When you purchase through links on our site , we may garner an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
TEXAS — Nearly four years afterNASA ’s OSIRIS - Rex spacecraft collected a sample from an asteroid , scientists are finally revealing the challenging typography of the place rock .
Among them , the near - Earth asteroid , known as Bennu , moderate a surprising reservoir of a mineral called Mg phosphate . These bright - white mote sprinkled in a sea of Bennu ’s blue rocks is a rare uncovering in astromaterials , scientists say .
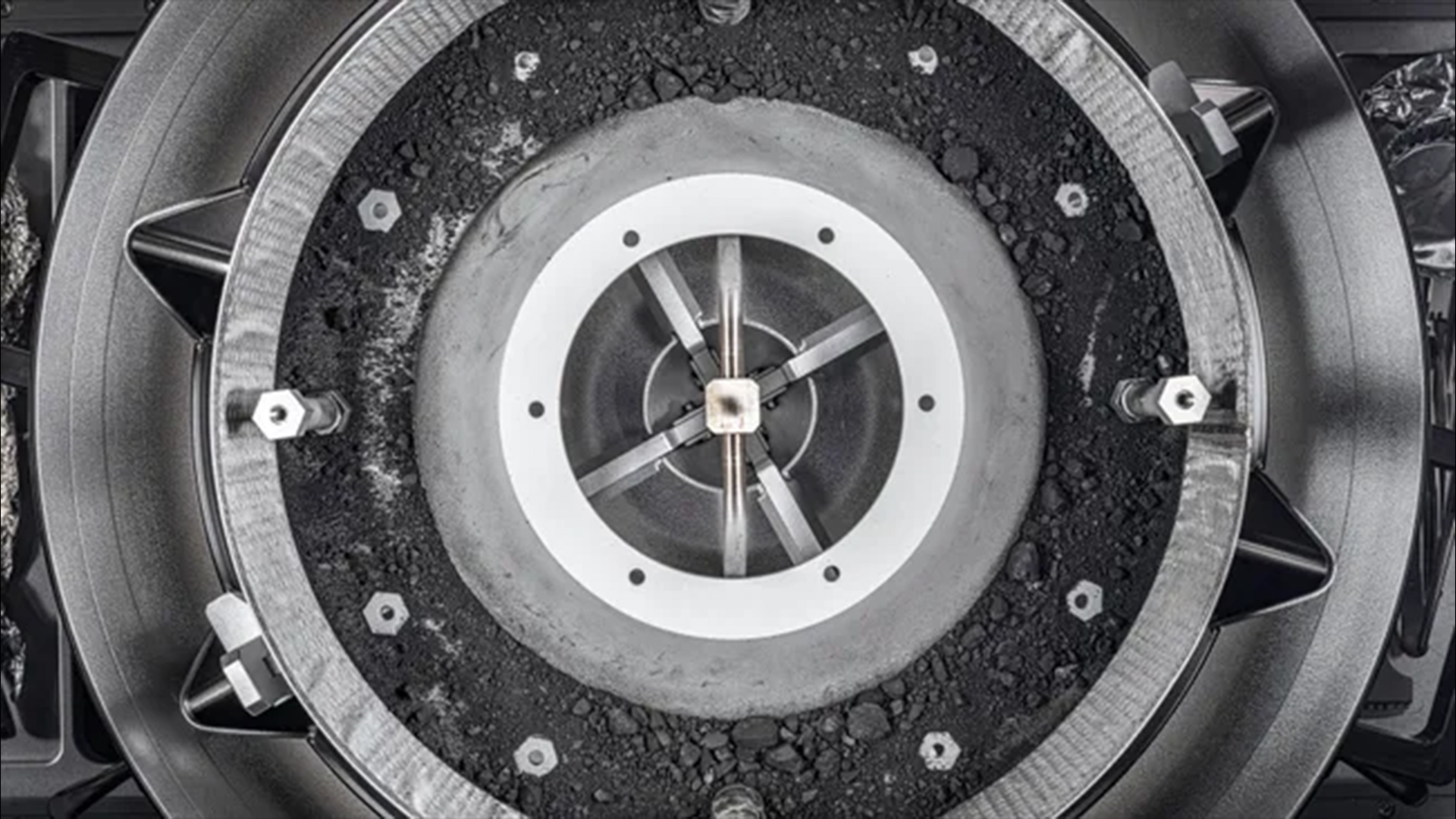

A close-up of NASA’s OSIRIS-REx sample trays, containing dust and rubble plundered from asteroid Bennu.
