When you purchase through links on our site , we may bring in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
The polar vortex circling the Arctic is swirling in the wrong direction after surprisal warming in the upper atmosphere trip a major turnabout event earlier this calendar month . It is one of the most extreme atmospherical uranium - turns seen in late memory .
In the past , disruptions to the frigid vortex — a circumvolve mass of cold atmosphere that circles the Arctic — havetriggered extremely cold conditions and stormsacross large parts of the U.S ..
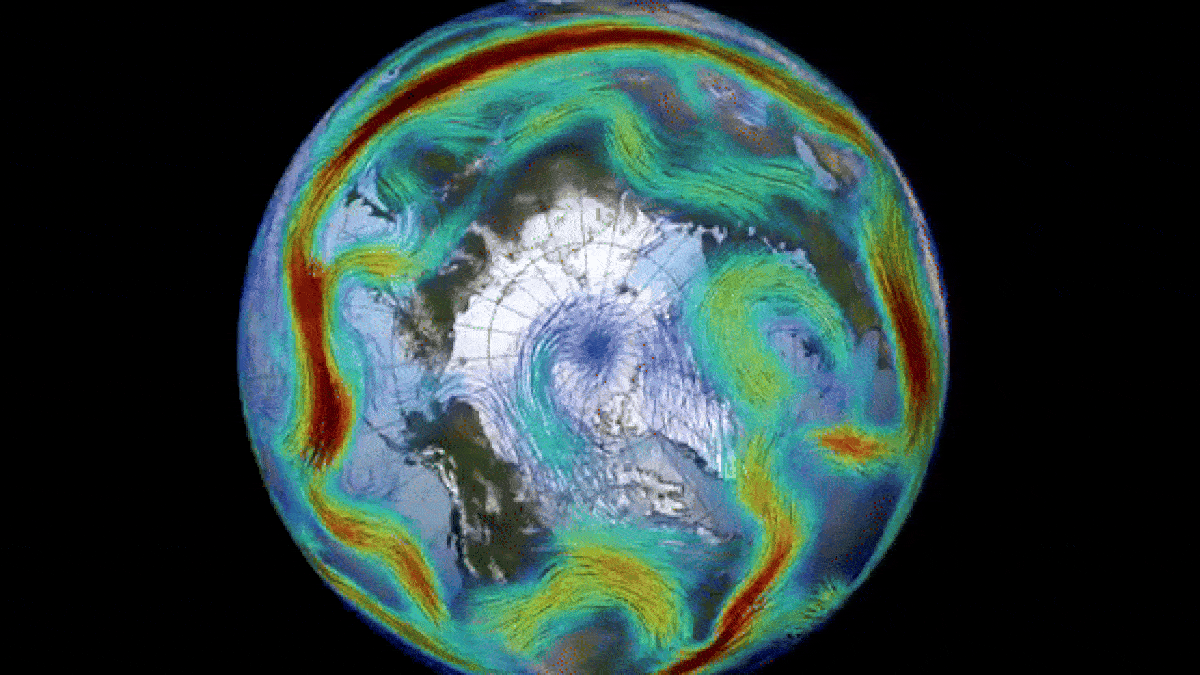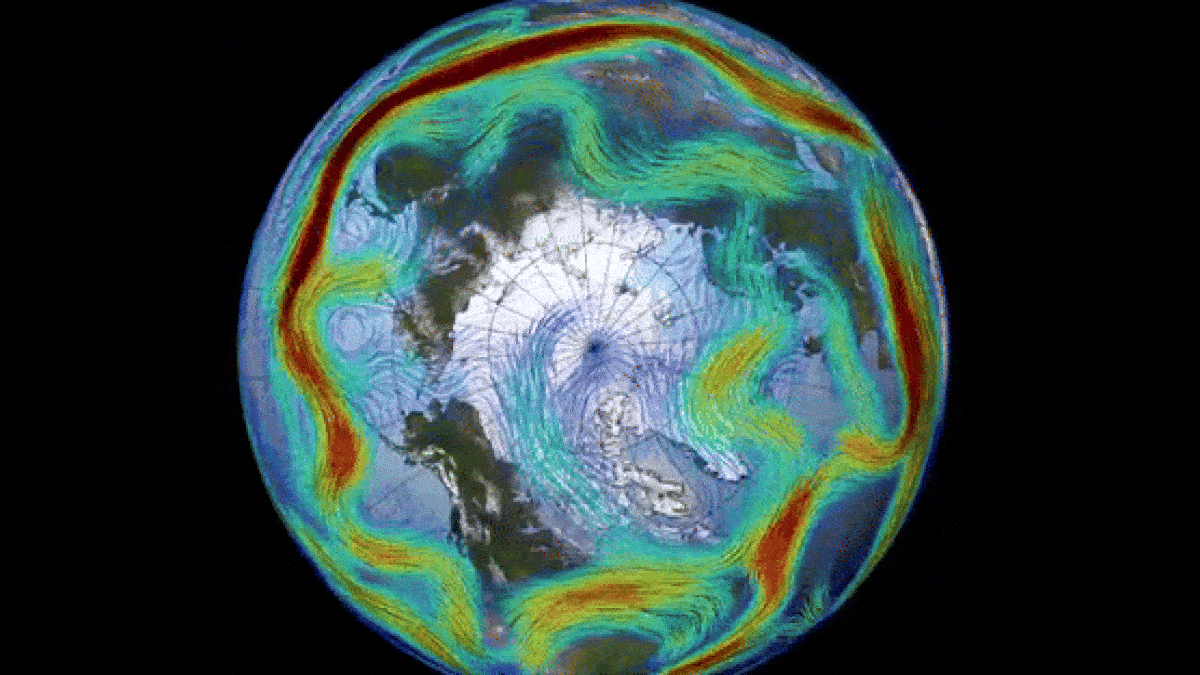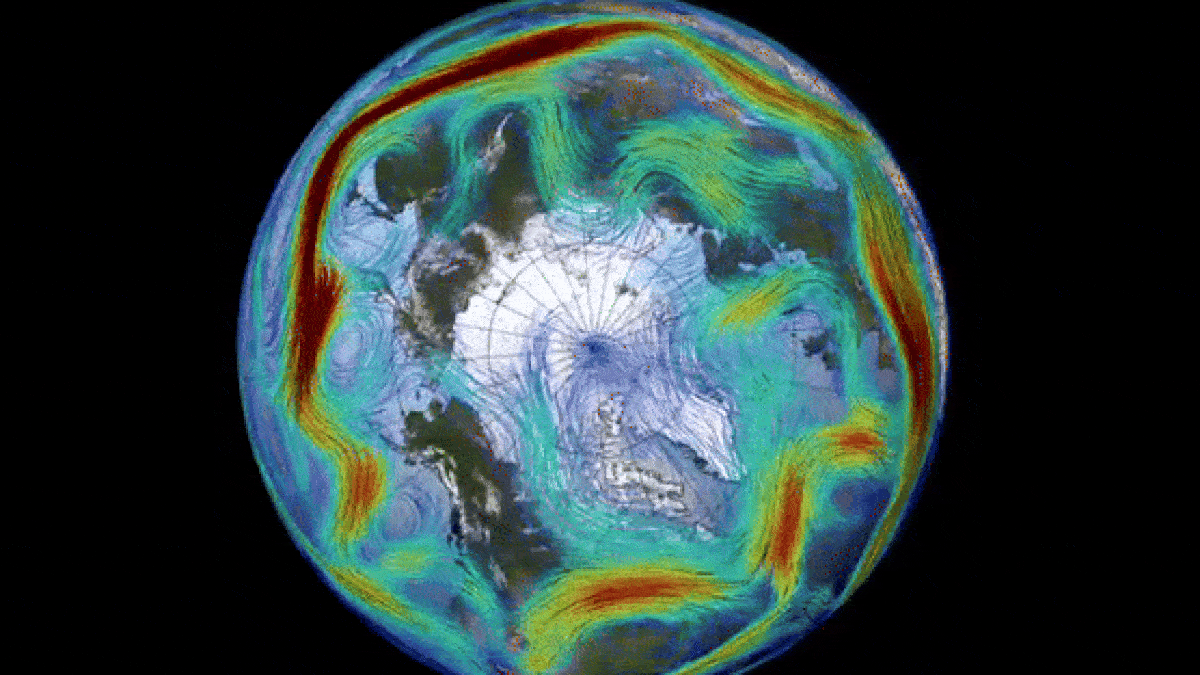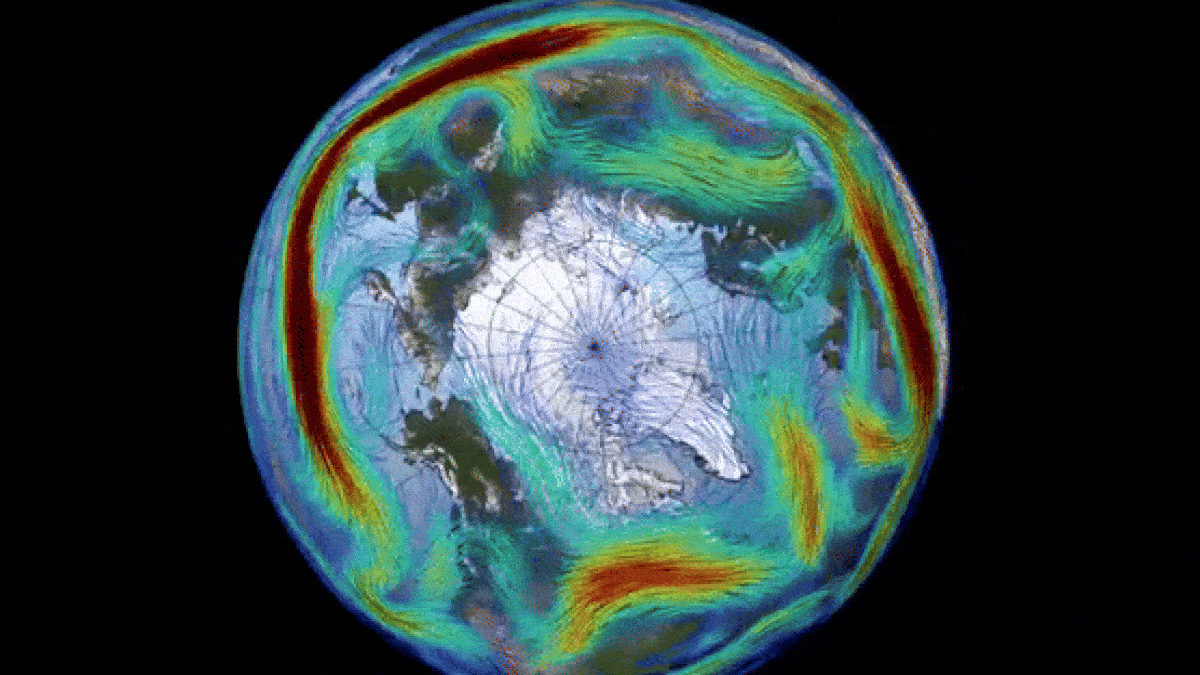
The polar vortex is a key driver of the polar jet stream (seen here).
The current change in the convolution ’s counsel plausibly wo n’t pass to a exchangeable " big freezing . " But the sudden electrical switch - up has caused a record - separate " ozone stiletto heel " above the North Pole .
