When you purchase through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
A strange , yellow , wanderer - like tool with four near - smutty optic and magnanimous bulbous claws has been pulled from the profundity of the ocean off Antarctica .
The never - before - seen animal is a sea wanderer — a distant relative of horseshoe Cancer and arachnoid that live on the ocean level , eat through a stalk - like trunk or else of a mouth and take a breather through their legs . scientist have discovered more than 1,000 species of sea spiders all over the macrocosm .
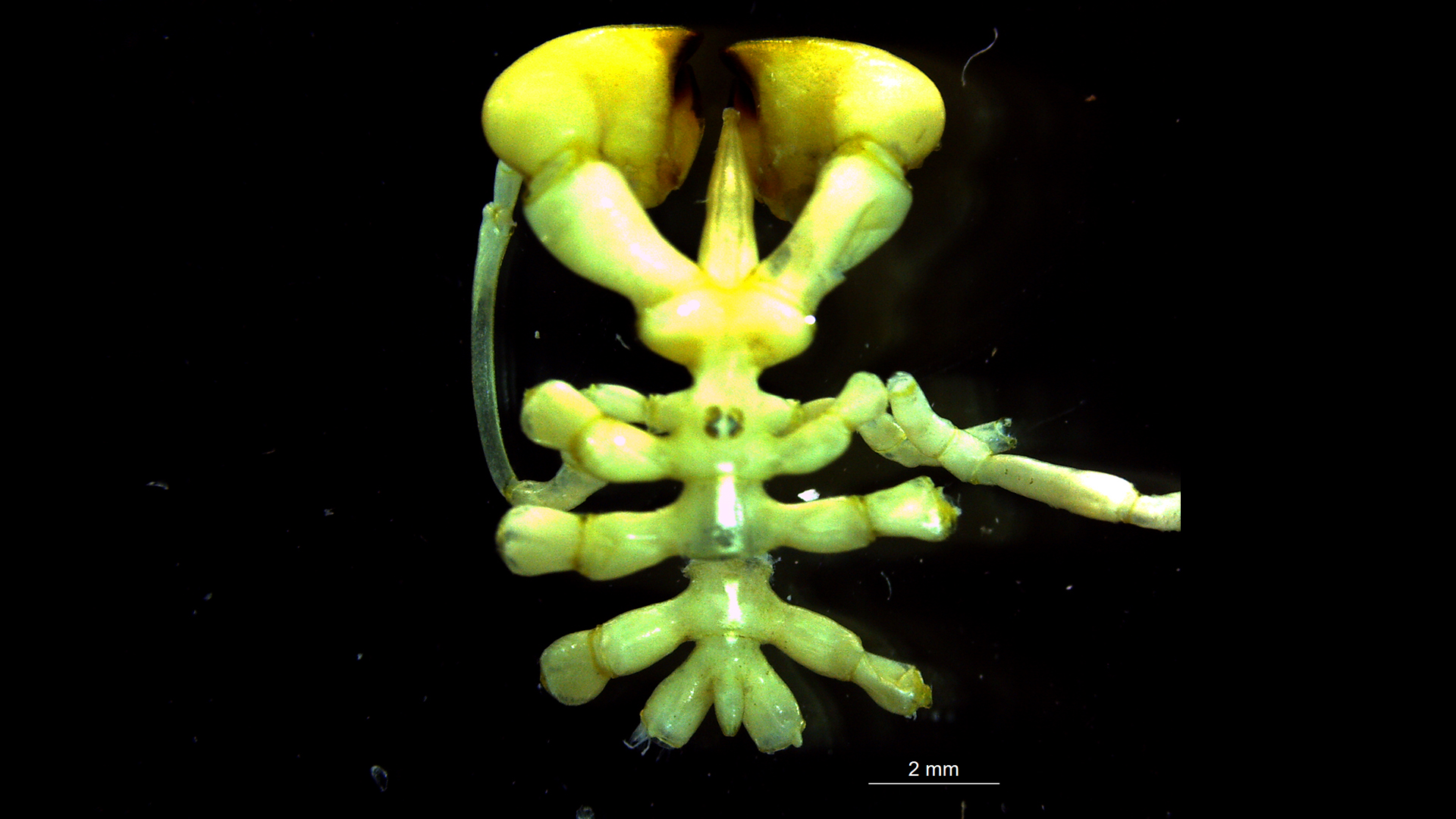
Austropallene halanychi is a newly discovered species of sea spider found off the coast of Antarctica.
The newfound species , Austropallene halanychi , was pulled from the sea floor in the Ross Sea , about 1,870 feet ( 570 measure ) below the Earth’s surface . In addition to all the other weird things about ocean spider , the new specie has gravid hook that wait like " fisticuffs gloves , " which it likely uses to seize hold of diffuse foods like anemones and worms , study carbon monoxide - authorAndrew Mahon , a biologist at Central Michigan University , enjoin Live Science . The bailiwick was published Nov. 28 in the journalZooKeys .
A. halanychi ’s soundbox is about 0.4 inches ( 1 cm ) long , but its leg load nearly 1.2 inches ( 3 cm ) long . That gives the species the lank see distinctive of many ocean wanderer — though some specie can grow much larger , reachingnearly 2 feet(60 cm ) wide .
Related : Sea spiders can regrow their anus , scientists discover
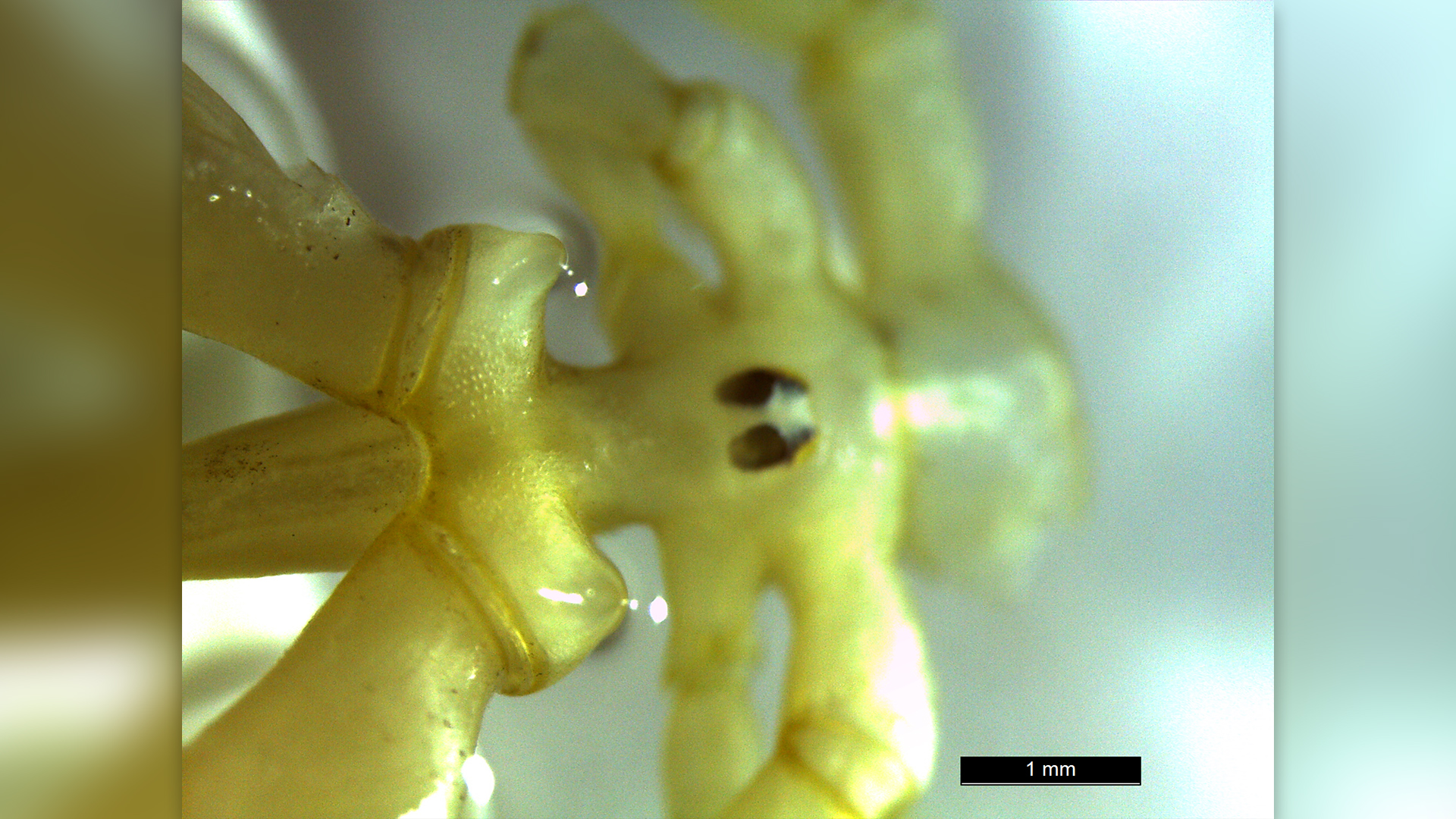

