When you buy through radio link on our web site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it function .
scientist reversed some sign of immune aging in mouse with a novel discussion that could one day potentially be used in world .
The Modern immunotherapy works by disrupting a natural summons by which theimmune systembecomes biased towards making one case of cellphone as it ages .
The new immunotherapy works by targeting stem cells destined to become one of two major subsets of cells in the blood, which become more dominant as we age.
The mouse study is an " significant " proof - of - concept , but it ’s currently difficult to gauge the signification of the findings , Dr. Janko Ž. Nikolich - Zugich , a prof of immunobiology at the University of Arizona who was not need in the enquiry , tell Live Science in an email . More work is needed to see how well the therapy shifts the immune system into a more youthful , in effect state .
All blood cellular phone , including immune cell and the red blood cells that carry oxygen around the eubstance , start aliveness ashematopoietic stem cells(HSC ) in the blood and bone marrow , the spongelike tissue paper found within certain bones . HSCs fall into two main categories : those specify to become so - called myeloid cells and those that will develop into lymphoid cells .
Myeloid cells include red rip cells and immune electric cell go to our broadly reactive first line of vindication against pathogen , including cellular phone calledmacrophages that gun trigger inflammation . Lymphoid cells include cellular phone thatdevelop a memoryof germs , such as T and B cell .
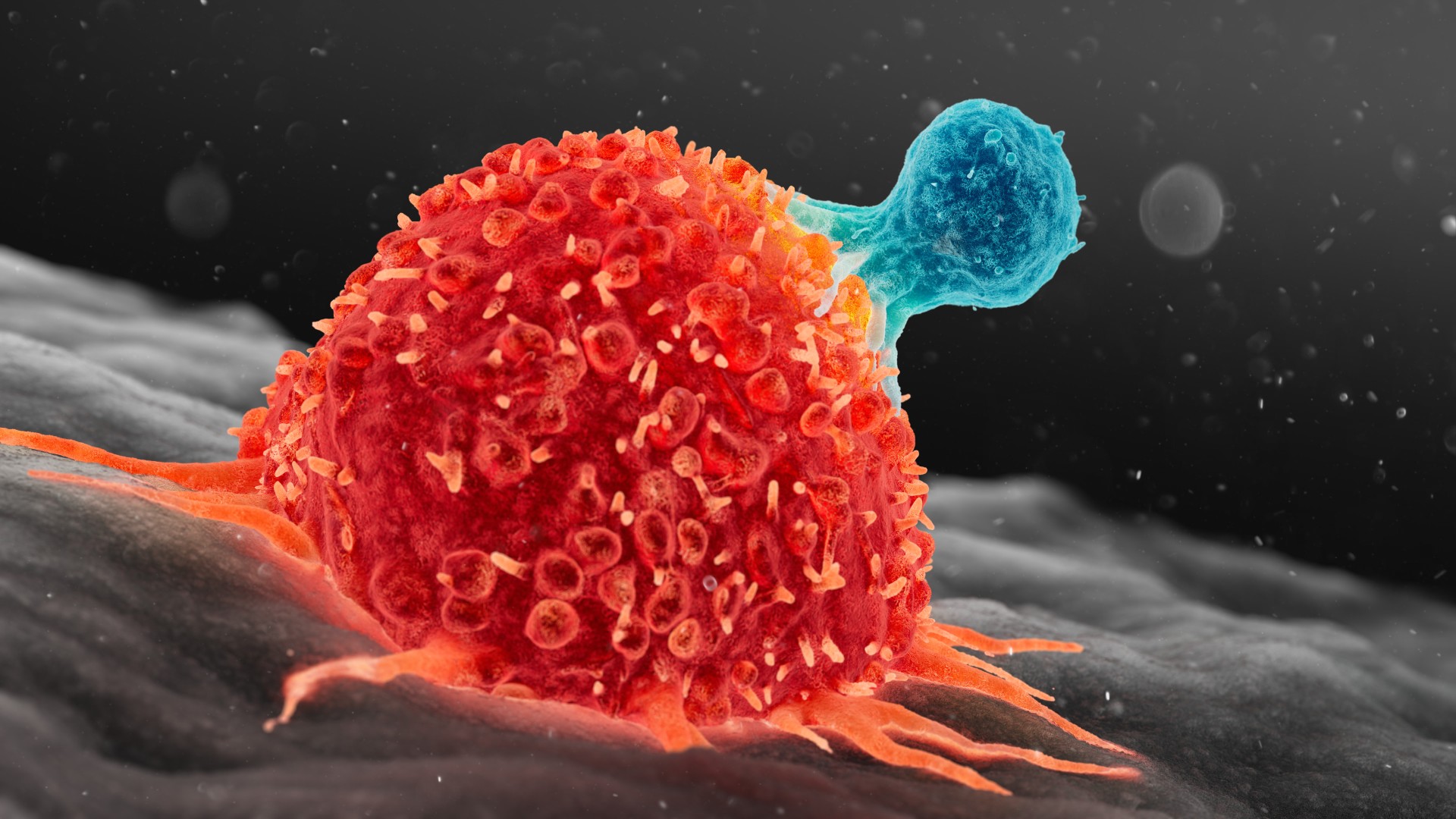
Lymphoid cells include T cells of the immune system, such as the one illustrated above attacking a cancer cell.
Related:‘If you do n’t have inflammation , then you ’ll conk out ' : How scientist are reprogramming the body ’s raw world power
As we age , the HSCs slated to become myeloid cellular phone step by step increase in turn and eventuallyoutnumber the lymphoid radical cellphone . This means we ca n’t respond toinfections as wellwhen we ’re one-time as when we ’re untested , and we ’re more probable to experiencechronic inflammationtriggered by increasing storey of myeloid cadre that trigger ignition .
In the new work , publish Wednesday ( March 27 ) in the journalNature , scientists modernize an antibody - based therapy that selectively targets and destruct the myeloid HSCs , thus restitute the balance of the two cellular telephone type and take a leak the rip more " vernal . " The antibody latch onto the point cells and ease up them to be destroyed by the resistant organisation .