The opposite vortex is most prominent during wintertime month and extends into the stratosphere — the second layer of the atmosphere up to around 30 miles ( 50 kilometers ) above the surface . The vortex whirl counterclockwise with wind speed of around 155 miles per hour ( 250 km / h ) , which is around the same speed as a class 5 hurricane , consort to theU.K. Met Office . A alike whirlpool also encircle Antarctica during the southern wintertime .
Polar vortices occasionally reverse temporarily . These event can last for days , weeks or months and are make by sudden stratospheric heating ( SSW ) , when the temperature in the stratosphere ascent by as much as 90 degrees Fahrenheit ( 50 degree Celsius ) in the space of a couple of days , according to theMet Office .
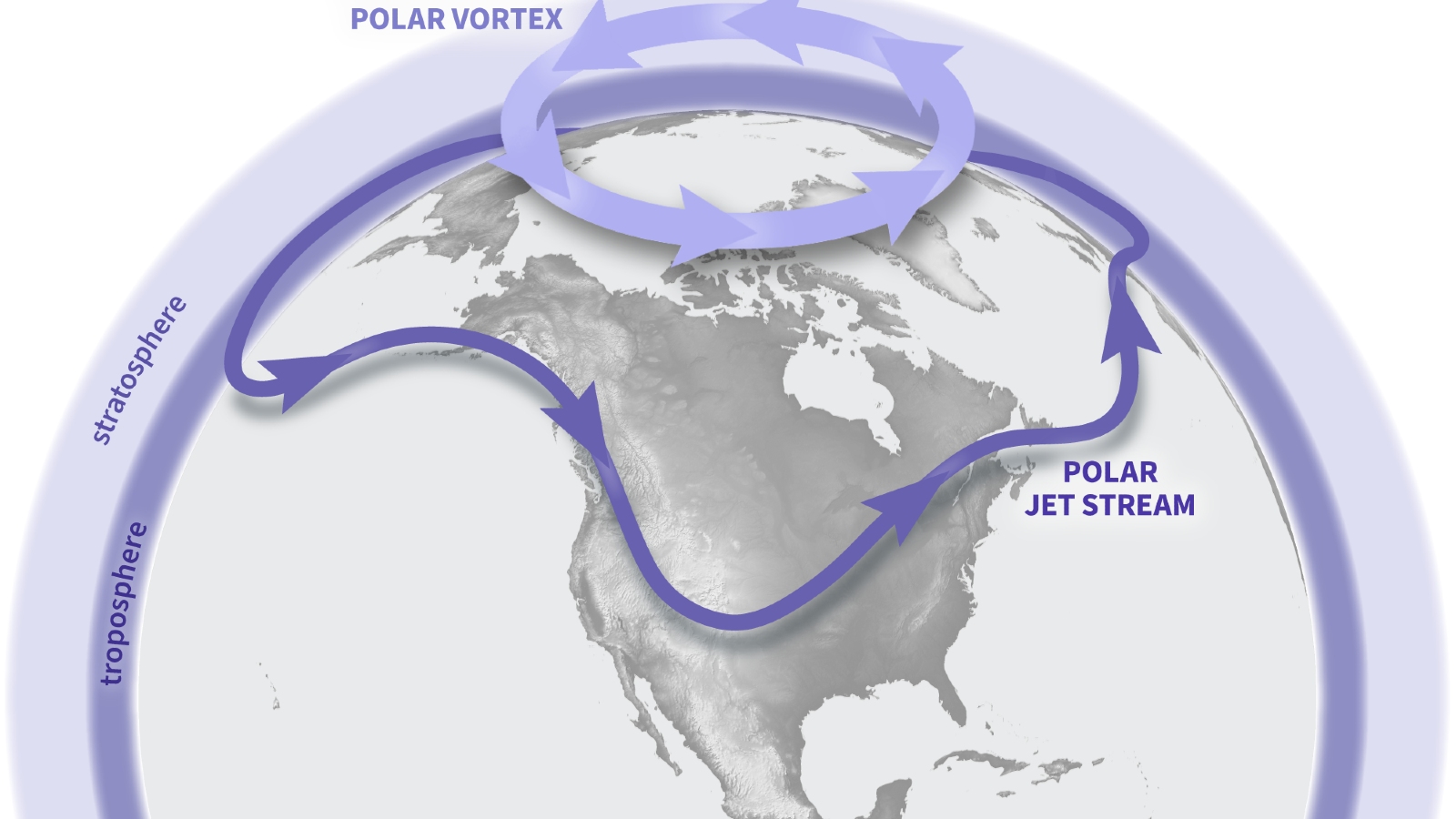
Changes to the polar vortex influence the jet stream, which can in turn impact weather across the Northern Hemisphere.
Related:‘One of the biggest on disc ' : Ozone jam bigger than North America opens above Antarctica
The sudden thaw is triggered by " planetary waves " in the atmosphere — contraction wave formed when air rises into a area of unlike tightness and is pushed back downwards by the force of Earth ’s spin . This process disrupts or reverses the whirl stream .
