When you purchase through link on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Inflammation can reawaken dormant viruses in the mind , which may help to explain why concussions often precede dementia , a new study finds .
Brain injuries like concussionsraise the risk of infection of dementedness , and the more blows someone takes to the head , the higher that jeopardy becomes , evidence suggest . scientist are investigating what hap in the encephalon after combat injury that might lead to changes bind to dementia — for case , a buildup of abnormal protein and the malfunction and death of brain cellphone . Such change are find inAlzheimer ’s diseaseandchronic traumatic encephalopathy(CTE ) , a disorder that ’s of late gained recognition in high - impact sport .
The virus that causes cold sores can get into the brain, fall latent and then reactivate following head trauma, a study hints.
Some scientist guess these changes may be link to a common virus : herpes simplex virus 1 ( HSV-1 ) , the source behind frigid sore .
Herpesviruses — a broad group that also includes the viruses behind varicella and infectious mononucleosis — have an ability to go dormant in the body and then after reactivate . " They can remain latent in your body forever , " said lead subject authorDana Cairns , a postdoctoral inquiry fellow at Tufts University . There ’s grounds that HSV-1 can somehow weasel its way into the brainpower and then lie there in wait , Cairns told Live Science .
link up : science laboratory - grown ' minibrains ' help reveal why traumatic brain wound raises dementedness hazard
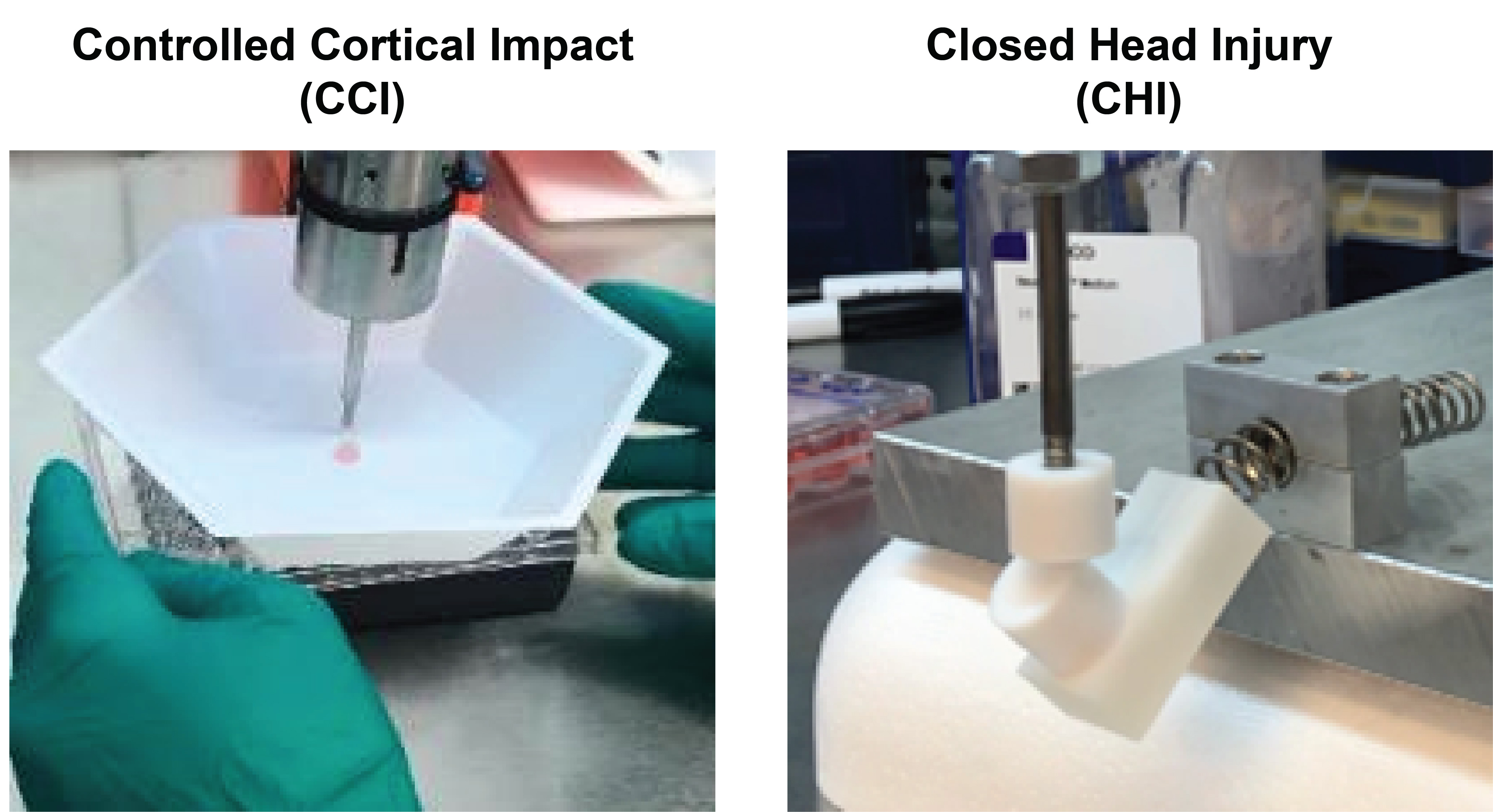
These are the two experimental set-ups used in the new study.
What ’s new here is that the researchers have demonstrated that forcible wound can spark latent viruses in the Einstein , saidDr . Gorazd Stokin , who leads a neuroscience research lab at the Institute of Molecular and Translational Medicine in the Czech Republic and was not demand in the new sketch .
The new research relied on miniature laboratory models of the brain , so more work will be needed to show that the results are relevant to people . " But it ’s a salutary first step to show something interesting , " say Stokin , who is also a consultant brain doctor at the Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in the U.K.
Viruses in dementia
The approximation of virus activate dementia is n’t new;Ruth Itzhaki , a co - author of the young paper , raised the notionin 1991 . Itzhaki and colleague had found the virus in the head of older adults who had choke of Alzheimer ’s . Theylater foundthat people who carry both the virus and ApoE4 — a factor variant that raises Alzheimer ’s risk — have a higher risk of the disease than those with ApoE4 alone . They also bump that latent HSV-1 can be reawaken by stress or immunosuppression .
" In those days , she incur a lot of pushback , " Cairns say of Itzhaki ’s early piece of work . This viral possibility of dementedness remain niche for decades , but in late years , interest has increased . Nowadays , scientist also have good tools to examine the hypothesis , includinglab - grow models of the human brain .
The new research , published Tuesday ( Jan. 7 ) in the journalScience Advances , used mentality example measuring only 0.2 inch ( 6 millimeters ) across . The spongy , doughnut - shaped social organisation are made of silk and imbued with base cells . With specific chemical substance , the stem cell are made to mature into various brain cells that run one written matter of ApoE4 . This genetic trait is " relatively common"among people with Alzheimer ’s , Stokin noted , so it ’s relevant to let in in a mentality model .

