When you purchase through connection on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it put to work .
scientist have developed a new equipment instigate by devilfish sucker that can fork out drugs without requiring needles or pills . They ’ve already tested it in humans in a small , myopic trial .
The 0.4 by 0.2 inch ( 1.1 by 0.6 centimeters ) patch can stay to the internal lining of the cheek , stretch across it and increase the engrossment of an attached drug .
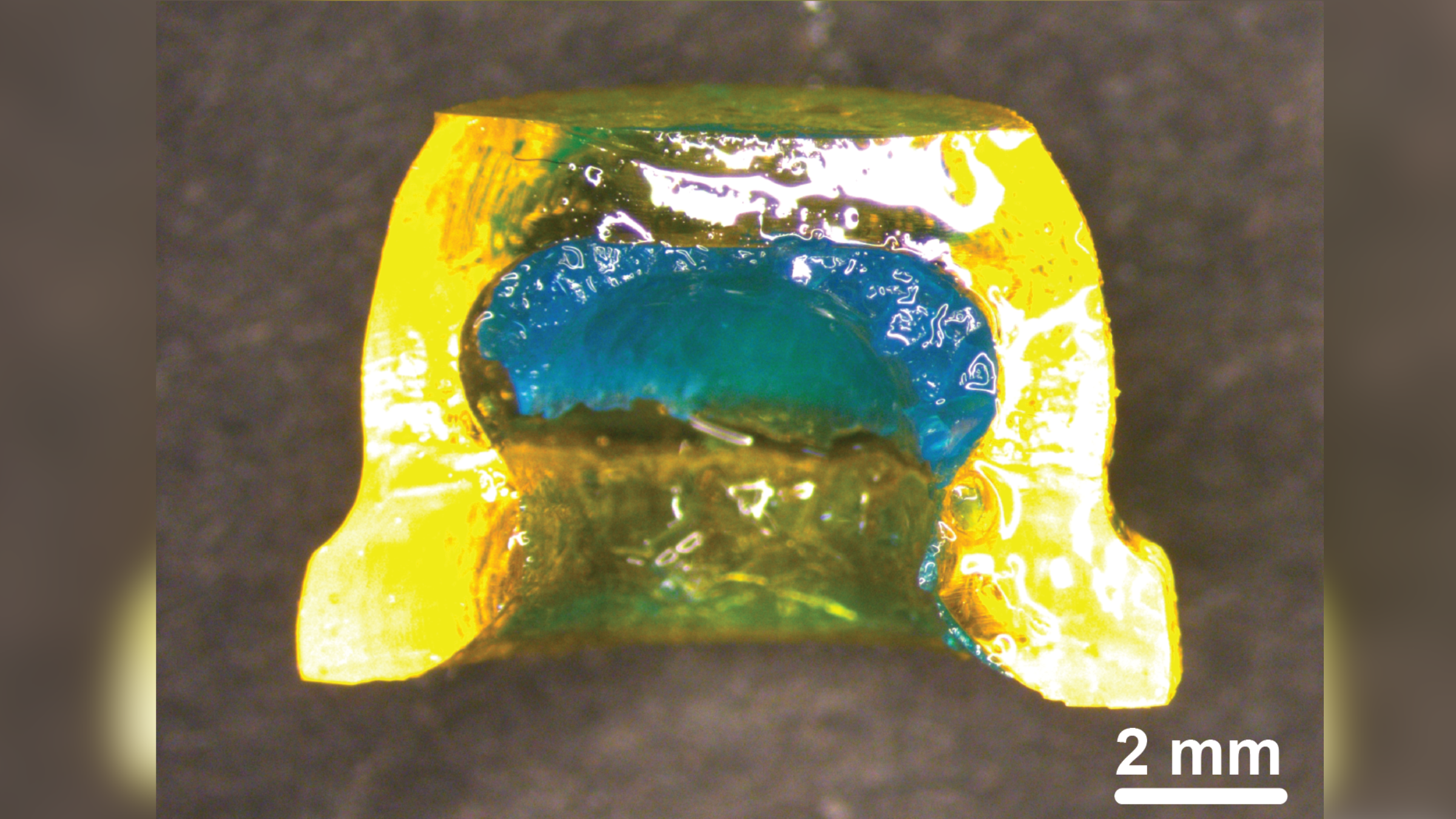
The new patch after being “loaded” with the drug desmopressin.
When used in dogs for three minute , the patch efficiently deliver two drug — desmopressin , which is used to treat excessive thirst and the urge to pee often , and semaglutide , the active element inOzempic and Wegovy , drugs that are severally used to treatdiabetesandobesity . A interlingual rendition of the plot of land without a drug attached was also safely used by 40 human volunteer for 30 minutes while they were able to talk , move around and rinse their backtalk with water .
Further ontogeny is need . However , the plot could represent a less invasive and more comfortable approach shot to drug deliverance , particularly for larger drugs that are poorly absorbed by the digestive organization so can normally only be throw in using needle .
come to : DeepMind ’s AI used to develop tiny ' syringe ' for inject gene therapy and tumor - killing drugs

The patch next to a one-euro-cent coin for scale.
" This is an interesting and well - design series of written report expanding the chain of mountains of drug delivery systems inspired by nature,“Adrian Williams , a prof of pharmacy at the University of Reading in the U.K. , who was not involved in the research , tell Live Science in an email . " stretch is known to increase the permeability of mucosal membrane [ the protective layer that lines your organs and cavum like the mouth ] , and is particularly promising for large biological drugs , such as peptides and protein , which tend to be ill absorbed and so are unremarkably given by shot . "
Other way of delivering large drug to the organic structure , for example viathe noseor usingmicroneedlesapplied to the skin or incapsules , can be inefficient and unmanageable to make , the study generator compose .
" compare to nasal bone obstetrical delivery system , we would proffer something which is much more straightforward to employ because you have the drug dose contained in the suction patch , you go for it on your mucosa and then you press . That ’s it,“Jean - Christophe Leroux , senior study writer and prof of drug expression and saving at ETH Zurich , told Live Science . " If you compare it to microneedles , it is less invasive , " he said .

The writer only tested the darn for a short meter so would demand to find out what would happen if it was used repeatedly . They ’d also want to determine which drug would operate with the technology : the fair game is large atom , such as those used to treat fleshiness or osteoporosis , but they ca n’t be too large to fit in the cupful , Leroux said .
Chris McConville , an associate professor in pharmaceutics , drug formulation and delivery at the University of Birmingham in the U.K. who was not involve in the research , told Live Science in an electronic mail that although the machine is interesting , it may not be very practical . The generator tried to mitigate the risk of accidental swallowing of the temporary hookup by using dental dental floss to link it to the unpaid worker ’s shirts , for example , but this need to be further explored .
— FDA approved a 1st - of - its - kind treatment made from human poop . What does it do ?

— Girl diagnose with fatal brain disease get a tailor - made drug within a year
— Tiny robot inspired by spermatozoon want to swim around your body delivering drug
The authors also used a compound that increases the absorption of drug call apermeation enhancerwith the patch , which could mask any benefit of using it .

" I am not certain what the gadget offers over buccal pad of paper [ drugs that stick to the inside of the mouthpiece and dissolve ] as it seems that it is the permeation enhancers that increase absorption , " McConville said .
The findings were published Wednesday ( Sept. 27 ) in the journalScience Translational Medicine .