When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it works .
NASA ’s PerseveranceMars roverhas spotted a strange object out of the nook of its " oculus " : a deep rock that resemble a clustering of hundreds of spider bollock . The careen , which was discovered on the slopes of Witch Hazel Hill on the rim of Jezero Crater , is lightly dusted with red sand and prominently out of station .
This rock , which the Perseverance squad call " St. Pauls Bay , " is float rock’n’roll , mean it was n’t found where it formed . As a result , it ’s lacking context clues that could explicate its foreign texture , concord to NASA’sstatement .
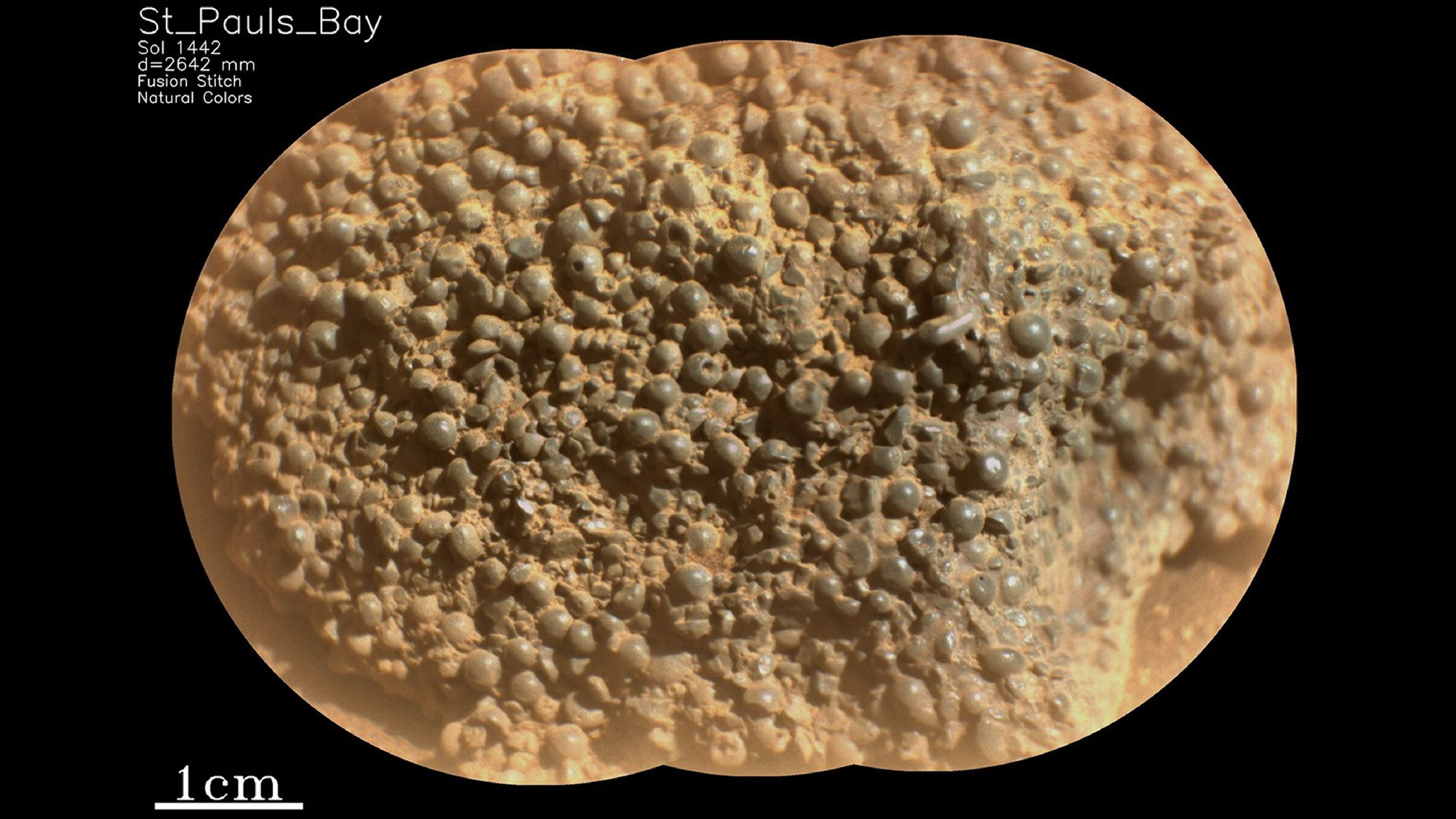

A close-up of an unusual Martian rock made up of hundreds of dark, round spheres stuck together, taken with the Mars Perseverance rover’s SuperCam Remote Micro Imager. The spheres that make up the rock are about 1 millimeter in diameter. Some are broken and slightly weathered, and some have tiny holes in them.
