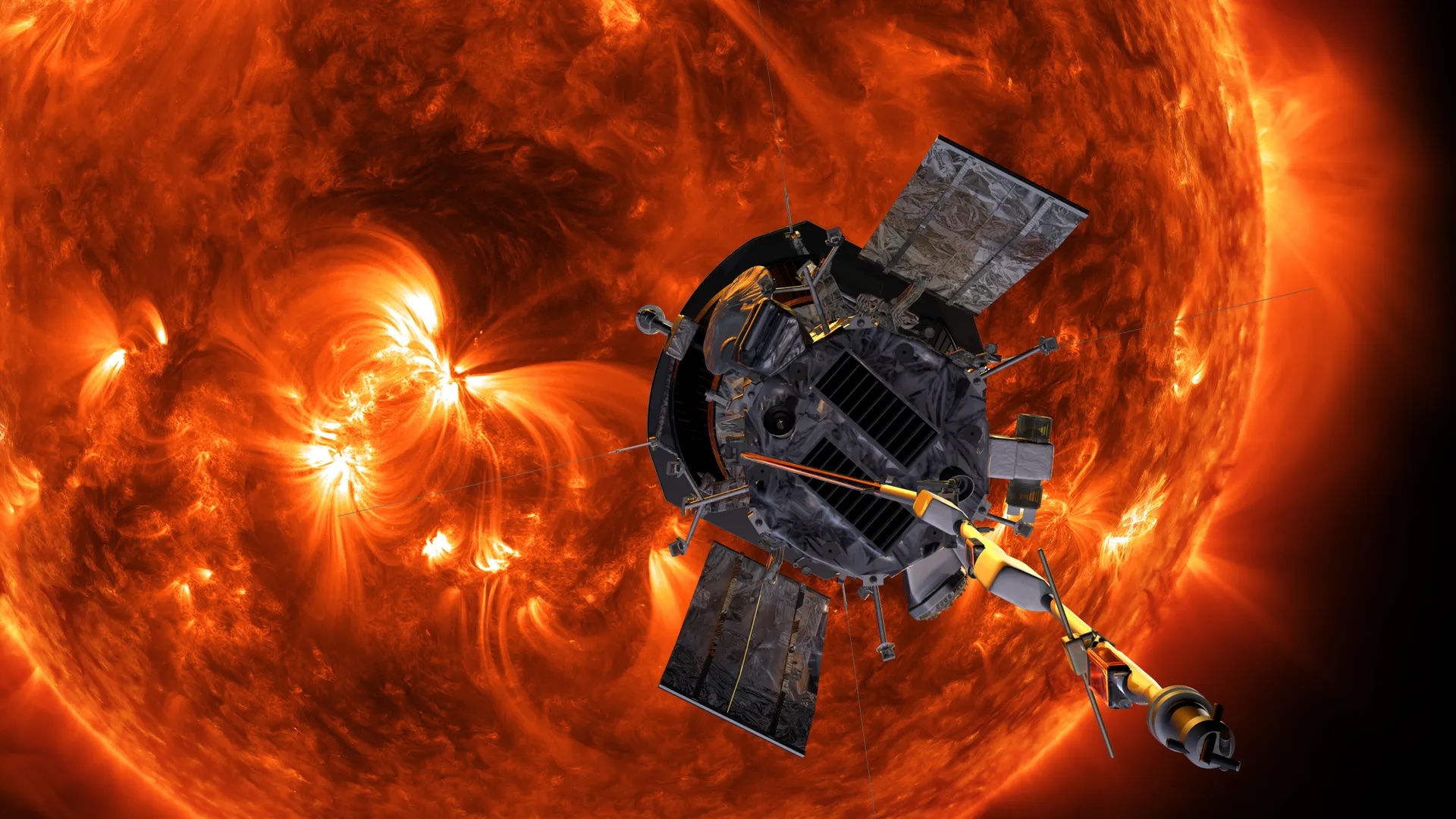
When you buy through links on our site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Oursuncould grow ruinous superflares far more often than antecedently thought — and one may even be due soon — harmonize to newfangled research .
