When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work out .
Earth ’s present - day climate change is human - rush , but the gravitative tower of other planets can also cause long - terminal figure climatic pattern by slightly convert our planet ’s electron orbit . Now , inquiry suggests that massive passing stars can interpolate Earth ’s path , too — and that these cosmic tugs may limit research worker ' power to study the link between preceding changes in Earth ’s orbit and our major planet ’s climate .
Aspects of Earth ’s path around the Sunday variety over prison term . For instance , the shape of Earth ’s electron orbit fault between being nearly circular and ovoid every 100,000 year or so , as Jupiter and Saturn pull on Earth . ThisMilankovitch cycleaffects how much solar actinotherapy our major planet receives , part altering our mood and sporadically sending us intoice ages .

A star in the Lizard constellation appears to be dragging a trail of stardust behind it.
pretense that are hightail it backward can help identify such change in planetary orbits . But like weather condition forecast , these measurements become less accurate over long time duo , becauseuncertainties in the planets ' path grow exponentially . Therefore , scientist antecedently believed they could predict Earth ’s path accurately only over the past 70 million years or so .
Such simulation have another defect : They consider thesolar systema house of cards . Yet , being part of theMilky Way , it receive intragalactic visitant fairly regularly . Starsare predicted to exceed within 200,000 astronomical units of the sun roughly 20 times every million years or so . ( One astronomical unit , or AU , is about 93 million miles , or 150 million kilometre , or about the average space between Earth and the sun . ) In fact , in December 2023 , researchers calculated that such a hotshot could , a billion years from now , quetch Earth from its orbit , possibly saving it from being consumed by the expound Dominicus .
Related:‘Runaway ' black yap the size of 20 million sun caught speeding through space with a trail of newborn star behind it
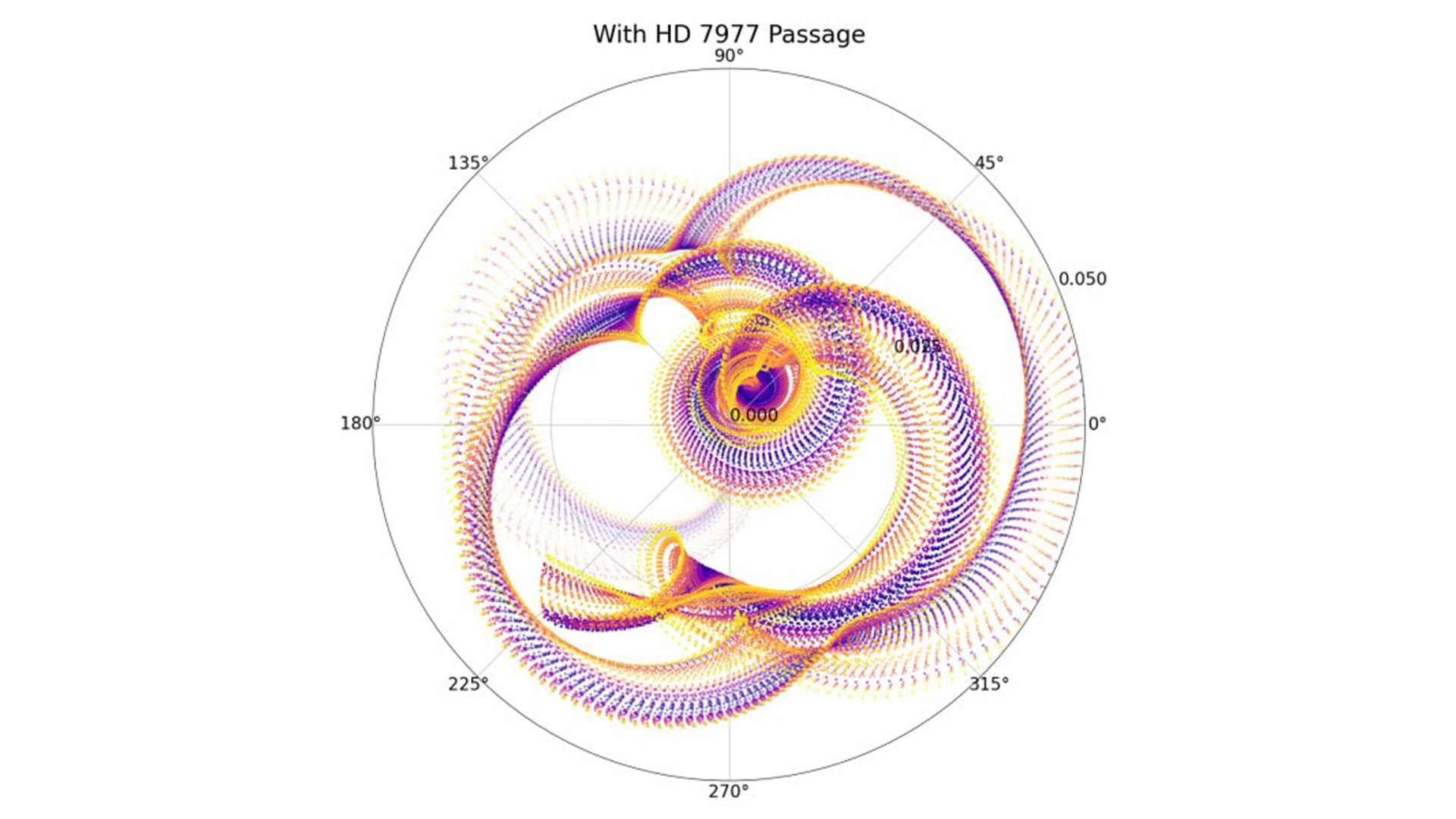
HD 7977’s close passage may have been one of the 10 most powerful encounters during our solar system’s history, introducing much uncertainty in measurements of Earth’s past orbit.
That field inspired two members of the same squad to attend into the impression that a passing ace may have had on Earth ’s orbit in the past tense .
" We just decided to see what would go on if we started wing a bunch of maven past the solar arrangement in simulations , " saidNathan Kaib , a elderly scientist at the Planetary Science Institute in Arizona . Kaib and co - authorSean Raymond , an stargazer at the University of Bordeaux in France , used computer framework to generate a hundred backward forecasts of the way of life of planet in the solar system . The research was published Feb. 14 inThe Astrophysical Journal Letters .
Each simulation ran until Earth ’s eccentricity ( the amount by which the planet ’s orbit deviant from a perfect rotary ) change from its current value by 10 % , after which point the model became unreliable . In some scenarios , the researcher allowed a sunlike hotshot to go about within 200,000 AU of the sun . They found that including a leading flyby gash the foretelling fourth dimension duad from 77 million yr to just 62 million years in the past . The researchers also discovered that the stars create a celestial half mask effect , tugging on the gas giants that then nudge Earth .