" It ’s no surprise that we ab initio thought this might be a contaminant , " saidJessica Barnes , an adjunct prof at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory ( LPL ) who ’s leading the phosphate analysis in the returned sample .
speak at the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference ( LPSC ) in Texas and on-line last workweek , Barnes said there are no practiced chemical substance analog of the mineral on Earth , either because it is too tenuous to survive the fall to Earth or vanishes soon after . Its bearing in Bennu ’s sample can be used to infer unlike instalment of geological activity on Bennu ’s parent body , she state .
The sample also show the widespread presence of glycine , the simplest amino group acid and a of the essence ingredient ofproteins , as well as other piss - brook minerals , include carbonate , sulfites , olivine and magnetite , all of which are touchable grounds that Bennu ’s parent body witnessed multiple piddle - related episodes before its shard coalesced into Bennu .
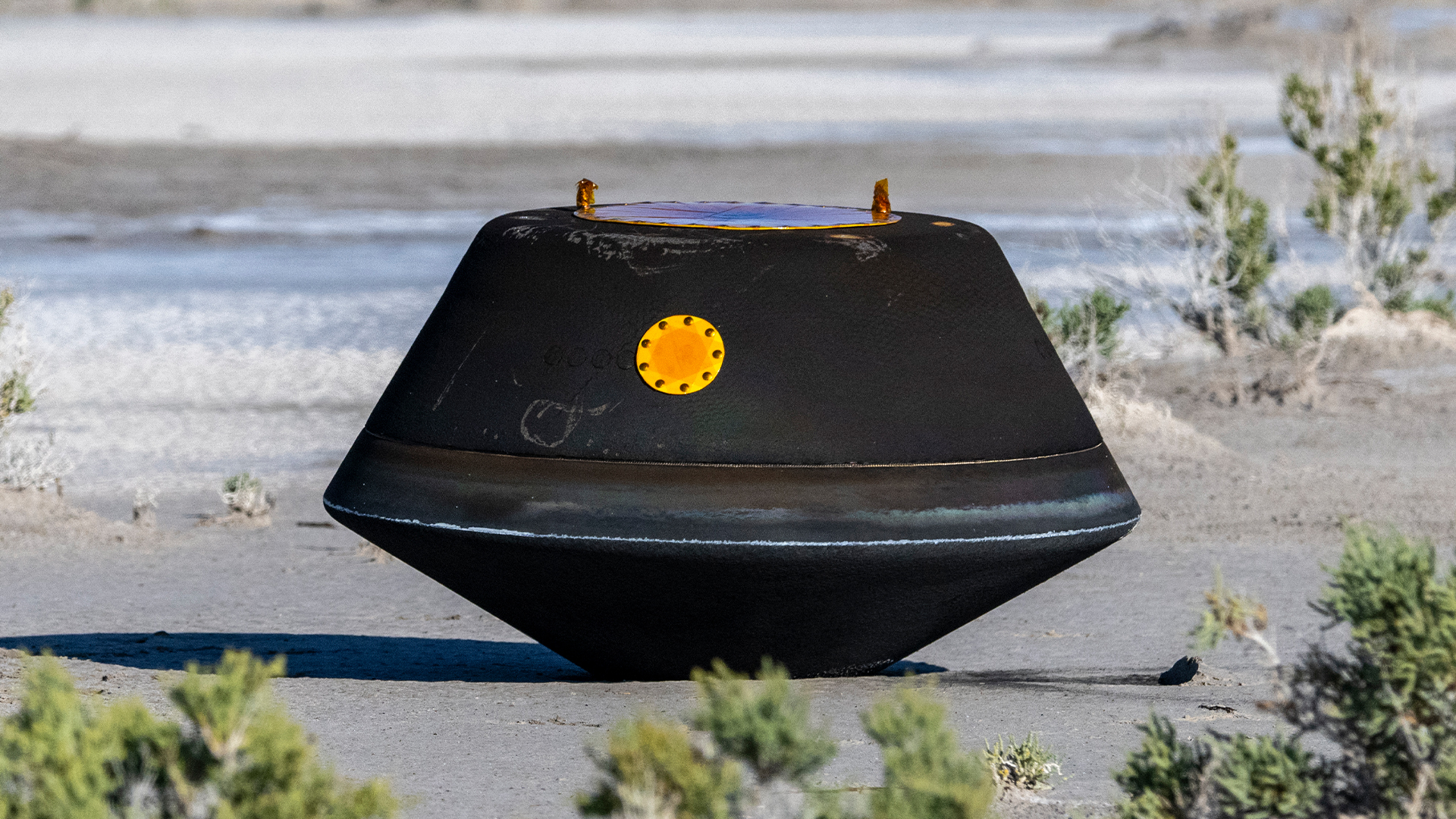

The sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is seen shortly after touching down in the desert, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, at the Department of Defense’s Utah Test and Training Range.