Superflares are solar megastorms grand of times more herculean than regularsolar flare , equal to ofwreaking incalculable damageas they fry electronics , wipe datum host and send planet whirl from blank .
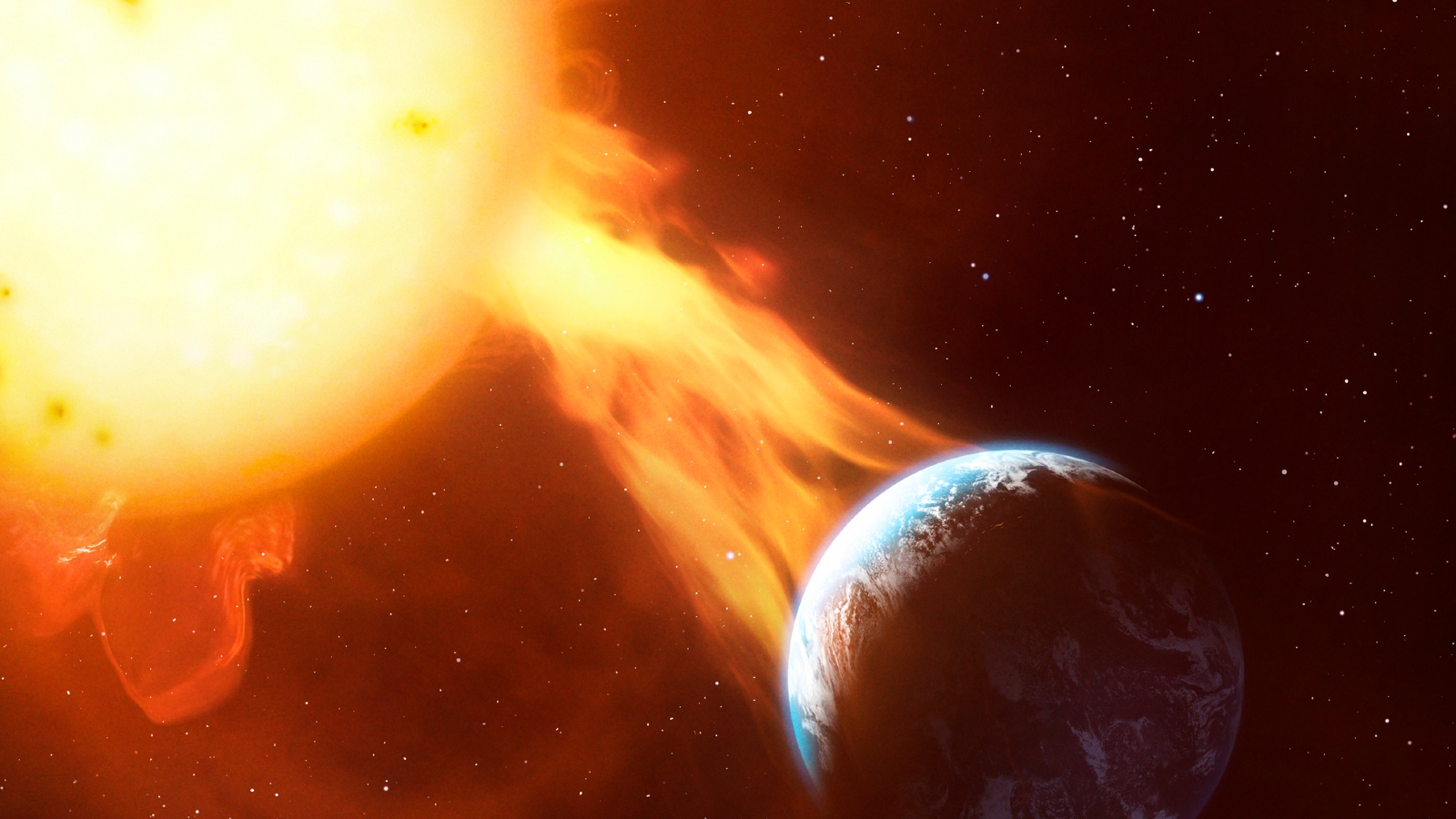

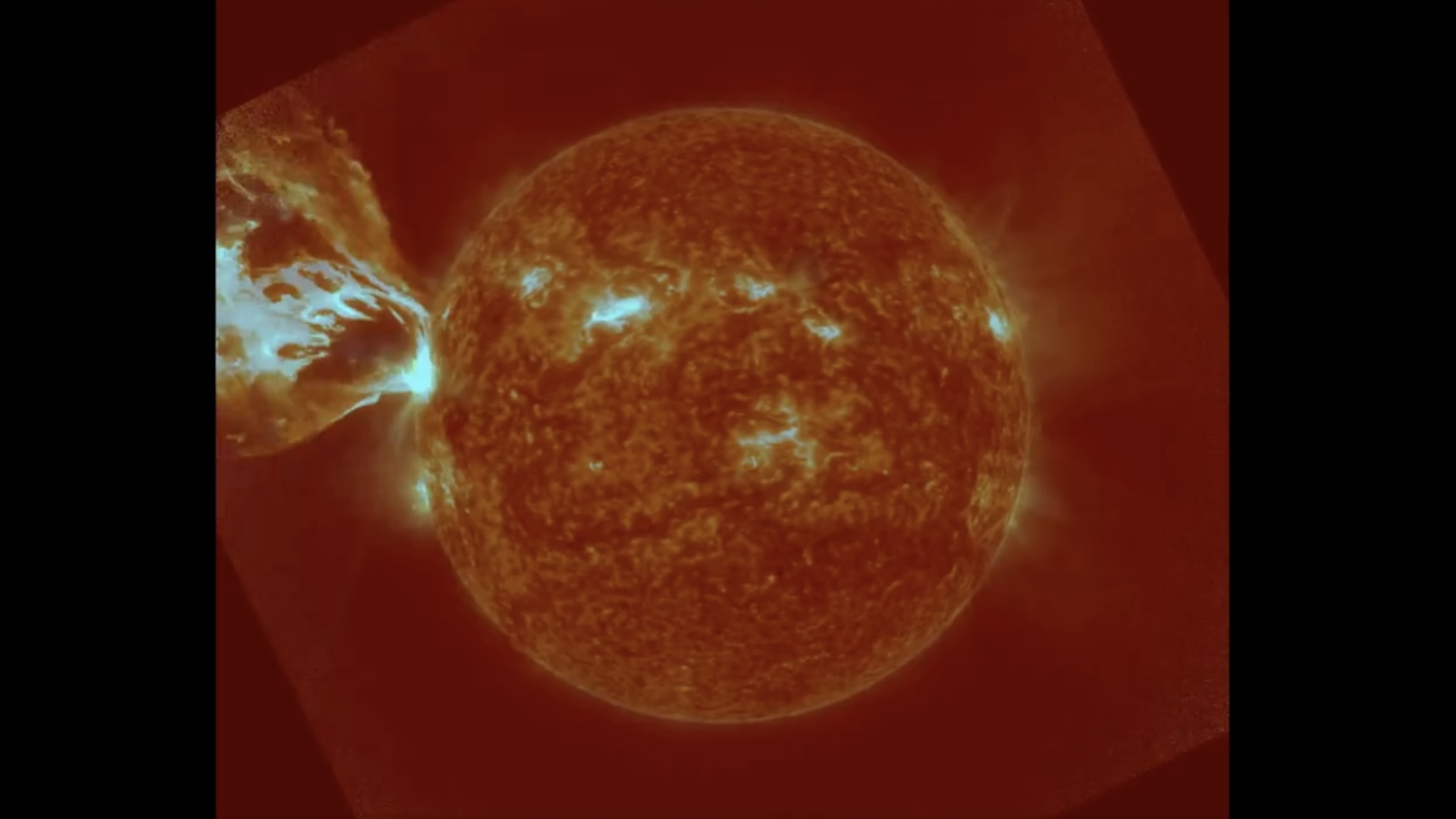
A conceptual image of the sun launching a massive fiery plume toward Earth.
