When you purchase through link on our site , we may pull in an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it bring .
scientist have plan a transistor that stores and action selective information like the human brain and can perform cognitive tasks that most artificial intelligence ( AI ) systems today contend with .
This engineering , known as a " synaptic transistor , " mimics the computer architecture of the human learning ability — in which the processing power and computer memory are to the full integrated and found in the same position . This differ from conventional computing architecture , in which the processor and memory are physically disjoined element .

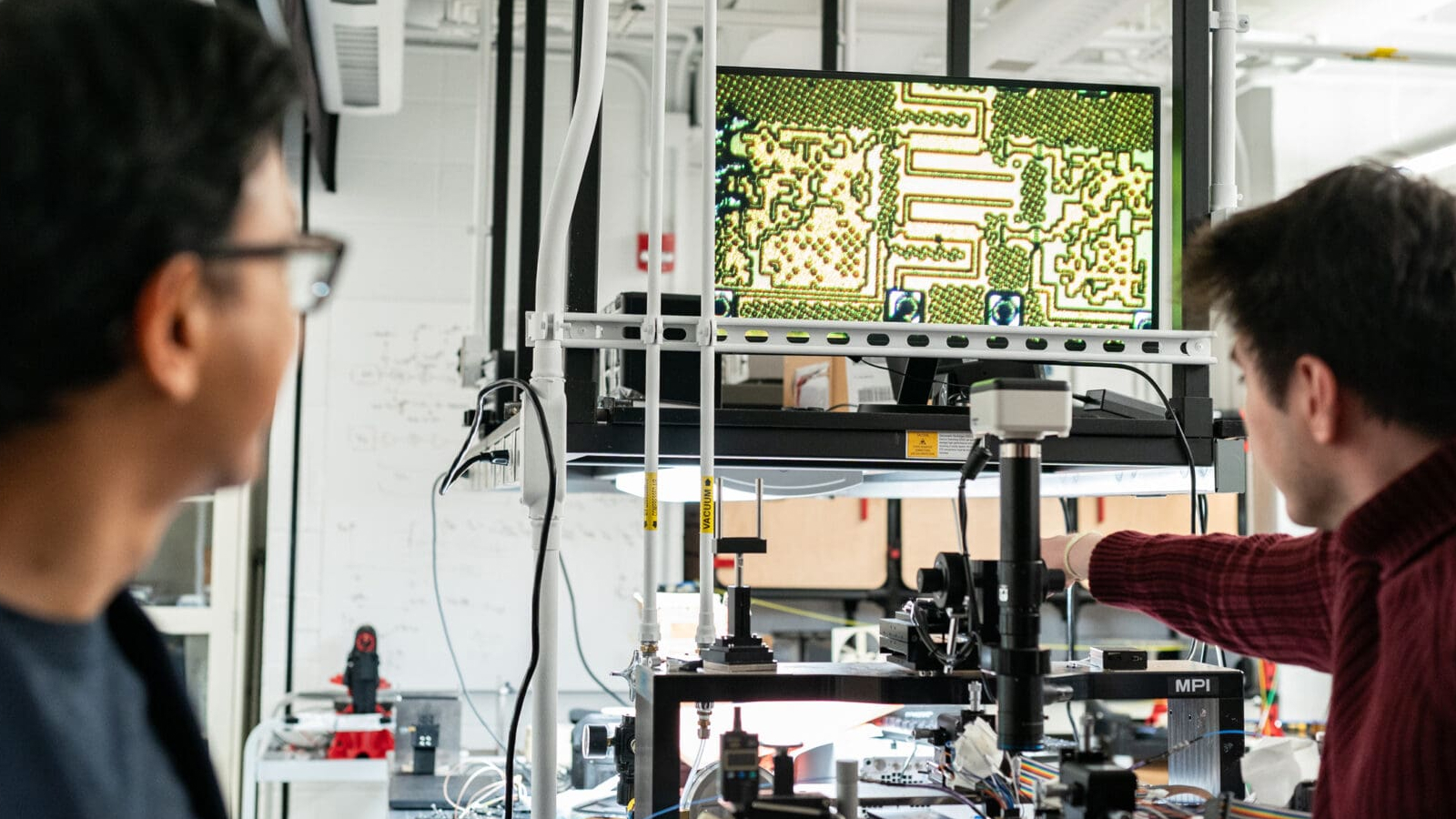
A schematic showing the different layers within the new technology.
