When you buy through link on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it turn .
ocular illusions play on the mentality ’s biases , tricking it into perceive images differently than how they really are . And now , in black eye , scientist have harnessed an optical deception to reveal hidden insights into how the brain processes ocular data .
The research focused on theneon - color - spreading illusion , which comprise patterns of thin lines on a solid setting . Parts of these lines are a different colour — such as lime green , in the example above — and the brain perceive these lines as part of a satisfying shape with a distinct border — a forget me drug , in this case . The unsympathetic soma also appears brighter than the lines hem in it .
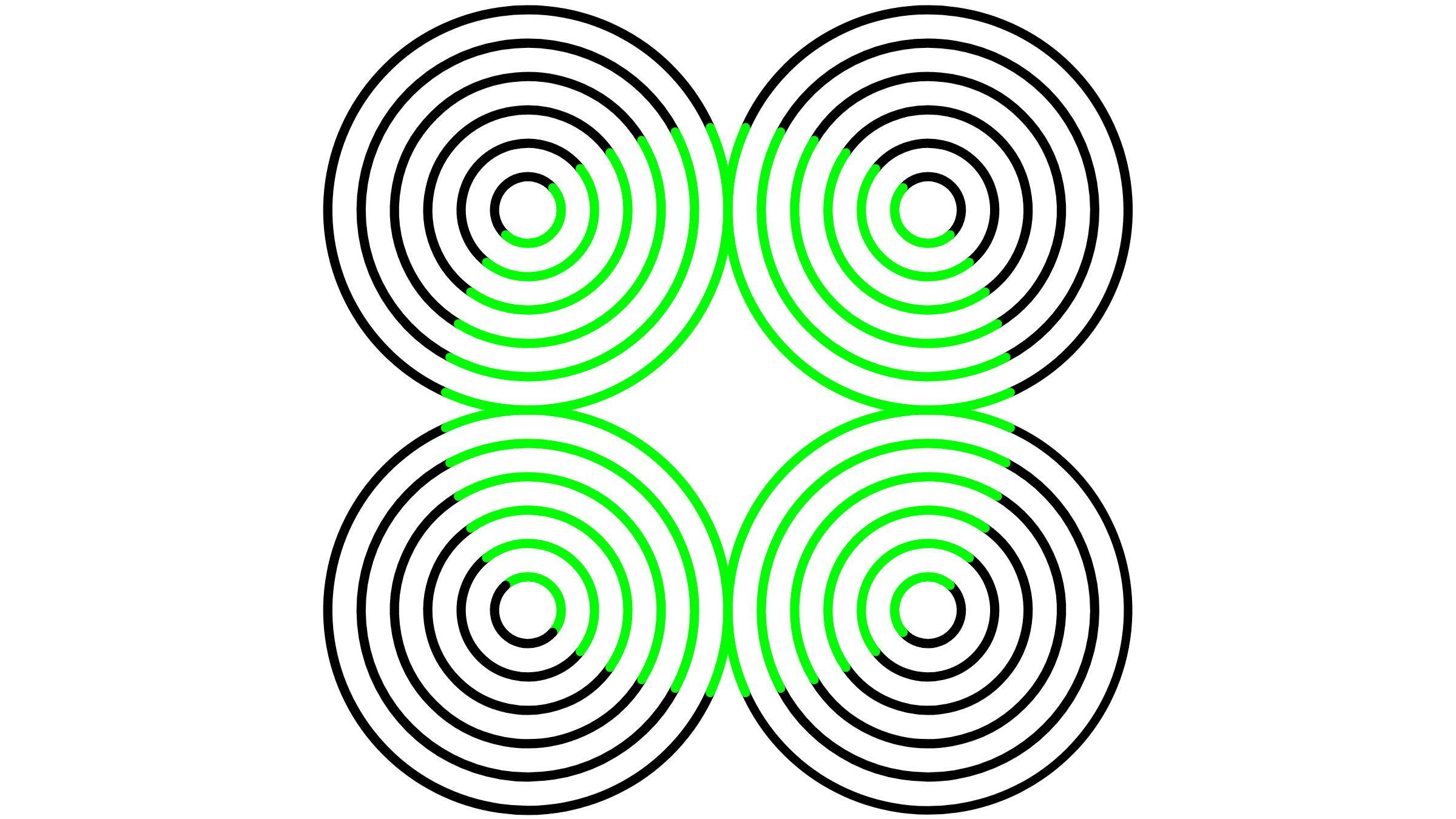
The new study investigated the perception of brightness in mice by looking at how they responded to an optical illusion called the neon-color-spreading illusion, an example of which is illustrated above.
It ’s well build that this fancy causes the human brain tofalsely fill in and perceivea nonexistent outline and luminosity — but there ’s been on-going argumentation about what ’s go on in the psyche when it happens . Now , for the first clip , scientists have demonstrated that the illusion influence on mice , and this leave them to peer into the rodent ' brain to see what ’s going on .
Specifically , they soar upwards in on part of thebraincalled thevisual pallium . When light hits our eye , electric signals are sent via nerves to the visual cortex . This area processes that ocular data point and broadcast it on to other areas of the brain , allowing us to perceive the world around us .