Past study , made by keep stars similar to our own , advise that superflares likely pass once every few thousand year . But now , a fresh sketch of 56,000 Sunday - like stars has revealed that stars like ours may experience powerful superflares much more often than we retrieve — around once every century . However , some important doubtfulness remain . The researchers bring out their finding Dec. 13 in the journalScience .
" Our results demonstrate that stars with Sun - similar [ stars ] … can indeed produce superflares,“Valeriy Vasilyev , a doctoral bookman at the Max Planck Institute forSolar SystemResearch , told Live Science in an email . " Ionizing radiation , ultraviolet light , and X - ray during a superflare ( as well as from a [ coronal tidy sum ejection , a blood plasma undulation launch from the sun ] if it come with the superflare ) can have significant shock . Details such as the impact on Earth ’s atmosphere , magnetosphere , and technological system are important field of study for further investigation . "
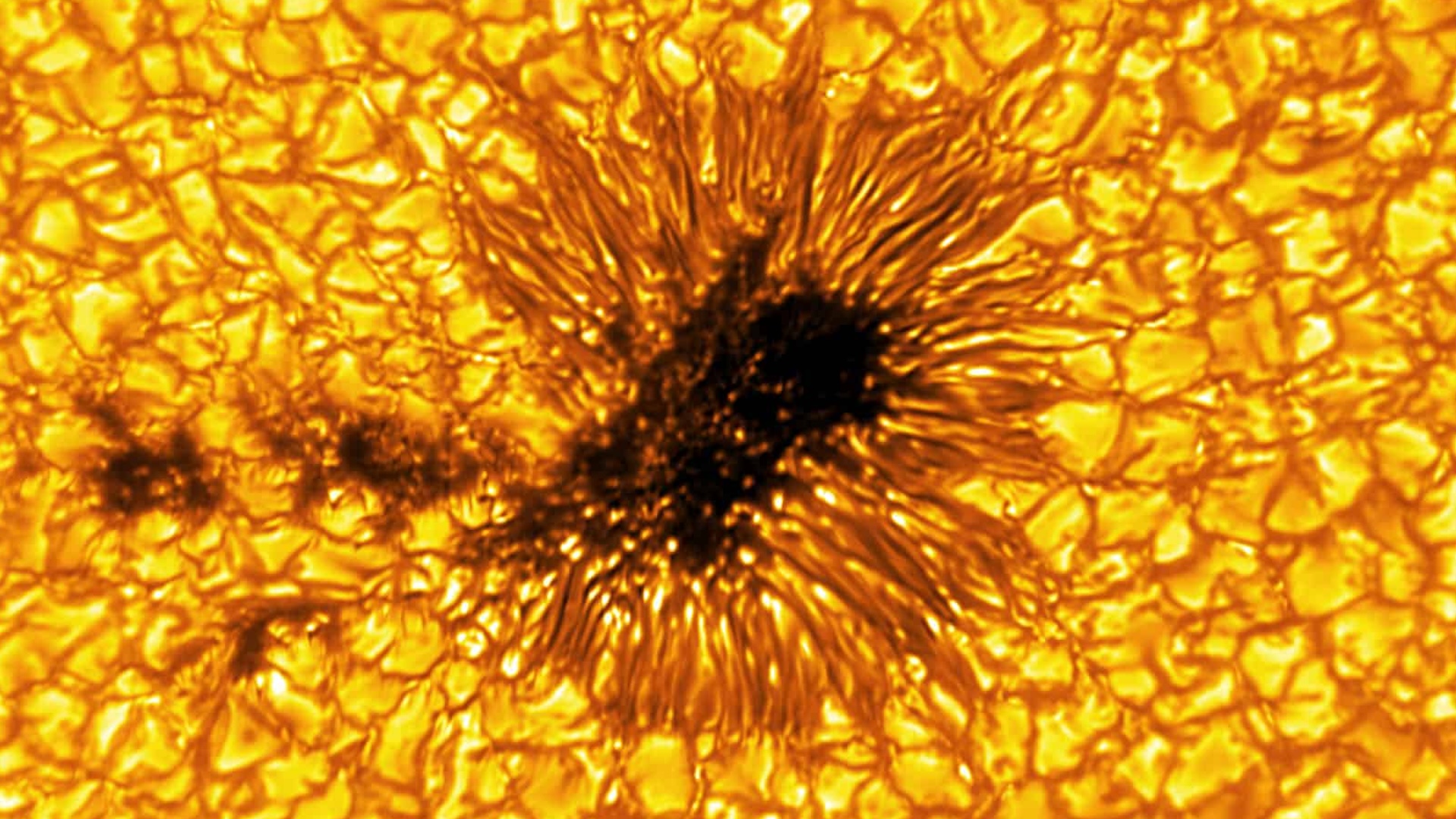
The sun is a gigantic bollock of plasma whose charged ion swirl over its surface to make powerfulmagnetic fields . As charismatic - field lines can not cross each other , sometimes these fields knot before suddenly snap to set in motion bursts of radiation calledsolar flare , which are sometimes accompanied by tremendous coronal bulk ejections ( CMEs ) .

