When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
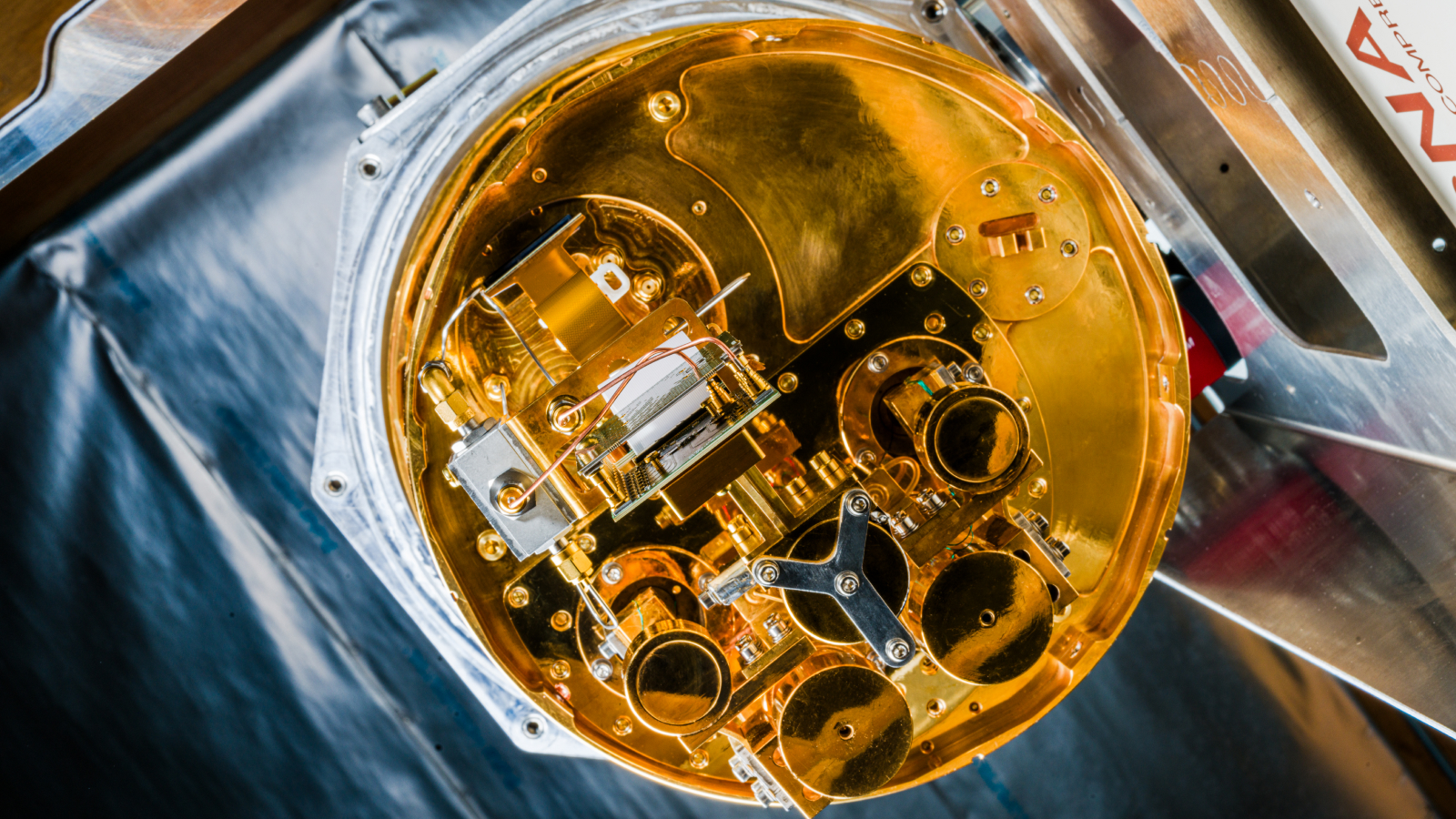
A breakthrough cooling technology could help invigorate quantum calculation and thresh costly preparation clip in key scientific experiments by weeks .
