When you purchase through tie-in on our website , we may earn an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it works .
New insight into how alone bacteria stand firm damage from actinotherapy could lead to better protection for humans — both on Earth and among the stars .
Deinococcus radioduransis anextremophile , a bacteria that can withstand weather that would belt down off most sprightliness - flesh . D. radiodurans ' power to resist radiationthousands of sentence strongerthan the deadly dose for humans has earned the germ the cognomen " Conan the Bacterium . "
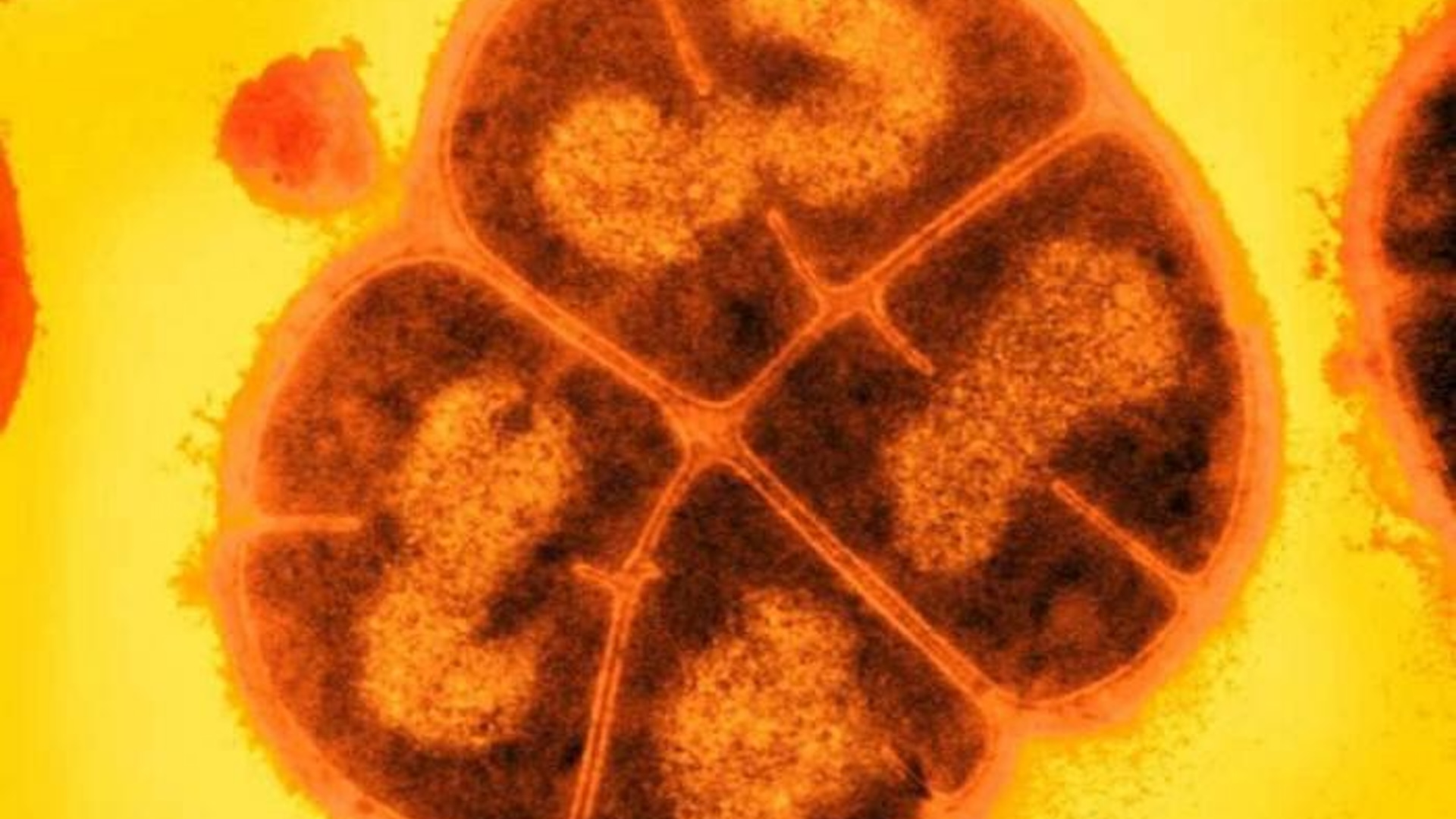
Dubbed “Conan the Bacterium,” this microbe can withstand radiation doses thousands of times higher than what would kill a human.
" Ionizing radiation — such asX - light beam , gamma ray , solar proton and galactic cosmic actinotherapy — is highly toxic to both bacterium and humans,“Michael Daly , a geneticist andD. radioduransexpert at Uniformed Services University in Maryland , told Live Science .
" In bacterium , actinotherapy can cause deoxyribonucleic acid wrong , protein oxidation and membrane to-do , run to cubicle death , " he explained . " In humans , radiotherapy photograph can result inacute radiation syndrome , increased cancer risk , and damage to tissues and organs . "
bear on : top-notch space sunscreen made from pelt paint could shield astronaut from radiation syndrome