The research worker infected these models with HSV-1 and then pushed the virus into quiescency with an antiviral drug . In retiring research , they had shown thatinflammationcould " come alive up " the virus and that this triggered brain - electric cell changes also seen in dementia . In that old piece of work , the research worker trigger the inflammation with chickenpox - zoster virus , the computer virus behind chickenpox and shingles .
But " there are other things besides infection that cause fervor , like injury , " Cairns said . " We desire to understand if peradventure injury could be doing something exchangeable . "
In the new subject , the team subjected the minibrains to models of two case of injury : severe injury , as if the skull had broken open , and concussion , in which the learning ability moves or twists in the skull . In the concussion experiment , the minibrains were place in 3-D - impress containers filled with fluid , interchangeable to the fluid that cushions the learning ability inside the skull . The encased minibrains were then put on a political program that was strike with a piston .

In both experiments , the brainpower models became wake and the HSV-1 in them reactivated . Dementia - related changes , like an accumulation of protein , showed up in these infected genius models , but not in wound - but - uninfected modelling that were used for compare .
The wicked - accidental injury experiment damaged the cells so badly that they shortly give way , but the cells in the concussion experiment survived and thus the experiment could be reprize . The more meter it was repeated , the worse the dementia - like pathology of the septic models became .
" The people that are expose to more continuing injuries over clip often clinically have the worst manifestation of neurodegeneration , " Cairns noted . " It [ the experiment ] really correlated very well with that concept . "

— Even mild concussions can ' rewire ' the brain , perhaps cause farsighted - terminus symptom
— electric stimulation could handle traumatic brain injuries
— ' Cold sore ' virus may have acquire extrusion thanks to Bronze Age smooching

extra experiment by the squad hinted that blocking kindling after wound could help block HSV-1 from reactivating and thus prevent the house of dementedness from turn out . This finding strengthened the team ’s overall answer , Stokin said . However , because the results have been shown in only minibrains , " trying to do the same in animal exemplar would be useful , " he added .
The researchers be after to continue experimenting with their brain role model to see what might stop HSV-1 from reawaken — for representative , anti - incendiary or antiviral drug may work , Cairns say .
" If you could block reactivation , or somehow control the viral burden … that would be good , " Stokin said , assuming herpes virus truly is a miss contact between brain injury and dementia .