When you purchase through links on our web site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists are test an alternative to the global position system ( GPS ) that uses phone sign to act as an emergency accompaniment for pilot burner in case their standard in - trajectory equipment is jam-packed or malfunctions .
The 31 operatingGPS satellitesorbit Earth double day by day , let loose precise signal that receivers on the ground can pick up and break down to find out how far aside they are from the orbiter . GPS twist use data from three satellites to precisely triangulate the substance abuser ’s precise location .

Although GPS is highly reliable, it isn’t immune from issues. Scientists have instead proposed using cellphone signals to navigate planes if GPS fails.
Although GPS is highly reliable ( the Federal Aviation Administration ( FAA)certifies itas exact to within seven meters 95 % of the time ) it is n’t resistant from offspring . GPS connexion can not be counted on in and around regions of conflict and can be jammed by malicious parties . Hackers can also " spoof " GPS signal to present pilots with misguide information about their location or direction of travelling . Beyond this , Global Positioning System systems can misfunction or terminate working altogether . If a commercial airliner lost its GPS signal , it could put everyone on display board at risk .
Beyond this , GPS system can misfunction or stop turn altogether . If a commercial-grade airliner were to miss its GPS signal , it could put everyone on board at risk .
Related :X - re vision chip gives phones ' Superman ' power to consider object through walls
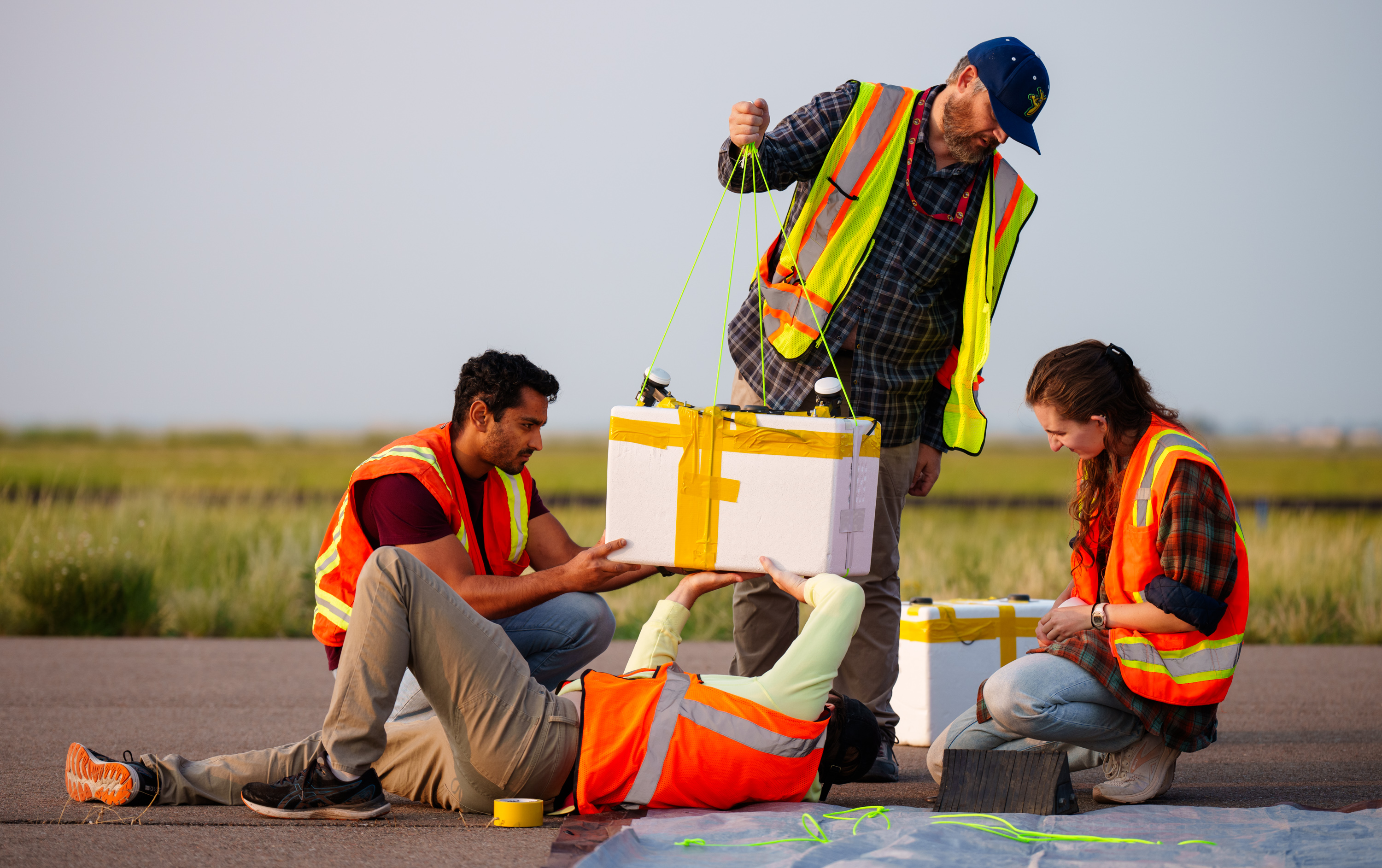

The scientists said the preliminary findings indicate that they detected cell tower signal beacons at an altitude of 82,000 feet.
" The impact of losing GPS could be felt throughout company , ” said tip writer of the studyJennifer Sanderson , an electrical engineer at Sandia National Laboratories and an expert in pilotage algorithms , in astatement .
The labor , carry out by investigator at Sandia National Laboratories and Ohio State University , aim to create a full-bodied condom cyberspace for airborne navigation systems that uses a drift receiver to detect wireless waves from communication theory planet and cellular telephone tower in relation to a plane . It then uses this information to ply pilot with piloting information .
Signals that can be used for navigation , even if that ’s not their think use , are cognise by scientists in the field as " signal of opportunity . " They may rely on processes such as theDoppler essence , in which wave become shell or stretched depending on whether they ’re go nearer to or far away from a defined period , to determine position and velocity .
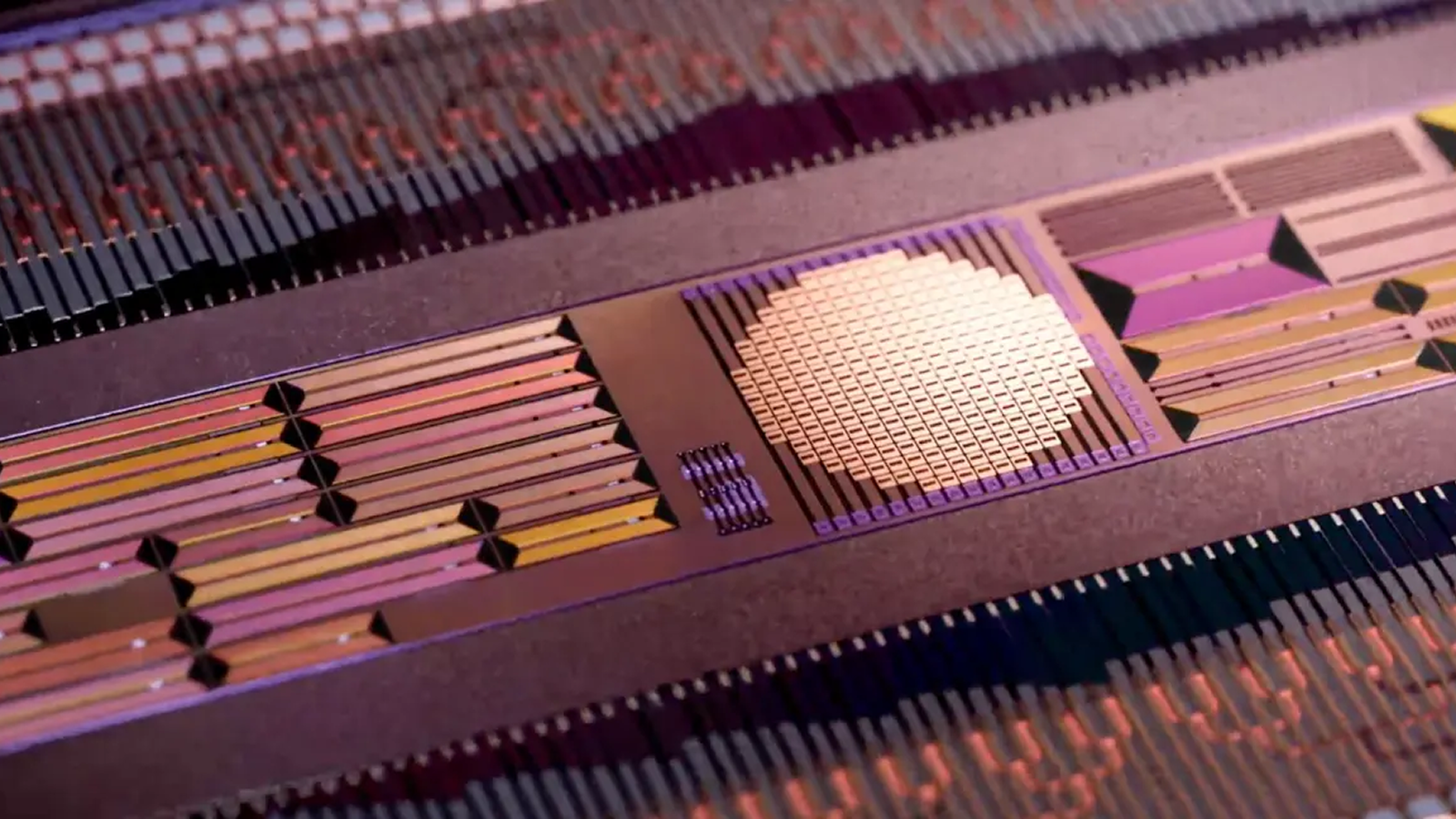
In this case , researcher whip antenna payloads to brave out balloon and get off them into the stratosphere — the stratum of Earth ’s atmosphere between about 4 and 31 geographical mile ( 6 to 50 kilometers ) above the satellite ’s surface — to sit down between the artificial satellite and towers and aim to detect their individual signaling . These payloads could theoretically pretend as emergency brake beacons if a pilot were to lose their GPS signals .
At present , the researchers have to manually determine which satellites commit which sign base on uncommitted reference book data . Going forward , the team will work on using algorithms to permit for consignment to mechanically distinguish satellites and how this connect to a user ’s spatial relation and velocity in material time .
" While we are still processing the flight of steps data , we believe our preliminary findings signal that we detect cell tower signaling pharos at our peak altitude of about 82,000 human foot [ 25,000 G ] , " Sanderson say . " If these signal are clean enough for navigation , it will importantly change what we think was possible for alternate navigation . "

— Cosmic - ray ' GPS ' system that track underground effort could change the way we respond to disaster
— Lost in space ? Here ’s a fresh method acting to bump your way back home
— What happens when a plane makes an emergency landing ?