Other scientists study the extraterrestrial H.M.S. Bounty chance abundant water - altered compound call phyllosilicates , as well as a plentiful collection of other organic and hydrated minerals . Phyllosilicates , which arestructurally boundto water in meteorite , may have been the cradles for organic and pee that scientists distrust were delivered to Earth ahead of time in its history .
touch on : NASA ’s most wanted : The 5 most serious asteroids in the solar system
‘A beautiful sample’
The sample , scooped from Bennu in 2020 by NASA’sOSIRIS - RExmission , yield to Earthin a protect capsule on Sept. 24 , 2023 . A day later , it was delivered for analysis at NASA ’s Johnson Space Center ( JSC ) in Houston , where a " tiger team " of scientist began a preliminary investigating of the stuff that had leak outside the space vehicle ’s sample gatherer . ( Two teasing screw on the container hat prevented approach to the mass of the take in sample until January , which is when scientistsofficially cataloged4.29 ounces , or 121.6 g , of collect material — double the initial forecasting . )
In a fleet of talks at the LPSC , the delegation team reported that the pit cataloged so far also disport a variety of textures , hydrous minerals and grounds for space weathering , as is expect from an airless , eons - onetime rock’n’roll .
" It ’s a beautiful sample , " saidSara Russell , a planetary scientist at the Natural History Museum in London whoanalyzed a small shard of the sample distribution . " Also , I would say it ’s not quite like any meteorite in our collection . "
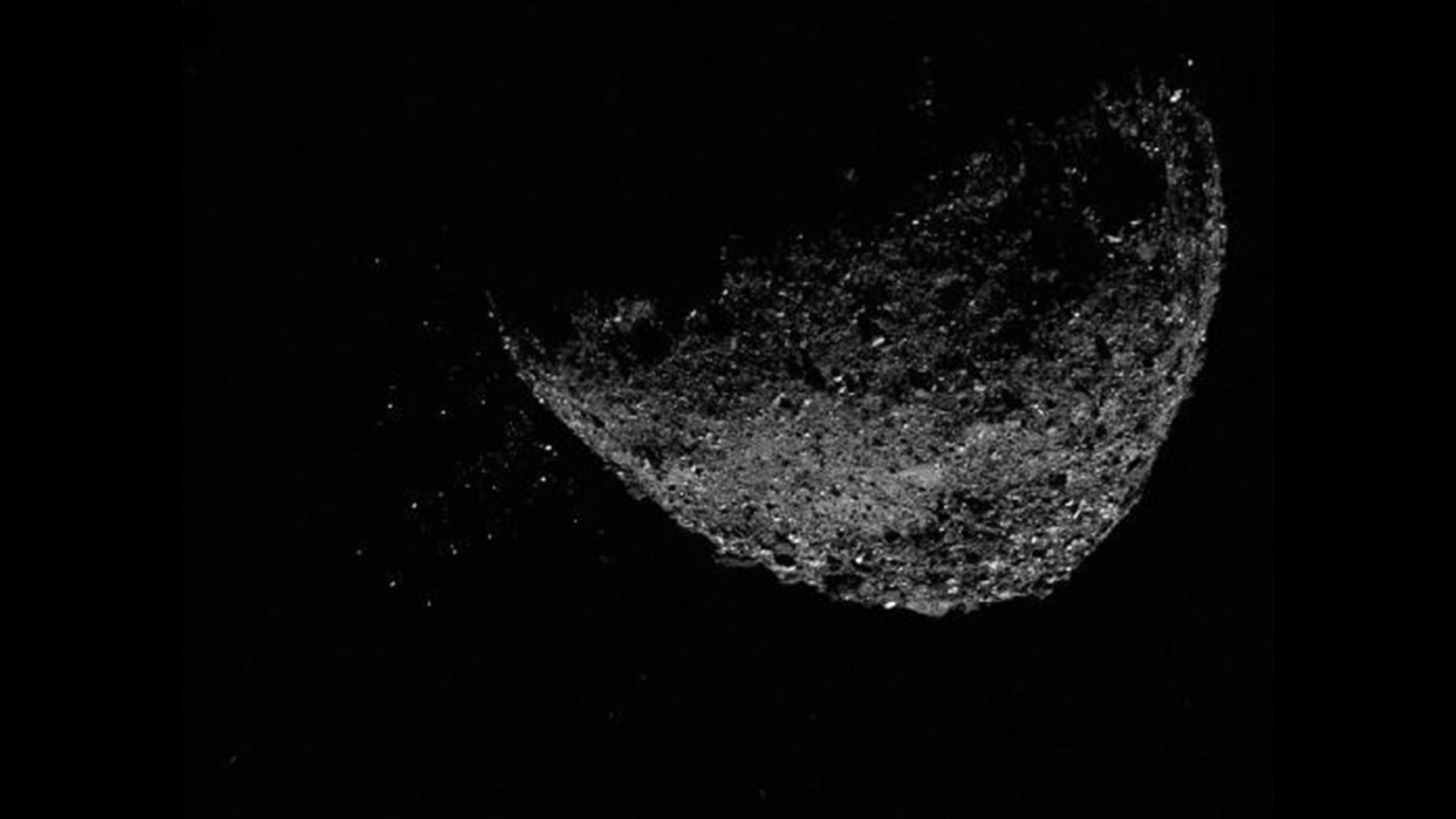
A view of asteroid Bennu ejecting particles from its surface on Jan. 6, 2019.
The most pristine asteroid sample ever
Unlike most meteorites , whose surface are altered by years - long exposure to Earth ’s air by the time they are found , pieces of Bennu are the most pristine infinite rocks scientist have ever held .