" The mental capacity has a fundamentally different architecture than a digital computer,“Mark Hersam , research Centennial State - drawing card and prof of material science , applied science and computing at Northwestern University , say in a program line . " In a digital computing machine , information move back and forward between a microprocessor and retention , which consumes a lot of energy and creates a chokepoint when attempting to perform multiple project at the same time . "
Because of its full integration between computing major power and memory , the synaptic transistor can accomplish importantly gamy energy efficiency and move data extremely tight , researchers wrote in the subject , published Dec. 20 in the journalNature . This new form of computing computer architecture is needed , the scientists said , because relying on schematic electronics in the age of self-aggrandizing data and the growing demand for AI computing workload will go to unprecedented energy consumption .
Related : In a 1st , scientists combine AI with a ' minibrain ' to make hybrid computer
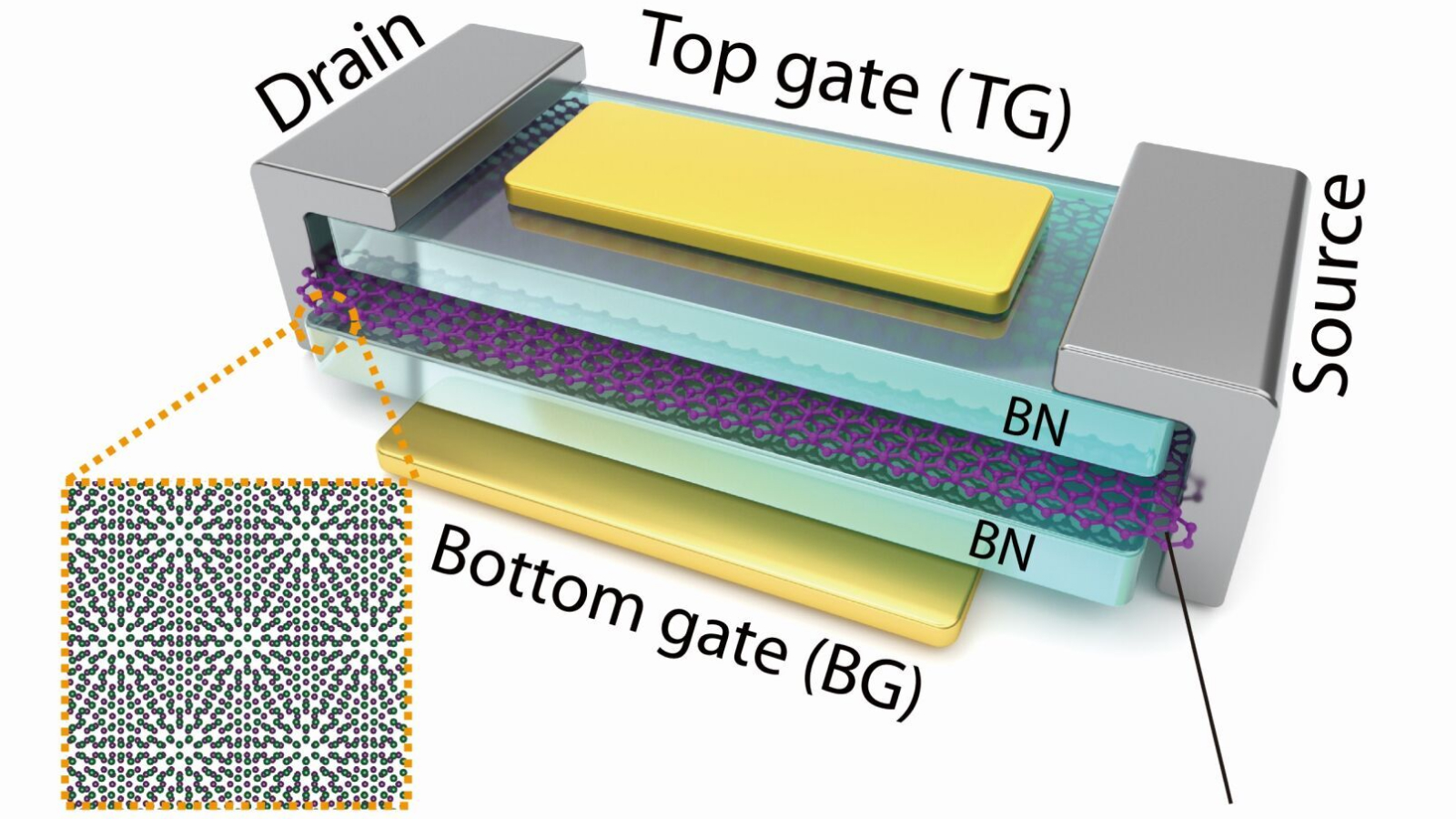
A schematic showing the different layers within the new technology.
scientist have build up synaptic transistors before , the researchers sound out , but they only operated at extremely cold temperatures . But the Modern transistor uses materials that work at room temperature .
schematic electronics pack transistors onto a Si wafer , but in the new synaptic transistor , the investigator stacked bilayer graphene ( BLG ) and hexagonal boron nitride ( hBN ) and purposefully twisted them to shape what ’s recognize as a moiré pattern .
When they rotated one layer relative to the other , unexampled electronic holding go forth that did n’t survive in either layer separately . father the junction transistor to act upon at room temperature require using a specific degree of twist and adopting a near - perfect alignment between hBN and BLG .