The current setback event in the Arctic began on March 4 . However , the wind are starting to slow down , hinting that the whirlpool will return to its normal flight soon , Spaceweather.com report .

" It was a substantial reversal,“Amy Butler , a clime scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( NOAA ) and author ofNOAA ’s new diametrical vortex blog , told Spaceweather.com . The upper of the reversed winds puts the upshot in the top six on book , she add up .
Disruptions to the polar vortex can impact weather in the U.S.,such as in 2019when amassive insensate frontdescendedacross the Midwest . These extreme conditions events occur when the polar vortex deforms the spirt stream — an air current that surrounds the frigid whirlpool — exposing lower parallel of latitude to turgid blobs of frigid Arctic air .
This calendar month ’s disruption did not change the shape of the blue jet stream , so atmospheric condition design are expected to remain largely unmoved , consort to Spaceweather.com .

However , the alteration in air temperature around the Arctic has sucked up magnanimous amounts ofozonefrom lower latitudes , create a temporary ozone spike — the opposite word of an ozone hole . presently , there is more ozone surrounding the Arctic than at this time during any other year on record , according to Spaceweather.com . However , this ozone spike will evaporate after the opposite vortex issue to normal
— liberal blob of red-hot pee in Pacific may be take a shit El Niño act weirdly
— Deadly cyclone ' Freddy ' may be the longest - last and most energetic violent storm ever register
— ' Gigantic jet ' that inject into blank may be the most powerful lightning deadbolt ever detected
The current reversal is the second of its kind this twelvemonth , follow a modest event in January that did cause a brief cold snap in some Department of State , Butler write in NOAA ’s polar vortex web log .
Historical records show that SSW effect are more likely to occur during El Niño or La Niña , the two contrast phase of a natural bike of major planet - wide warming and cooling . During these phases , world weather systems become more unsound , which set the stage for more frequent reversal outcome , Butler wrote in the NOAA blog .

We are currentlyin the thick of a major El Niño , which could make further reversals or disruptions more likely over the next class or so .












