When you purchase through link on our site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it act upon .
Scientists have revealed how much of the vast deep sea storey humankind has observed , and it ’s a hugely small amount .
According to a new written report published May 7 in the journalScience advancement , just 0.001 % of the cryptic seafloor ( anything below 656 feet , or 200 measure ) has been explored — despite it covering about two - third of Earth ’s surface . This area is approximately equivalent to the size of Rhode Island .

Scientists estimate we’ve explored just 0.001% of the deep ocean seafloor.
" There is so much of our ocean that remains a mystery,“Ian Miller , main science and creation ship’s officer at the National Geographic Society , which contributed to the discipline ’s funding , say in a instruction . Miller was not himself an source of the cogitation .
The deep sea floor is characterized by Brobdingnagian pressure and about - freezing temperature , and is home base to avariety of strange and often elusive creatures . It play a essential role in carbon storage , and is believed to host many unknown species — some of which could be medically or scientifically valuable .
Most of what we know about this seafloor is base on visual imaging from man submersibles , remotely operated vehicles ( ROVs ) , self-reliant underwater vehicles ( AUVs ) , or towage cameras tether to ship .
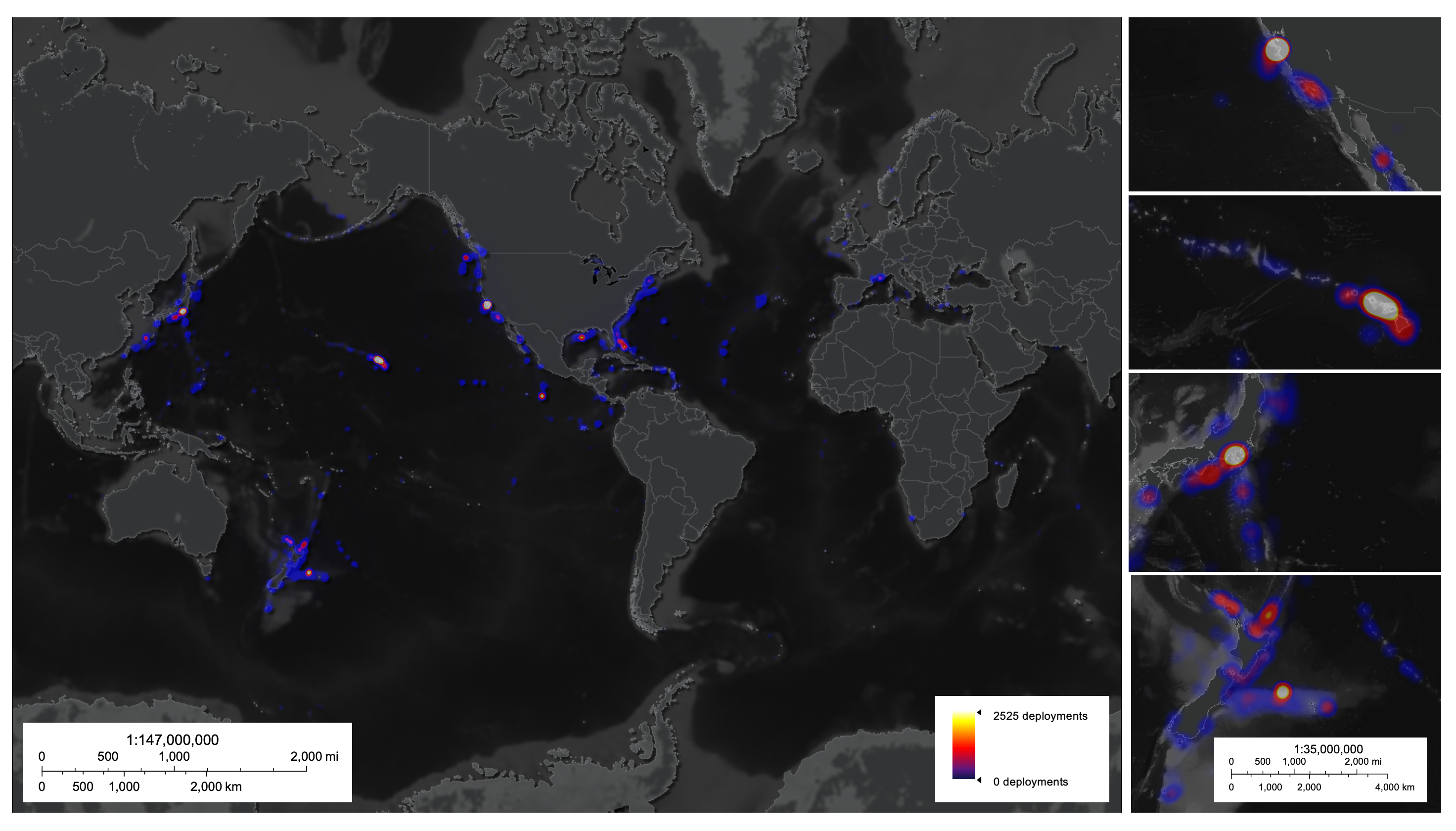
Deep-sea dive activity has been concentrated in a small number of locations, particularly Monterey Bay, USA, Hawai’i, USA, Suruga and Sagami Bays, Japan, and New Zealand.
In the Modern study , research worker analyzed the proportion of deep seafloor that had been visually search by accumulate 43,681 phonograph recording of deep ocean dives that included visual imaging .
They used two methods to reckon how much of the deep seafloor had been observe by humans , one tracking the course of vehicles along the seafloor used in each nosedive , and the other using time spent by the vehicle at the ocean floor . For the dive route method , they guess that a total of 822 square mile ( 2,129 square kilometre ) had been observed . Using the time - based method , they estimated a visual ocean floor insurance coverage of 1,476 square miles ( 3,823 sq / km ) .
Related : What percentage of the sea have we mapped ?
The researchers concluded that over the track of all our deep sea exploration , we have only observed between 0.0006 to 0.001 % of the thick seafloor since 1958 .
These estimates are found only upon seafloor observation from approachable record however , and the researchers remark that oil and gas and telecom company may have explore much more of the seafloor , but not made these records public .
" As we present accelerated threats to the deep sea — from climate change to potential excavation and resource using — this modified exploration of such a huge region becomes a vital problem for both skill and policy , " work lead authorKaty Croff Bell , president of the non-profit-making organization Ocean Discovery League and National Geographic Explorer , tell in the argument .

