When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate delegation . Here ’s how it play .
Immune signatures in the blood may flag if someone hasovarian cancerup to four year earlier than conventional methods used to diagnose the disease , young research evoke .
Ovarian cancer isone of the deadliest cancers , with a five - yr survival rate of less than 51%.Around 70 % of ovarian Cancer the Crab patientshave in high spirits - grade ovarian Crab ( HGOC ) , in which cancerous mobile phone look particularly abnormal and aremore likely to farm and spread than low - grade cancers .
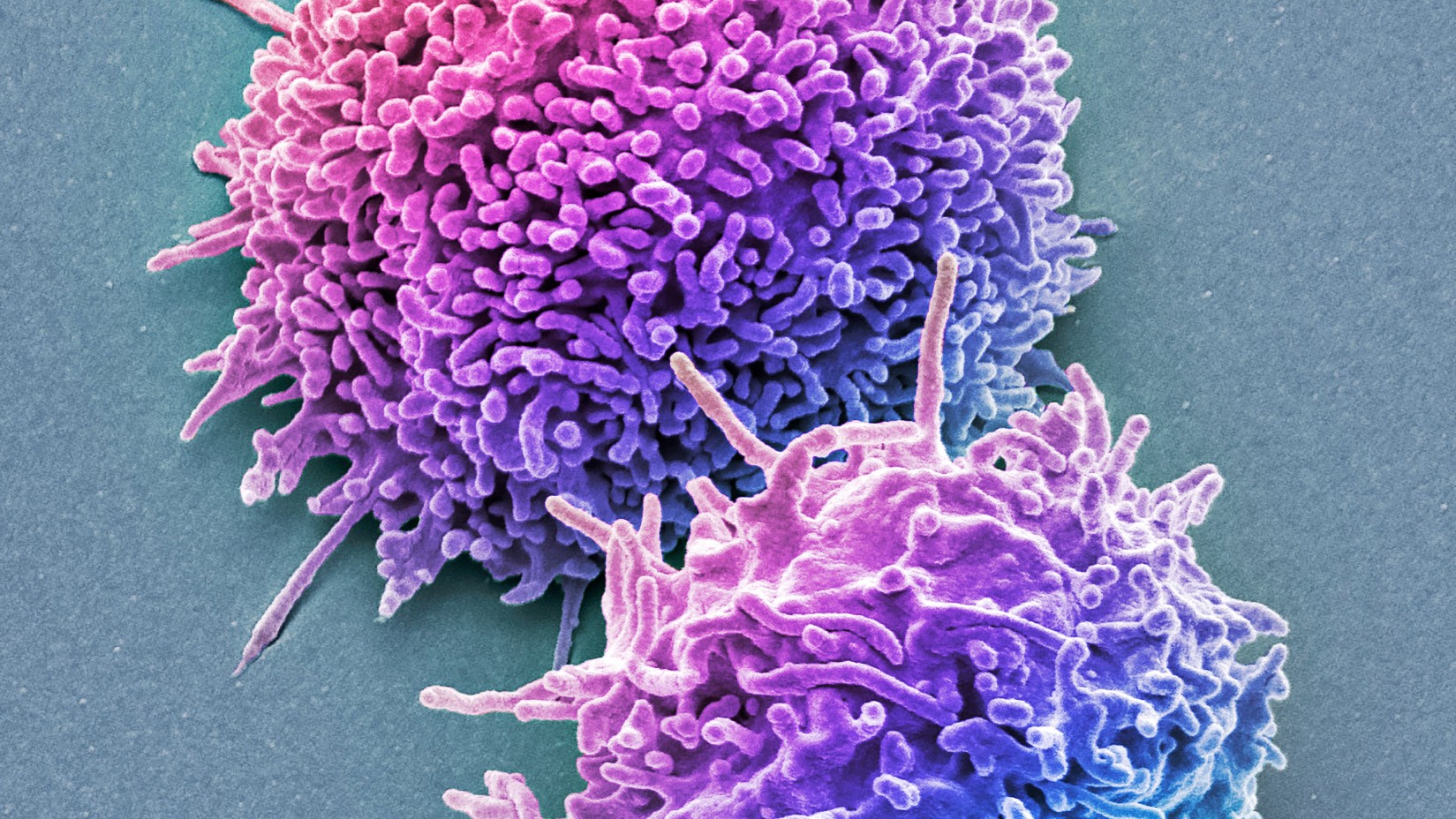
A new study suggests that differences in the number of immune cells called T cells in the blood that specifically attack cancer cells could signal ovarian cancer years earlier than previously thought possible.
As with many cancers , other diagnosis and treatment — such as with surgical procedure and chemotherapy — are primal to retentive survival . If this character of cancer is place — that is , fix to theovariesor the fallopian tubes — around 93 % of patient are have a bun in the oven to survivefor five or more years after diagnosis .
regrettably , most patients are not diagnosed with HGOC until the cancer isat an forward-looking phase , think of it has disperse to somewhere else in the trunk . In these cases , the five - year natural selection rate may be as low as 31 % .
Related : Gen Xers will have high genus Cancer rates than baby boomer , report forecasts

One cause for this is that HGOCdoesn’t have specific symptomsin the other microscope stage of the disease . Also , during this clip , tumors are very small and established biomarkers — such as theCA-125 blood mental testing , which discover elicit levels of a cancer - related protein — are not raw enough to discover them .
However , the finding of a raw study , published June 14 in the journalCell Reports Medicine , may serve doctors diagnose ovarian cancer much preferably , allowing for earlier intervention before the cancer has disperse and , potentially , long survival of the fittest .
In the work , research worker discovered a blood - based immune biomarker that they say could be used to detect HGOC up to four years before most cases are currently diagnosed .

They uncover this biomarker after analyze blood sample taken from 466 patients who , within five year of their sampling being drawn , run on to be diagnose with ovarian cancer using conventional clinical test .
Specifically , the team noticed firm differences in the numbers ofimmune cellscalled T cells in their roue that were primed to recognize and attack cancer prison cell , compared with those find within the blood of a comparison mathematical group of woman who did not go on to develop malignant neoplastic disease .
These signals could be find two to four years before diagnosing and show that the immune organization is actively fighting the disease , the study authors said .

The research is still in its early stages . However , this " unprecedented find " could one day inform the development of new tests that find this newly identified biomarker , the squad said .
— Immunotherapy to treat genus Cancer gave wage hike to 2nd cancer in highly rarefied case
— young mRNA vaccinum for pernicious brain cancer trigger a strong immune response

— Woman ’s sudden sightlessness in 1 eye revealed hidden lung cancer
" former detection of ovarian Crab could mean the difference between sprightliness and expiry for millions of women,“Bo Li , co - senior study author and a researcher at the Children ’s Hospital of Philadelphia ’s Center for Computational and Genomic Medicine , said in astatement .
" We trust our findings can be a gamechanger , supply insights for the development of an immune - based biomarker to discover early - level ovarian Cancer the Crab . "

Ever wonder whysome people build up muscular tissue more well than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? Send us your motion about how the human body work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the capable assembly line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your doubtfulness answered on the website !
leechlike worm evoke risk of cervical genus Cancer , study finds
Cancer the Crab : Facts about the diseases that cause out - of - control cell growth

What ’s hiding under Antarctica ’s internal-combustion engine ?