ionize radiation removes electrons from atoms . This termination in reactive particle calledfree free radical , which are unstable , and in large enough number , candamage DNA , proteins and cell .
D. radiodurans ' power to resist this damage comes from aunique combination of factor : a protective cell wall , efficient mend mechanisms to fix radiation - induced DNA wrong , and a collection ofantioxidantsthat diffuse loose root word .
In a new subject field , issue Dec. 12 in the journalPNAS , Daly and his colleagues took inspiration from a powerful antioxidant made byD. radioduransto contrive their own version of the antioxidant .

Complexes inside the bacterium that containmanganeseprotect its protein from radiation by remove the free stem that can damage them . This leaves those proteins free to perform vital cellular functions , such as deoxyribonucleic acid repair . The researchers make a lab - made version of the complex by combining charged manganese subatomic particle , or ions , with a phosphate ion and a especially designed peptide , or shortsighted chain ofamino acids . The peptide was establish on the amino acids that are most common inD. radiodurans .
The investigator dubbed their novel antioxidant manganese - strung-out peptide ( MDP ) .
" I started as a sceptic , " say study co - authorBrian Hoffman , a professor of chemical science and molecular bioscience at Northwestern University . " I distrust that MDP ’s efficacy was nothing more than the ' sum of its parts . ' "

However , Hoffman said he was surprised to light upon that the character interacted to make a more potent whole . " This is the ' secret sauce , ' " he said .
Experiments that measured how strongly the part of the complex bound together showed that manganese alone did n’t form strong enough bonds with the designed peptide to be protective . Adding the phosphate ion strengthened the attachment and produced a complex that could withstand over 12,000 times the human lethal dose of ionise radiation .
link up : How radioactive is the human dead body ?

Now , the research worker are using special technique to analyse the structure of MDP , in hopes of see how it ’s put together , why it do work so well , and how to make it even more effective . The final result could have widely - reaching lotion .
" spaceman on deep - place missions are exposed to chronic high-pitched - degree ionizing radiation , in the main from cosmic irradiation and solar protons , " Daly said . " MDP — a simple , toll - good , nonpoisonous and highly effective radioprotector — could be administered by word of mouth to palliate these place radiation endangerment . "
He added that , " for manned charge to Mars , which may extend over a class , radioprotection will beessential for the crew ’s safety . "

nearer to home , Daly and Hoffman want to explore MDP ’s potential difference for ameliorate health on Earth .
— Bacteria could survive underground on Mars for hundreds of millions of geezerhood , new study find
— colonise Mars may require humanity to tweak its DNA

— Teeny tardigrades can live space and deadly radioactivity . Scientists may eventually know how .
" Acute radiation syndrome , which take severe immunologic complicatedness , might be preventable with MDP , " Daly said . " There ’s also a well - pick out link betweenradiation resistance and aging . " So perhaps MDP could be a likely discourse to battle metabolic aging .
However , more research is needed to develop safe , good forms of MDP for use in world . With time , though , Hoffman , Daly and their confrere anticipate MPD ’s potential in everything from health attention to space travel .

Ever marvel whysome people build muscle more easily than othersorwhy lentigo number out in the Dominicus ? charge us your questions about how the human body play tocommunity@livescience.comwith the capable line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the site !