Related : The mastermind - bend secret behind century of opthalmic illusions has ultimately been reveal
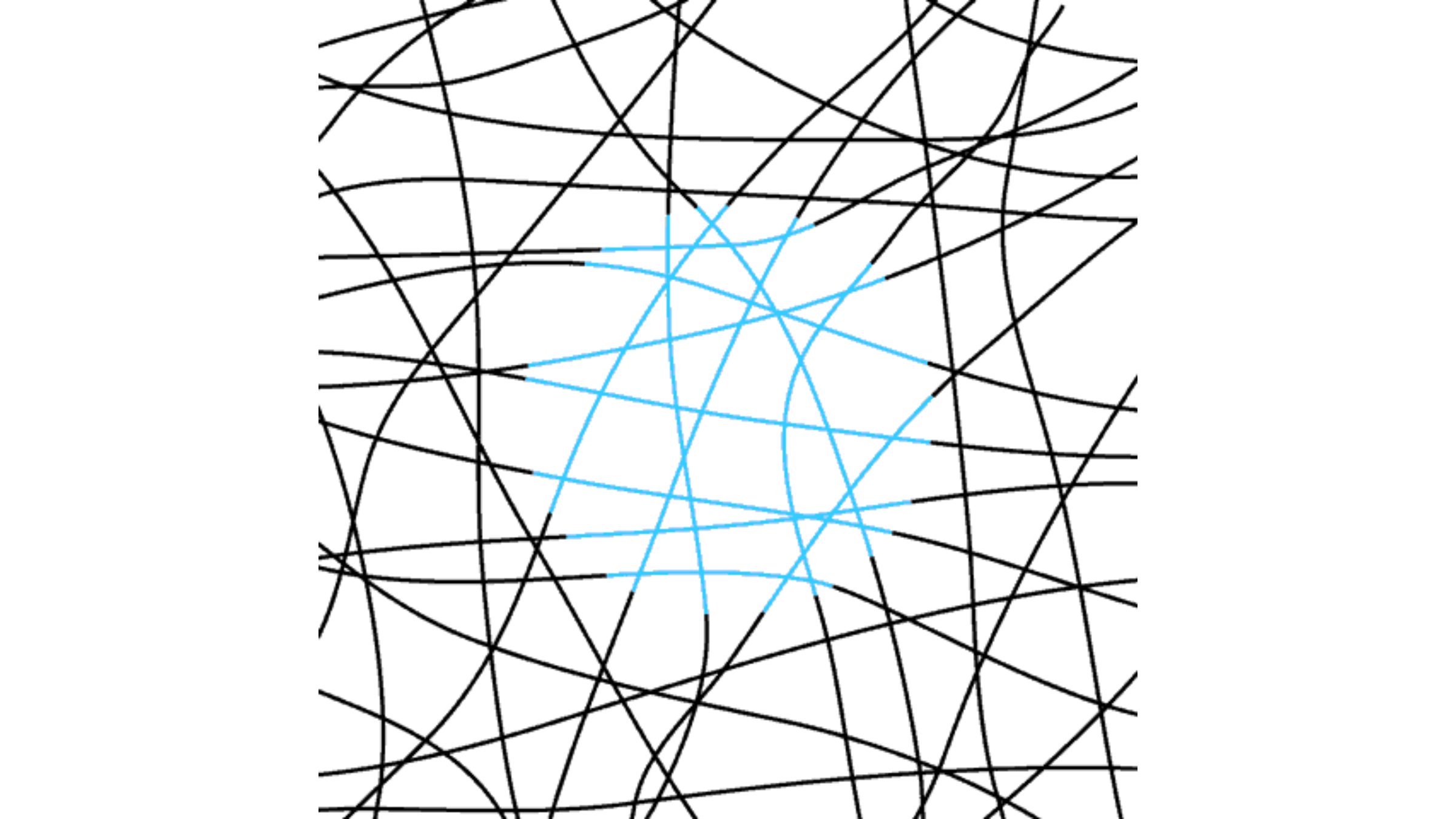
This is an alternative version of the neon-color-spreading illusion. In this case, the brain perceives the colored blue lines as belonging to a blue circle, but in reality, the background is still white and the blue lines don’t form a closed shape.
The ocular cortex is made of six layers of nerve cell that are progressively amount V1 , V2 , V3 and so on . Each layer is responsible for processing different feature article of images that hit the middle , with V1 neuron handling the first and most canonic layer of information , while the other layers belong to the " higher visual area . " These neuron are responsible for more complex visual processing than V1 neurons .
Until now , scientist have debate the extent to which V1 neurons answer to illusive brightness , such as the brightness people perceive when reckon at the neon - colouring - spread magic trick . In a serial of laboratory experiments in mice , researcher have now depict that these neuron toy a fundamental part in this process and that their activeness is also normalize by feedback from V2 neurons . So there ’s a burst back and forth between these different layers of the optical cortex .
This knowledge may pad our sympathy of consciousness , the researchers enjoin in a paper published April 23 in the journalNature Communications .