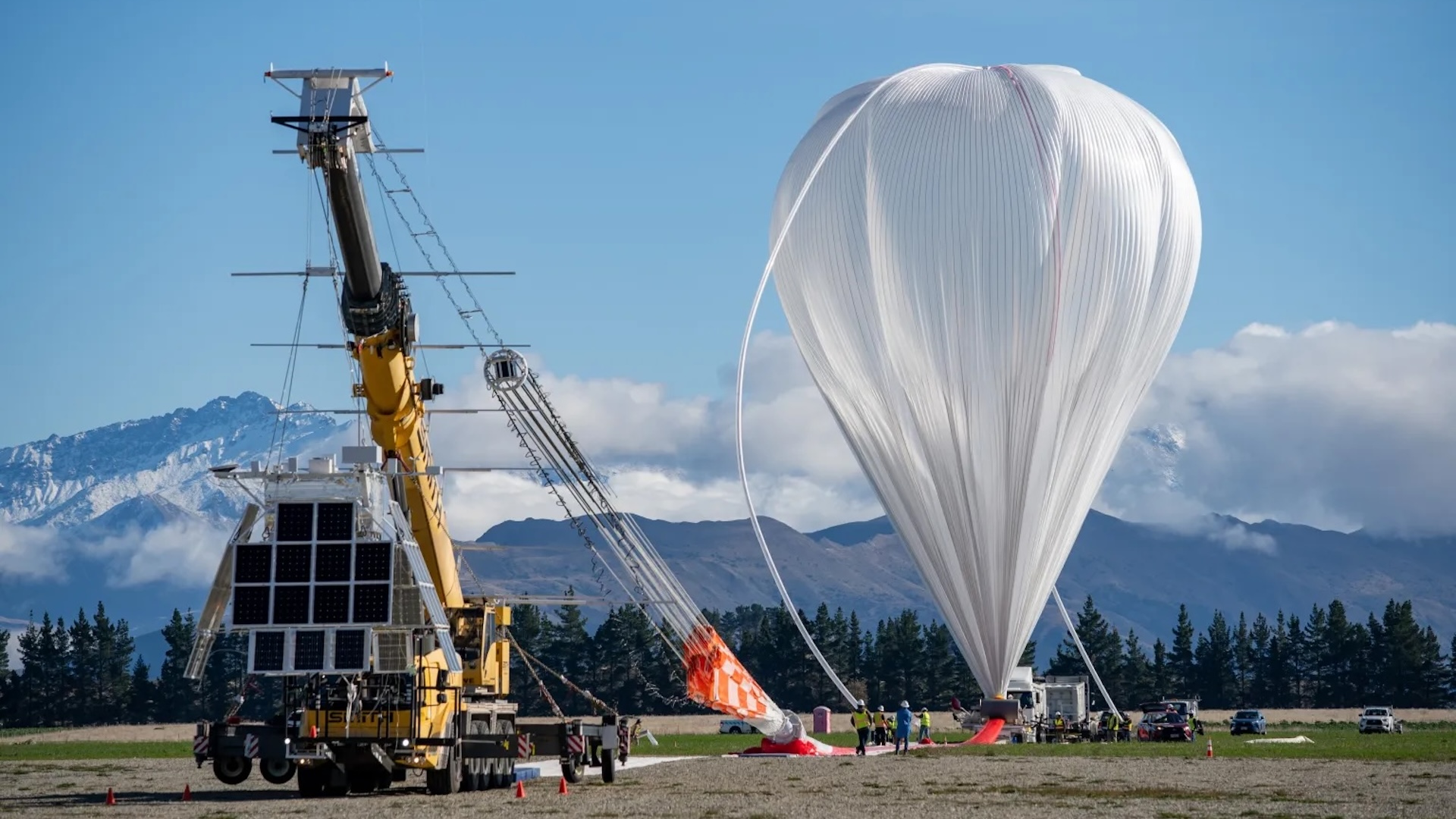

Previous tests of the engineering science pick out place between 5,000 and 7,000 human foot ( 1,500 to 2,100 m ) , whereas this new project has sent payloads as high as 80,000 feet ( 24,300 megabyte ) . If the payload can faithfully turn back navigational data from this altitude , it could have real - world welfare for air travel .
Although the payload float at in high spirits altitudes to better have signals from both communications satellite and cellphone column on the soil far below , it ’s not a foolproof method . orbiter focus their radio waves down to Earth for an optimal signal on the ground , so picking unassailable signal up at conditions balloon tallness is n’t vouch .
Researchers will have to gradually improve sensing capacity and speed to account for this potential for fault down the production line .