If these outbursts are facingEarth , the hug drug - rays and ultraviolet radiation produced by the flares knock electrons fromatomsin the upper atmospheric state , forming an ionise screen that high - frequence receiving set wave can not jounce off that leads to tuner blackout . These blackouts happen over the expanse alight by the sun during the prison term of the flare and last one or two hours .
Related : Ancient solar storm smashed Earth at the wrong part of the sun ’s cycle — and scientist are concerned
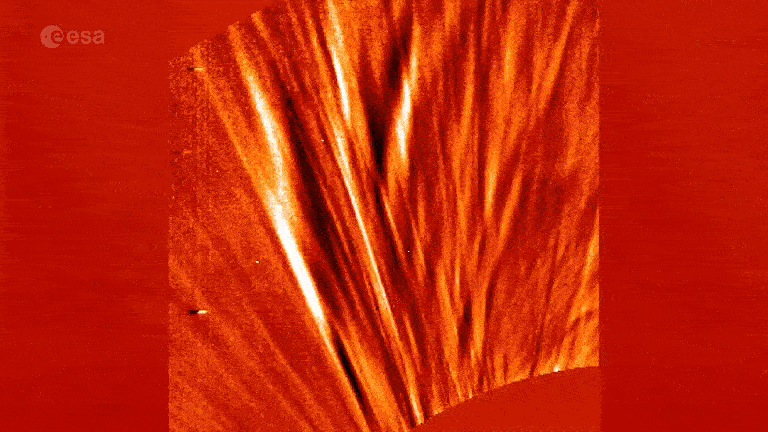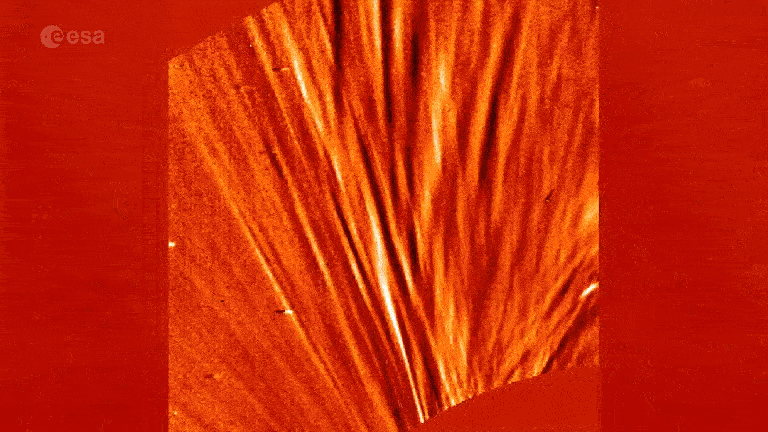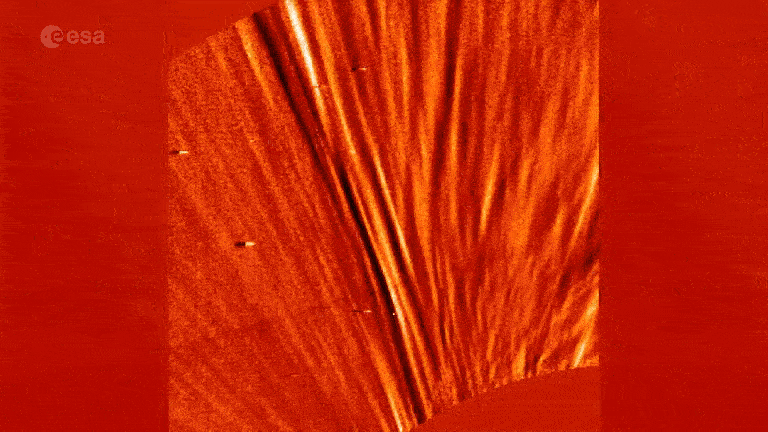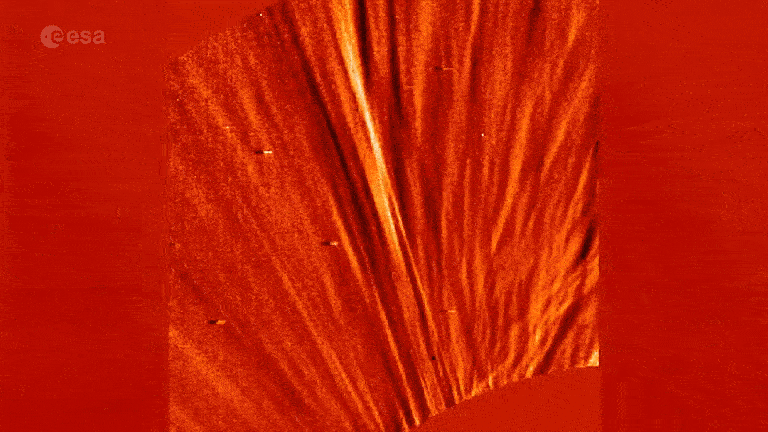
One of the bombastic solar storms in late history was the 1859Carrington Event , which released about the same energy as 10 billion 1 - megaton nuclear bomb calorimeter . After slamming into Earth , the herculean flow of solar particles set telegraph arrangement around the world on fervency and caused break of day bright than the light of the full moon to appear as far south as the Caribbean .
Yet some evidence , such assudden ear in radiocarbon levelsfound inside ancient tree ring , advise that our sun could be up to of producing flares hundreds of meter hard than the Carrington Event . If point toward Earth , these storms could prove to be fatal .
To investigate the likelihood of a superflare being produced by our sun , the investigator behind the new work usedNASA ’s Kepler space telescope to study 56,450 stars , identify 2,889 superflares amount from 2,527 maven like our sun between 2009 and 2013 .
Compared to previous subject field , this is a meaning step up in the frequency of devastating superflares , a final result the researchers assign to biases in past experimentation , such as only measure star with rotation menses exchangeable to our sunshine .