It is n’t just the geologic setting that ’s missing , either . Something caused the tilt to move from its original localization , and that movement could reveal insights about Martian geology . possibly this rock ‘n’ roll formed when a meteorite struckMars , vaporizing rock before it condense into the little granules image in the pic . If this was the grammatical case , the careen could have originated far from its current resting station , and it could unwrap how meteor excise tape drive materials on Mars , NASA noted .
Related:‘Spiders on Mars ' fully awakened on Earth for first time — and scientist are shrieking with joy
It ’s also possible that the rock tramp down Witch Hazel Hill , consort to NASA . It may have originated from one of the darker layer on the mound that scientists have detected from compass . Closer study of Witch Hazel Hill could separate scientists what those dark layers are made of . If they ’re interchangeable in composition to St. Pauls Bay , it could indicate a stratum of volcanic activity , an old meteor rap , the presence of groundwater in the past times , or something else entirely , NASA representatives compose in thestatement .
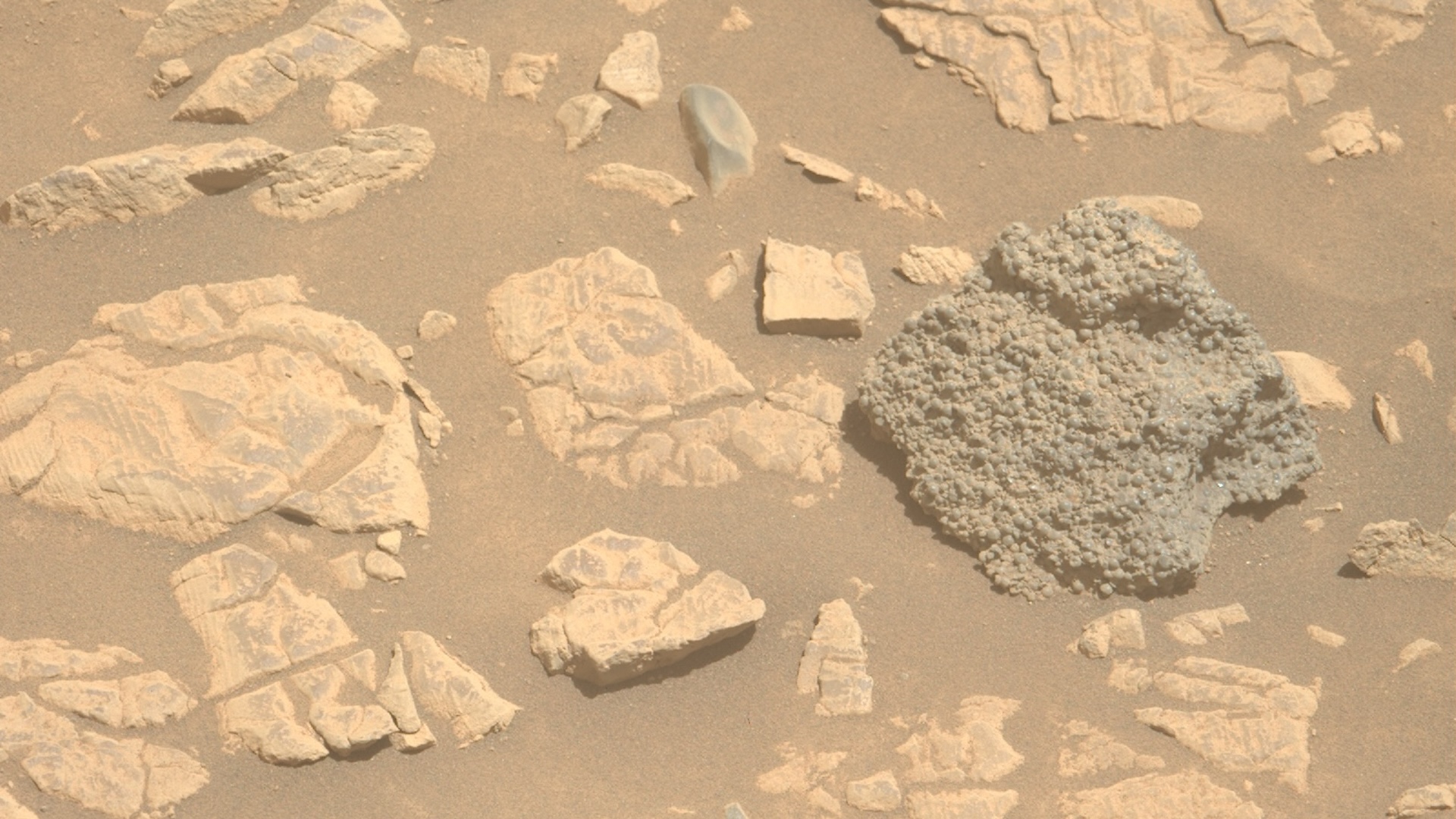

The mysterious rock, named “St. Pauls Bay,” is surrounded by lighter rocks and red-brown sand.