Kaib and Raymond then moved from the full general to the finicky , zeroing in on the star that passed the solar organisation most recently , just 2.8 million years ago : the sun - sizing HD 7977 . Calculations suggest HD 7977 in all likelihood approached the sun at a space of 13,200 AU but may have issue forth as close as 3,900 AU . If the diminished length was true , the investigator discovered that the prognostication window of Earth ’s orbit diminished to just 50 million years ; beyond then , the celestial orbit became too eccentric to forecast .
— A ' runaway star ' could keep Earth from extinction a billion years from now . Here ’s how .
— Why do icing years happen ?

— Earth barreling toward ' hothouse ' nation not date in 50 million years , epic new clime record show
This shortened forecasting meter windowpane has gravel climatologists who study ancient Earth ’s mood , because many believed that thePaleocene - Eocene Thermal Maximum , an interval of orbicular thawing around 56 million geezerhood ago , occur when Earth ’s cranial orbit swing our major planet extra close to the sun . Now , however , with Earth ’s path no longer dependable , the climatologist have to investigate other reason , like geological factors .
The subject ’s findings have deduction for the hereafter , too . Kaib suppose the next slate prima visitor isGliese 710 , which will pass within 10,000 to 15,000 AU of the sun 1.3 million years from now . But , he lend , " whether this fluster decreases our ability to augur the Earth ’s future orbital evolution is an open question . "