The authors come in the therapy into mouse maturate 18 to 24 month , or roughly the equivalent of being between 56 and 69 geezerhood oldas a man .
They then extracted HSCs from the mouse after discourse and analyzed them , revealing the gnawer had a smaller percentage of the myeloid HSCs than untreated mouse of the same age .
This effect live on for two months . Compared with untreated mouse , the deal mouse also make more primitive deoxythymidine monophosphate cells and mature B prison cell . These cells can go on to mould memory cadre , which are directly need in the immune attack ; in the typeface of the B cellular phone , they can formantibody - producing blood plasma cells .

" Not only did we see a transformation toward cells involved in adaptive immunity , but we also observed a dampening in the levels of inflammatory proteins in the treated animals,“Dr . Jason Ross , lead work author and postdoctoral research worker at Stanford University , say in astatement . Specifically , the researchers interpret that the level of one proinflammatory protein fell in the treat mouse . This protein , called IL-1beta , ismainly made by myeloid cells .
Eight workweek billet - intervention , the researchers vaccinated the mice against a computer virus they ’d never been exposed to before . The black eye that had received the immunotherapy had more pertinent resistant responses to inoculation than the untreated mouse , producing more T cubicle against the germ .
" We believe that this study represent the first steps in implement this strategy in humankind , " Ross say . However , other experts have cautioned against chute to conclusions .

Nikolich - Zugich noted that , although the researchers measured variety in the identification number of naive T cells in the mice , they did n’t look at the subroutine of the organ that makes them : thethymus . The team also go through reductions only in IL-1beta and not other incitive proteins . They also did n’t try whether the mice ’s baseline immunity to new infections could be meliorate with this therapy , without vaccination , he say .
— Worldwide , the life - straddle gap between the sex is shrinking
— Epigenetics linked to the maximum life story spans of mammal — include us

— Sped - up ' biologic ageing ' linked to worse memory
what is more , the bailiwick did n’t deliberate likely long - term side effects of the handling , such asanemia , or a deficiency in cerise blood cells , saidDr . Ilaria Bellantuono , a professor in musculoskeletal aging at the University of Sheffield in the U.K. who was not involved in the research .
Although an " interesting " study , more piece of work is needed to understand whether it can make for " meaningful variety " in the immune system , Bellantuono severalise Live Science in an email , whether that of mouse or humanity .

Ever marvel whysome people build muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckle total out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the dependent telephone circuit " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the website !