Scientists often need to generate temperatures close toabsolute zerofor quantum computer science and astronomy , among other usance . cognize as the " Big Chill , " such temperatures keep the most sensitive electric tool free from noise — such as temperature changes . However , the refrigerators used to achieve these temperatures are highly dearly-won and inefficient .
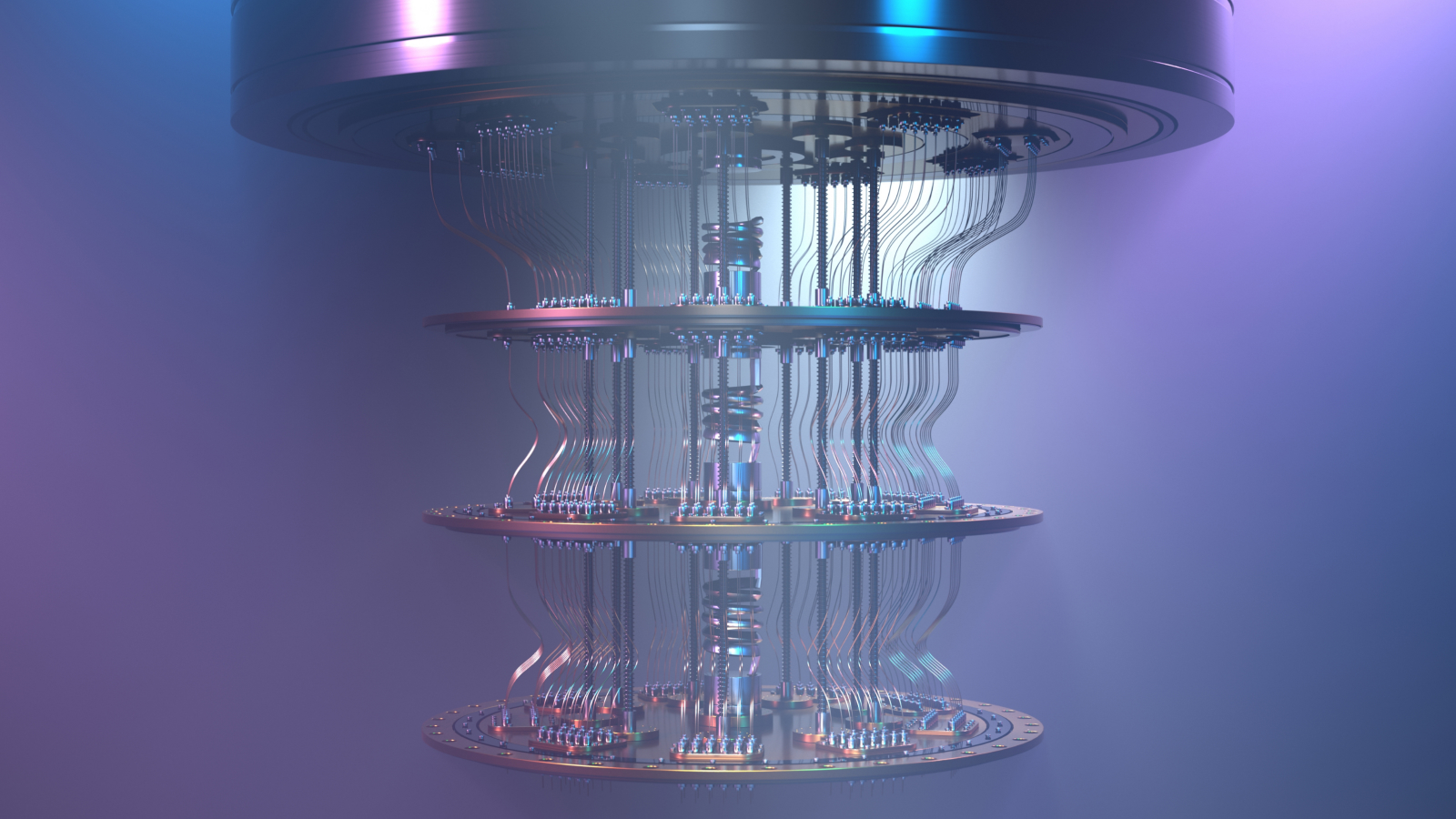
New discovery in cooling technology could help bring quantum computing to life sooner than expected.