The research worker tested the bit by first training it on data so it could learn to recognise patterns . Then they showed the chip fresh sequences that were similar to the education datum but not the same . This process , eff as associatory learning , is one that most machine get wind system ca n’t do well .
" If AI is mean to mimic human thought , one of the lowest - level tasks would be to classify data , which is merely sorting into bins , " Hersam say . " Our destination is to make headway AI technology in the direction of high - level thinking . Real - earthly concern conditions are often more complicated than current AI algorithms can deal , so we tested our new devices under more complicated weather to assert their advance capabilities . "
— Google ’s ' mind - reading ' AI can tell what music you take heed to based on your brain signals

— AI Can Now Decode Words forthwith from Brain wave
— Gemini AI : What do we know about Google ’s answer to ChatGPT ?
In one exercise , the researchers trained the AI to detect the chronological succession 000 . The investigator then asked the AI to key out similar pattern — for example , by presenting it with 111 and 101 . The successiveness 000 and 111 are n’t the same , but the AI figured out they were both three digits in a run-in .

This seems simple enough , but today ’s AI dick skin with this type of cognitive reasoning . In further experiments , the researchers also threw " curveballs " at the AI by giving it incomplete patterns . But the AI using the chip still demonstrated associatory learning , the researchers said .
" Thus far , we have only apply the moiré synaptic electronic transistor with hBN and BLG , " Hersam told Live Science in an electronic mail . " However , there are many other two - dimensional material that can be stack into other moiré heterostructures . Therefore , we believe that we have only just begun to scratch the surface of what is possible in the emerging field of moiré neuromorphic computing . "
The feature the scientists observed in this experimental electronic transistor could prime future generation of the engineering science to be used in highly Energy Department - efficient chips that power in advance AI and machine eruditeness systems , Hersam add up .