" The discovered relationship between V1 and V2 in processing the legerdemain implies that cognizance is a top - down process , " as react to a bottom - up process , co - authorMasataka Watanabe , an associate professor in the section of systems innovation at the University of Tokyo , tell Live Science in an electronic mail .
Top - down processingrefers to the way our brains render our surroundings by taking anterior experience into account , rather than alone swear on visual stimuli alone . By contrast , pure bottom - up processing would take the different features of an image and flick them together like puzzle art object , making a logical motion picture without stimulation from a person ’s memory .
Other studies have impliedthat consciousness is a top - down - physical process , but this shiner study provides direct grounds for it , Watanabe aver . The answer is n’t black and ashen though , as some indicate that consciousness likely arises froma mixture of both .

Related : topnotch - detailed map of mind cell that keep us awake could amend our savvy of cognizance
What is the new evidence ? In the study , mice were show a combination of Ne - colour - spreading illusions and other , interchangeable - search patterns that did not trigger the fantasy . at the same time , Watanabe and colleagues measured the natural process of neurons in the rodents ' brains with implanted electrode .
The team also measured whether the mice see the conjuration as bright by assessing how much the pupils in their eyesdilated or constricted . This reply matched that seen in humankind when we comprehend changes in light levels .

V1 neurons respond to both illusory and non - illusive images , but they take longer to respond to the former . This supports the hypothesis that V1 neuron need feedback from high optic area to work these types of illusions , the squad report .
— How this trippy head game will make you see an ' flourish black trap '
— This optical illusion tricks you into seeing dissimilar colors . How does it ferment ?

— A new type of opthalmic thaumaturgy flim-flam the Einstein into seeing dazzling re
The researchers then essay through an experiment inhibiting the activity of the higher ocular area neuron , finding that V1 neurons were less probable to respond to the illusions . This put up further evidence that a gamey - level feedback cringle is needed to perceive the deception .
Going forward , the team plans to deal further studies in which they ’ll mess up with the activeness of higher visual field nerve cell in mouse , Watanabe said . They go for that this will spill more light on the neural mechanisms underlying consciousness in mice , and by extension , in humankind .

Ever wonder whysome hoi polloi work up muscle more well than othersorwhy freckles number out in the Lord’s Day ? post us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your inquiry answered on the website !