However , scientists with the National Institute of Standards and Technology ( NIST ) — a U.S. politics agency — have built a new prototype refrigerator that they arrogate can reach the Big Chill much more quickly and expeditiously .
The researcher published the details of their fresh machine April 23 in the journalNature Communications . They claimed using it could economise 27 million watts of power per twelvemonth and reduce world energy ingestion by $ 30 million .
A new breed of refrigerator
schematic menage electric refrigerator work through a procedure of desiccation and condensation , perLive Science . A refrigerant liquidity is pushed through a special low - pressure pipe call an " evaporator coil . "
As it evaporates , it absorb warmth to cool the inside of the electric refrigerator and then passes through a compressor that turns it back into a liquidness , raising its temperature as it is radiated through the back of the fridge .
Related:‘World ’s unadulterated silicon ' could pass to first million - qubit quantum computing chips
To achieve want temperatures , scientist have used pulsation tube refrigerators ( PTRs ) for more than 40 years . PTRs use helium petrol in a similar operation but with far better assimilation of heat and no moving parts .
While good , it consumes Brobdingnagian sum of money of vigour , is expensive to run , and pick out a farseeing time . However , the NIST investigator also discovered that PTRs are needlessly ineffective and can be greatly improve to reduce chill time and broken overall cost .
In the field , the scientists aver PTRs " bear from major inefficiencies " such as being optimized " for performance only at their root word temperature " — normally near 4 Kelvin . It imply that while cooling down , PTRs play at greatly ineffective levels , they impart .
The team found that by adjusting the excogitation of the PTR between the compressor and the refrigerator , helium was used more efficiently . While cooling down , some of it is normally pushed into a respite valve rather than being pushed around the circuit as intend .
Quantum computing at a fraction of the cost
Their propose redesign includes a valve that contract as the temperature drops to prevent any atomic number 2 from being desolate in this way . As a final result , the NIST team ’s modified PTR achieved the Big Chill 1.7 to 3.5 time quicker , the scientist tell in their paper .
“ In smaller experiments for prototyping quantum lap where cooldown time are before long like to picture times , dynamic acoustic optimization can well increase measuring throughput , ” the researchers wrote .
The researchers tell in their study that the new method could trim at least a week off experiment at the Cryogenic Underground Observatory for Rare Events ( CUORE ) — a facility in Italy that ’s used to depend for rare events such as a presently theoretic form of radioactive decay . As small background noise as possible must be achieve to incur exact results from these facilities .

— Temperatures cold than space reach here on Earth using superconducting Adam - ray optical maser
— Error - set qubits 800 times more reliable after breakthrough , pave the means for ' next point ' of quantum computing
— Future quantum computers will be no match for ' outer space encoding ' that uses light to beam information around — with the first orbiter launching in 2025

Quantum reckoner need a exchangeable level of closing off . They apply quantum bit , or qubits . Conventional computers store information in bit and encode data with a value of either 1 or 0 and perform calculation in chronological sequence , but qubits occupy a superposition of 1 and 0 , thanks to the laws ofquantum car-mechanic , and can be used to process calculations in parallel . Qubits , however , are incredibly sensitive and need to be separated from as much background noise as possible — including the tiny fluctuations of caloric energy .
The research worker said that even more effective cool down method could theoretically be achieved in the near future , which could go to fast invention in quantum computer science space .
The squad also enunciate their their technology could instead be used to achieve super cold temperature in the same time but at a much lower cost , which could gain the cryogeny industriousness , cutting price for non - time - intensive experiments and industrial applications . The scientists are currently working with an industrial married person to release their better PTR commercially .