The sea spider was identified as a new species by its large bulbous claws.
What ’s more , this new species is likely just a drop-off in the bucket when it come to the undiscovered wildlife live at the bottom of the Southern Ocean — an ecosystemhome to everythingfrom brightly one-sided sea stars and otherworldly nautical worms to parasite and cold - water precious coral .
" The benthic environs in Antarctica is an area of skill that we ask to keep exploring , " Mahon said . " There ’s so much down there that every time we go , we chance new thing . "
To discover more about this environment , investigator shed nets recondite underwater to pick up whatever might be hang around at the bottom . After pulling the net up , they sort everything they caught and preserve each specimen before shipping them back to labs for further analysis .

— What is the fully grown spider in the humans ?
— Wolf spider mama wearing crown of babies get in stunning photograph
— Horrifying video reveals molting spider rustle in cleaning lady ’s pinna

But with so many potentially new species to key , it can take metre to go through all the samples.A.halanychiwas first pluck up in 2013 by the Nathaniel B. Palmer , a U.S. research vessel . Recently , Mahon and his colleagueJessica Zehnpfennigtook it out of repositing and identified it as a coinage novel to science by study its body shape and genetics .
Yet research worker may also be run out of time to analyze the Antarctic seafloor . As the mood keeps change , warm amniotic fluid may threaten the future of some of the coinage living in this isolated and unique ecosystem , Mahon said . One of the reason that researchers keep hit the books the Antarctic seafloor , he say , is to help describe and protect this biodiversity before it ’s too recently .
Starving cannibalistic spiders wo n’t hunt their siblings , but they ’ll quickly dine on their corpses

Asian solitudinarian wanderer : The arachnid that gets stronger after boot out its own penis
The unvarying surveillance of innovative life could exacerbate our brain function in way we do n’t fully interpret , disturb study suggest