" I can not recite you how refreshing it is to see some sample distribution where everything is n’t altered to sulphate and all sort of muck , " said squad memberTim McCoy , a conservator of meteorites at the Smithsonian ’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington , D.C. , whichreceived a sample distribution of the asteroidto analyze last November . " You ’re seeing it literally the day it flow — it is singular to see something that fresh . "
Many of the cataloged rocks from Bennu are " hummocky boulders " with uncut , " emery paper - similar grain , " articulate squad memberAndrew Ryan , a inquiry scientist at LPL at the University of Arizona . A 1.4 - inch - wide-cut ( 3.5 centimeters ) , 0.23 - ounce ( 6.6 gm ) rock is " by far our large booty from the Earth’s surface of Bennu , " he allege , motion toward fresh 3D scans of the rock take at the curation research lab at JSC .

Most metrical mineral confirm multiple anticipation made from outback smell out data collected from OSRISIS - REx as it approached Bennu . " We got it correct with the remote perception , " saidHarold Connolly , a geologist at Rowan University in New Jersey , " and that feeds at once into how we are analyzing the sample distribution and test our speculation . "
So far , the analysis has been consistent with the leading theory that Bennu broke off from a much large asteroid about 2 billion to 700 million years ago . For instance , the latest psychoanalysis shows Bennu ’s rocks littered with impact - related breccia , which are rock fragments loosely held together like pebble in concrete .
— NASA grabbed a whopping 120 grams of rubble from asteroid Bennu , and it may contain the seed of life

— ' What is that material ? ' : Potentially hazardous asteroid Bennu stumps scientists with its odd make-up
— NASA is locked out of its OSIRIS - king asteroid sample because of 2 faulty fasteners
" These breccias probably did n’t form on Bennu , " said McCoy , who ’s leading the research on these feature . " They forge on the parent asteroid and then in of themselves became Boulder that were comprise into Bennu . "

It is still unclear precisely when they formed .
" We ’re still in the very early day of this very punctilious body of work , " McCoy say . " There ’s a destiny we do n’t know . "














