When you purchase through data link on our site , we may take in an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
investigator have identify a new mintage of ancient humankind , which they have namedHomo juluensis , meaning " big head , " based part on a very tumid skull bump inChina .
But what is this new species , and how does it help paleoanthropologists translate hominin variation in the MiddlePleistocene epochabout 300,000 to 50,000 years ago ?
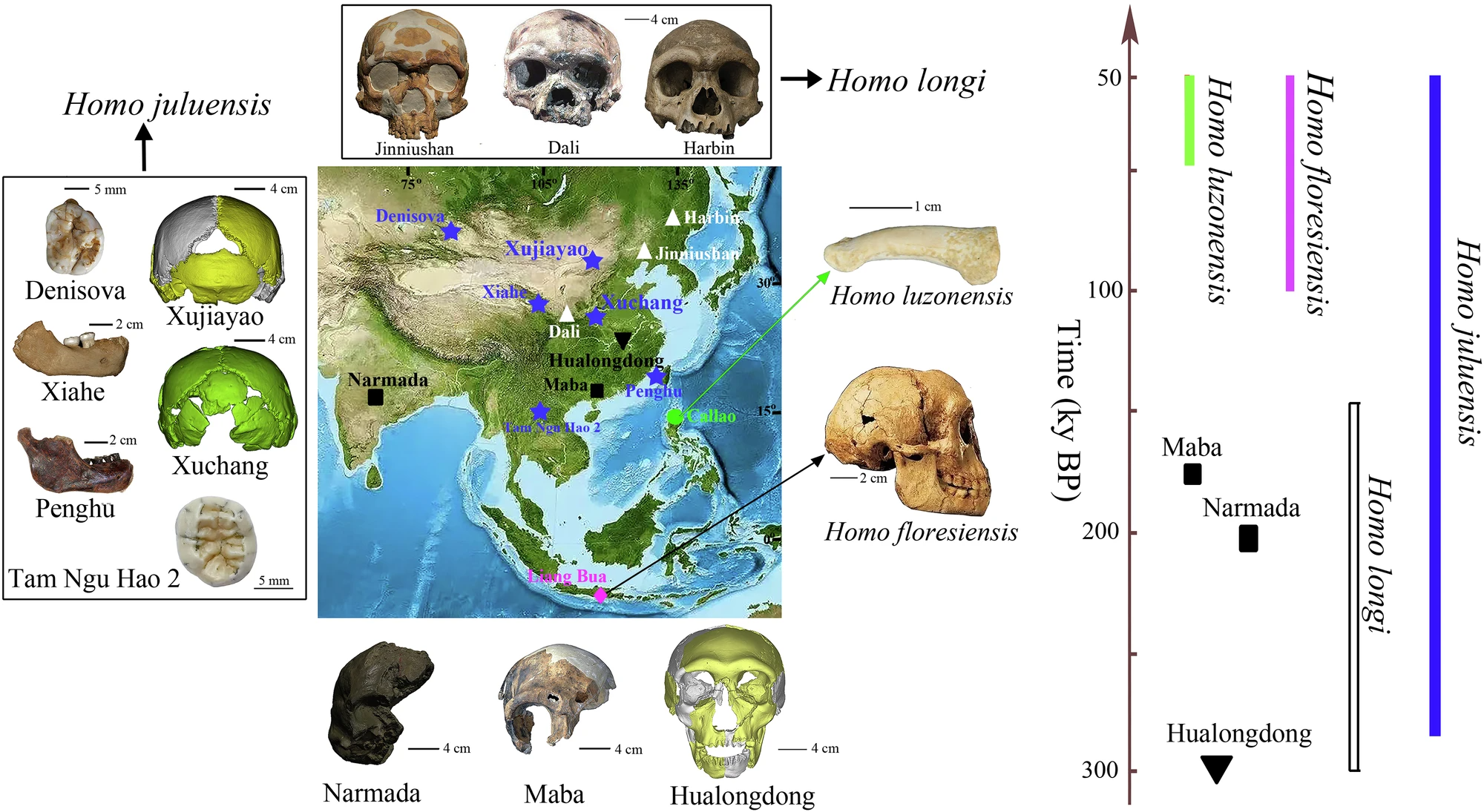
A diagram shows hominin sites in central Asia along with the fossils discovered there.
After ourH. sapiensancestors evolvedroughly 300,000 year ago , they apace spread out of Africa and into Europe and Asia . For 10 , paleoanthropologists have sample to figure outhow hominins were evolvingprior to the arrival of modern humans , specially between about 700,000 and 300,000 twelvemonth ago , whenmultiple other early human existed . For illustration , anthropologists have found fossils from species likeH. heidelbergensisin western Europe andHomo longiin central China , though not everyone agreed each of these act a disjoined species . These fogy have also been lumped into catch - all term like " archaicH. sapiens " and " Middle PleistoceneHomo , " and are sometimes colloquially called " the muddle in the Middle . "
write about the dodo hominin grounds from China in the journalThe Innovationin 2023,Christopher Bae , an anthropologist at the University of Hawai’i at Mānoa , Xiujie Wu , a paleoanthropologist at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences , and colleagues wrote that continuing to use these catch - all terms has stymie attempts to amply understand the evolutionary relationship among our ascendent .
Related : Strange , 300,000 - year - old mandibular bone unearthed in China may number from vanished human lineage