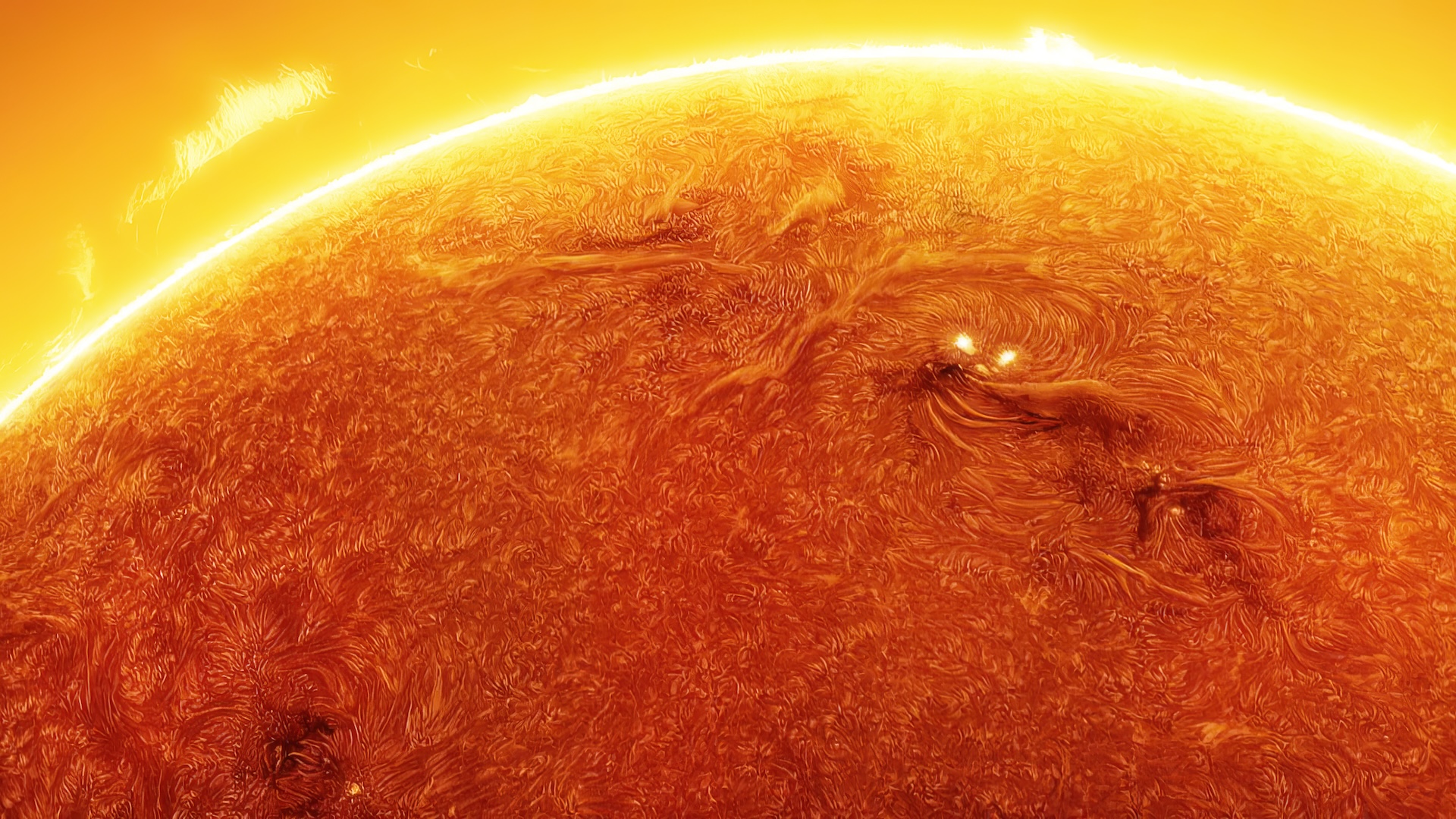

As most rotation point ( which are tied to solar activity ) are difficult to detect , this run a lot of star topology like ours to be eject from prior observations . But the astronomers behind the study developed a new method to make around these biases .
" We employed a Modern flare detection method developed by our group to identify flash sources in light curves and images with sub - pixel resolution , accounting for subservient effect , " Vasilyev said . " This method has been apply for the first time to detect superflares , enabling the analysis of a much larger sample of asterisk . "
— An ' net Revelation of Saint John the Divine ' could ride to Earth with the next solar storm , new enquiry warns

— devastate solar storms could be far more common than we think
— Solar storms might be do gray heavyweight to get lost
However , despite their troubling findings , some assumptions within the work persist unexplored . These include possible unobserved divergence between our own sun and the Dominicus - similar star they observe flaring . For example , 30 % of these flaring stars exist in binary span — two stars orbit a shared center of somberness — which could be triggering superflares through tidal interactions .

Loose ends such as these will need to be investigate further before we can be certain that the sun is likely to pummel Earth with a superflare soon , the researchers say .
In the meantime , they recommend better forecasting of the sun to predict when it might throw its next extreme tantrum — an effort which will be helped by the planned launching of theEuropean Space Agency ’s Vigil probe in 2031 .
" I hope people will cautiously investigate [ this question ] after reading our paper , " Vasilyev allege .