— Mars careen samples may contain evidence of foreign life , but can NASA get them back to Earth ?
— Perseverance rover watches a solar occultation on Mars
— ' Perfect ' Mars careen sample bore from the Red Planet in historic mission
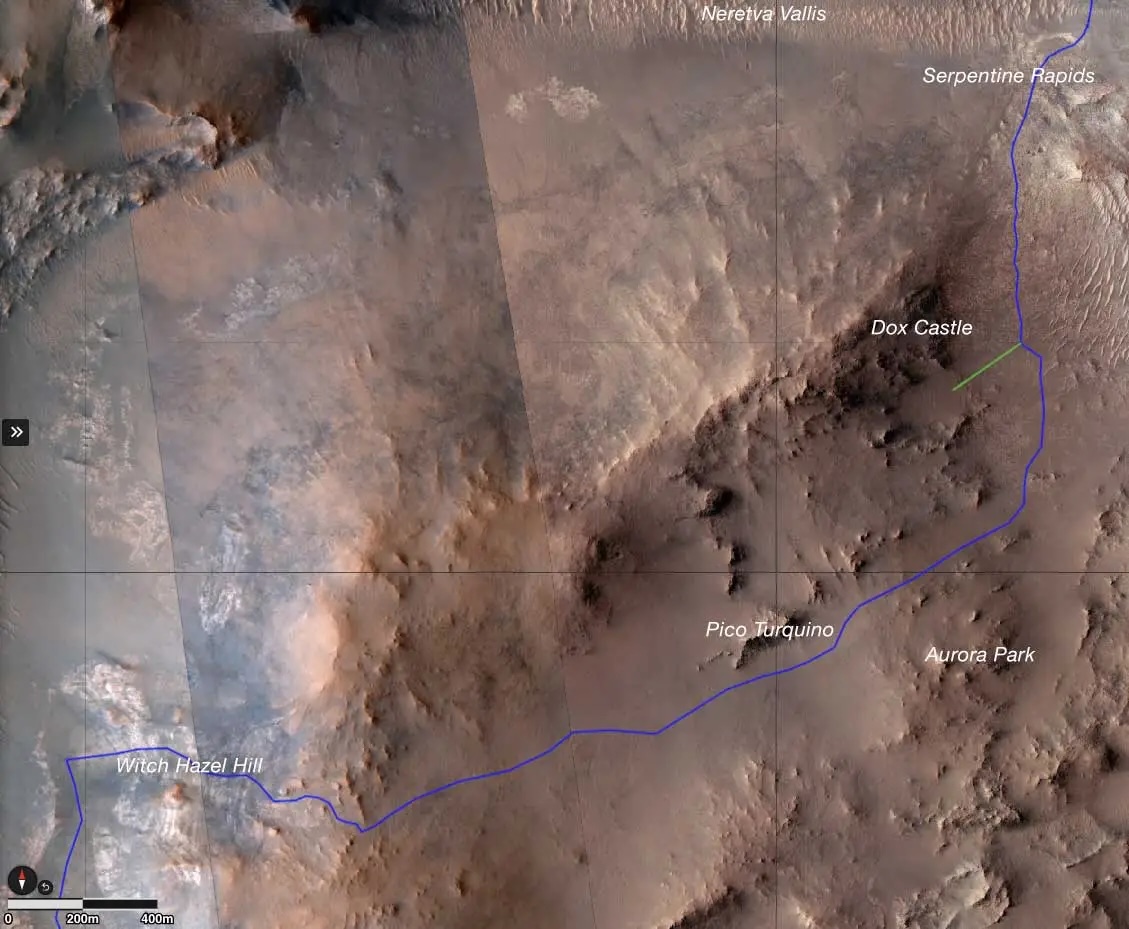
This map shows the approximate path Perseverance has taken to reach Witch Hazel Hill, with important landmarks labeled. Some of the landmarks are places where Perseverance took rock samples.
Rocks like St. Pauls Bay give scientists important clew about how the Red Planet has change over time . Their geological formation and transportation reveal complex interactions between water , stone and geological forces on Mars , which can aid serve whether the planet could have harbored life in the past .
If Witch Hazel Hill once had groundwater , some of the rock samples Perseverance has been collectingmight curb fossilized microbic life . NASA ’s Mars Sample Return mission , currently planned for sometime in the 2030s , will scoop up these careen sample and return them to Earth for further study .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your show name .