In a written report published May 2024 in the journalPaleoAnthropology , Wu and Bae described a bent of unusual hominin fossils that were found X prior at Xujiayao in northern China . The skull was very large and wide-eyed , with someNeanderthal - similar features . But it also had traits coarse to modern humans and toDenisovans .
" Collectively , these fogey represent a raw form of large brained hominin ( Juluren ) that was widespread throughout much of eastern Asia during the Late Quaternary [ 300,000 to 50,000 years ago ] , " they publish .
Now , in a commentary published Nov. 2 in the journalNature Communications , Bae and Wu say that the growing fogy record in east Asia requires newfangled terminology . Splitting " archaicHomo " in this area into at least four species — H. floresiensis , H. luzonensis , H. longiand the newly namedH. juluensis — will help research worker well see the complexity of recent human phylogenesis , they argue .

The newly namedH. juluensisis based on fossils that date to between 220,000 and 100,000 years ago from Xujiayao and Xuchang , a site in fundamental China . In 1974 , power shovel discovered more than 10,000 stone artefact and 21 hominin fogy fragments representing about 10 different mortal at Xujiayao . All of the cranial bones show that these hominins had tumid brain and thick skulls . The four ancient skull from Xuchang are also very large and similar to those of Neanderthals .
In wait at the mixture of trait present in these groups of fossil , Wu and Baedecided in the May 2024 paperthat " they stand for a new hominin universe for the region , namely Juluren , meaning ' large mind people ' . "
AlthoughH. juluensisis taxonomically a new hominin species , that does not intend they were genetically isolated . They may have been the product of mating between different types of Middle Pleistocene hominins , including Neanderthals , theywrote , " indorse the idea of persistence with hybridizing as a major force shaping human evolution in eastern Asia . "

AlthoughH. juluensisis not yet commonly accepted , the name is growing on experts .
— 1.5 million - year - old footprints reveal our Homo erectus ancestors lived with a 2d proto - human mintage
— Ancient human ancestor Lucy was not alone — she populate aboard at least 4 other proto - human species , issue inquiry suggest

— From ' Lucy ' to the ' Hobbits ' : The most famous fossils of human relatives
" figure are important both in evolutionary biota and in anthropology . A name is a mental prick that enable us to intercommunicate with other people about a concept , " paleoanthropologistJohn Hawksof the University of Wisconsin – Madison write in aJune 16 blog post . " I see the name Juluren not as a replacement for Denisovan , but as a way of referring to a particular grouping of fogey and their potential place in the internet of ancient groups . "
Chris Stringer , a paleoanthropologist at the Natural History Museum in London , evidence Live Science in an email that his own employment with Chinese colleagues suggest theH. juluensismaterial may in reality suit better withH. longi . " I do n’t think having a large braincase is a very utilitarian defining characteristic , " he said . " However , Xuchang certainly does seem different , with more Neanderthal - like trait , so its compartmentalisation is less certain . "

In astatement , Bae pronounce that naming a new species helps clarify the fogy book , particularly in Asia . " Ultimately , this should aid with science communication , " he said .









