide . "
Related:10 unexpected ways Neanderthal DNA affects our wellness
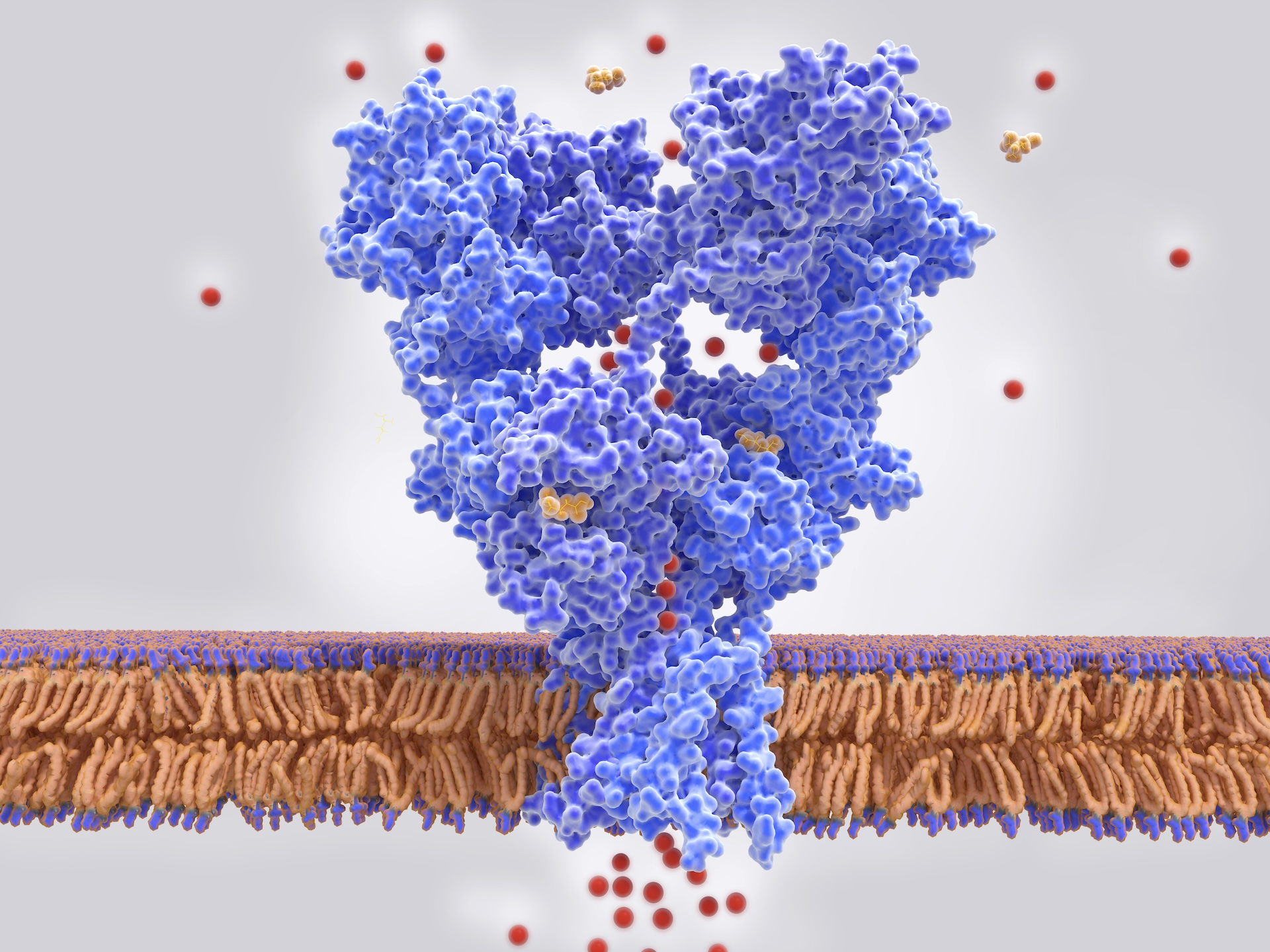
Two of the genetic risk factors for restless legs syndrome that were identified in the new study code for receptors (blue structure) that bind to the chemical messenger glutamate.
This breakthrough could also be used to help predict a person ’s peril of evolve RLS , the study authors write in their paper .
RLS , also called Willis - Ekbom disease , cause people to experiencean unpleasant crawl or creeping sensation in their legs , as well as the irresistible itch to move them . These sense impression are often more intense in the evening or at night , while people are rest . The condition isthought to be underdiagnosed , and when it is diagnosed , itsexact drive is often unknown . RLS can arise due to another condition , such as Fe deficiency , kidney disease orParkinson ’s , and it ’s likely connect to disfunction in part of the brain that usesdopamineto ascendence campaign .
There iscurrently no curefor RLS , but certain intervention , such as anti - seizure drugs , can help ease a person ’s symptoms .

In the new study , the research worker pooled the data from several , tremendous genome - encompassing association studies , which compare the DNA of masses with a given disease to that of people without it . In all , the new research include datum from more than 116,000 the great unwashed who had RSL with more than 1.5 million people without the term .
Notably , all those included were of European derivation , which may fix the relevance of the determination in other demographic .
The investigator found no strong differences in transmissible risk factors between the sexes , even though RLS is more common in women . They recollect this suggests that RLS is rule by a combination of genetic , environmental and hormonal factors , so the genetic risk loci do n’t prescribe a individual ’s risk in closing off .

Among the newfound danger loci , the team hunted for genes that might already be targeted by existing okay drug — the goal was to get treatments that potentially be give to patients in the near future .
— ' Fossil viruses ' imbed in the human genome linked to psychiatrical disorders
— unexampled genetic cause of intellectual disablement potentially uncovered in ' dust DNA '

— The same genetic mutation behind gorillas ' small penises may embarrass birth rate in men
They notice 13 endangerment locus targeted by existing drugs , including two genes that code for so - calledglutamate sensory receptor . These sensory receptor are protein found on nerve cells that play a vital function in the transmission of signals throughoutthe neural system . Preliminaryclinical trialssuggest that targeting these two sense organ genes with anti - epileptic drug — namely , perampanel and lamotrigine — can benefit some patients with RLS .
In summation to identifying potential drugs , the team ran a statistical analysis to see if RLS raise the jeopardy of any other conditions . This suggested that RLS may be a risk of exposure factor for developingtype 2 diabetes , although retiring studies on thepotential link have found mixed results . As such , " these event should not be overinterpreted , " the researchers cautioned — they require to be corroborate in succeeding research .

Despite their restriction , the determination may bring doctors one stride closer to being able-bodied to predict someone ’s risk of infection of evolve RLS and sympathise the wider impacts the condition has on the great unwashed ’s wellness , the team said .
Ever marvel whysome the great unwashed build brawn more easy than othersorwhy lentigo fall out in the sun ? Send us your interrogation about how the human soundbox works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject strain " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question serve on the website !
Legendary ' women of the sea ' in South Korea freedive well into their 80s . A new subject field hints at how .

What is xeroderma pigmentosum ? The rare genetic disorder that forces citizenry to avoid sunlight
What ’s shroud under Antarctica ’s ice ?