" We necessitate a much better understanding of the deep sea ’s ecosystems and processes to make informed determination about resourcefulness management and preservation , " she said .
Additionally , they found that 65 % of all these observations of the cryptic seafloor had been carried out within 200 maritime Admiralty mile ( 230 nautical mile ) of the coast of the U.S. , Japan , or New Zealand , and 97 % of read cryptic - ocean dives had been performed by only five countries : the U.S. , Japan , New Zealand , France , and Germany .
The researchers also note that geomorphological features like ridges and canyons saw a disproportionate amount of exploration , liken to areas such as abyssal plain stitch and seamounts .

— Atlantic sea current are weakening — and it could make the climate in some regions unrecognizable
— Global sea levels lift a whopping 125 feet after the last internal-combustion engine historic period
— Ocean ’s ' heart ' is slowing down — and it will affect the entire satellite ’s circulation

" If the scientific community were to make all supposal about terrene ecosystem from reflexion of 0.001 % of [ the entire land country of Earth ] , it would equate to an assessment region … smaller than the country domain of Houston , " the source wrote in the paper .
The bias in areas of the ocean floor that have been explored , and by whom , further limits our understanding of the full seafloor , the researchers added . The investigator carry a demand for a more ball-shaped effort to research a wide-cut chain of the sea trading floor and its features for rightfully understand and protect this little - sleep together environment .
" Deep - sea exploration led by scientists and local communities is essential to better understanding the satellite ’s largest ecosystem , " Miller said . " If we have a better understanding of our ocean , we are sound capable to conserve and protect it . "

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .








