When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate direction . Here ’s how it make for .
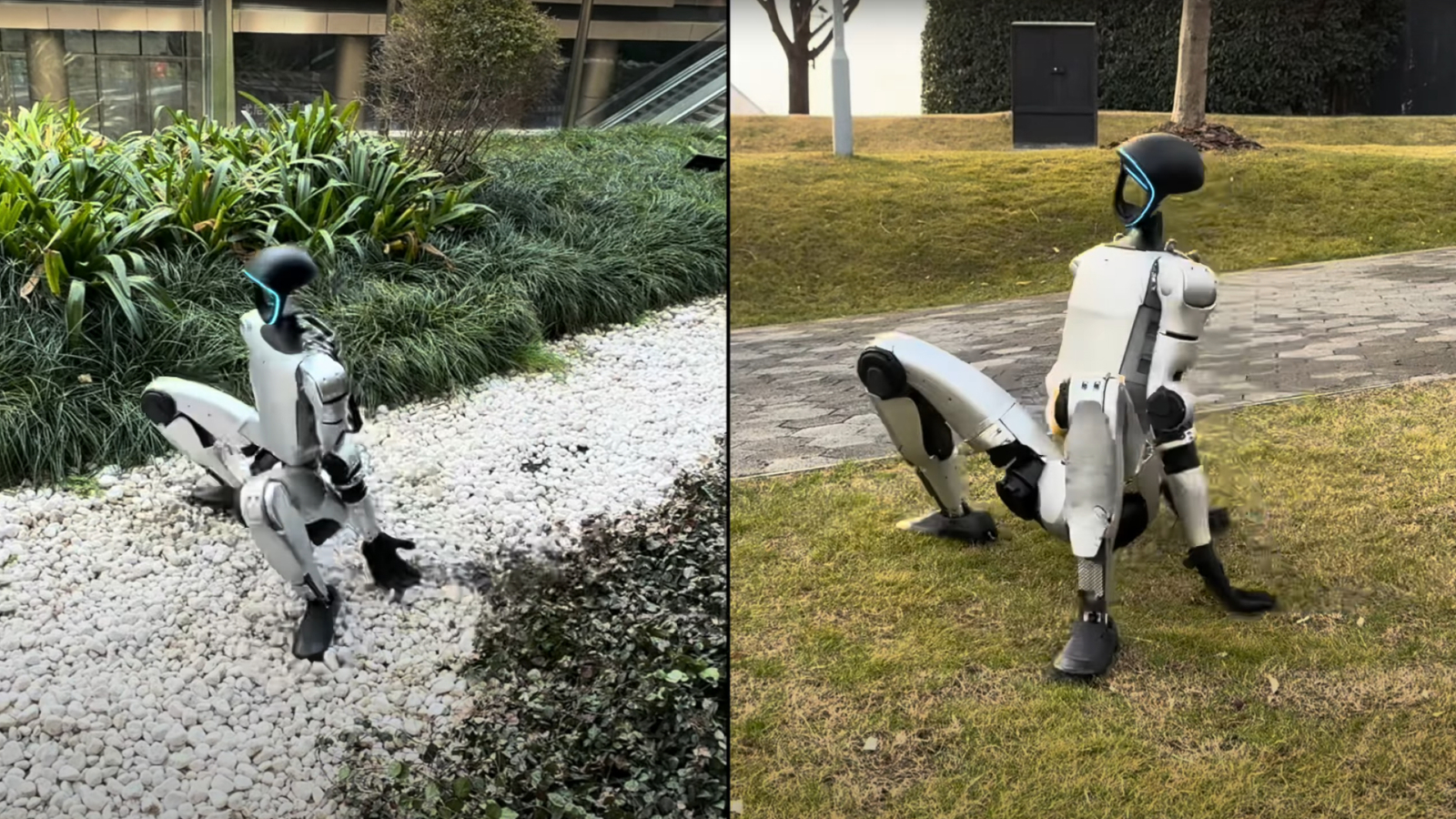
New inquiry suggest a smartphone app can replace all the different systems and technologies presently postulate to do motion seizure , a process that interpret body movements into computer - generated double .
The app , dubbed " MobilePoser , " uses the data obtained from sensors already embedded in various consumer devices — including smartphones , earbuds and smartwatches — and combines this information withartificial intelligence(AI ) to track a person ’s full body position and position in space .
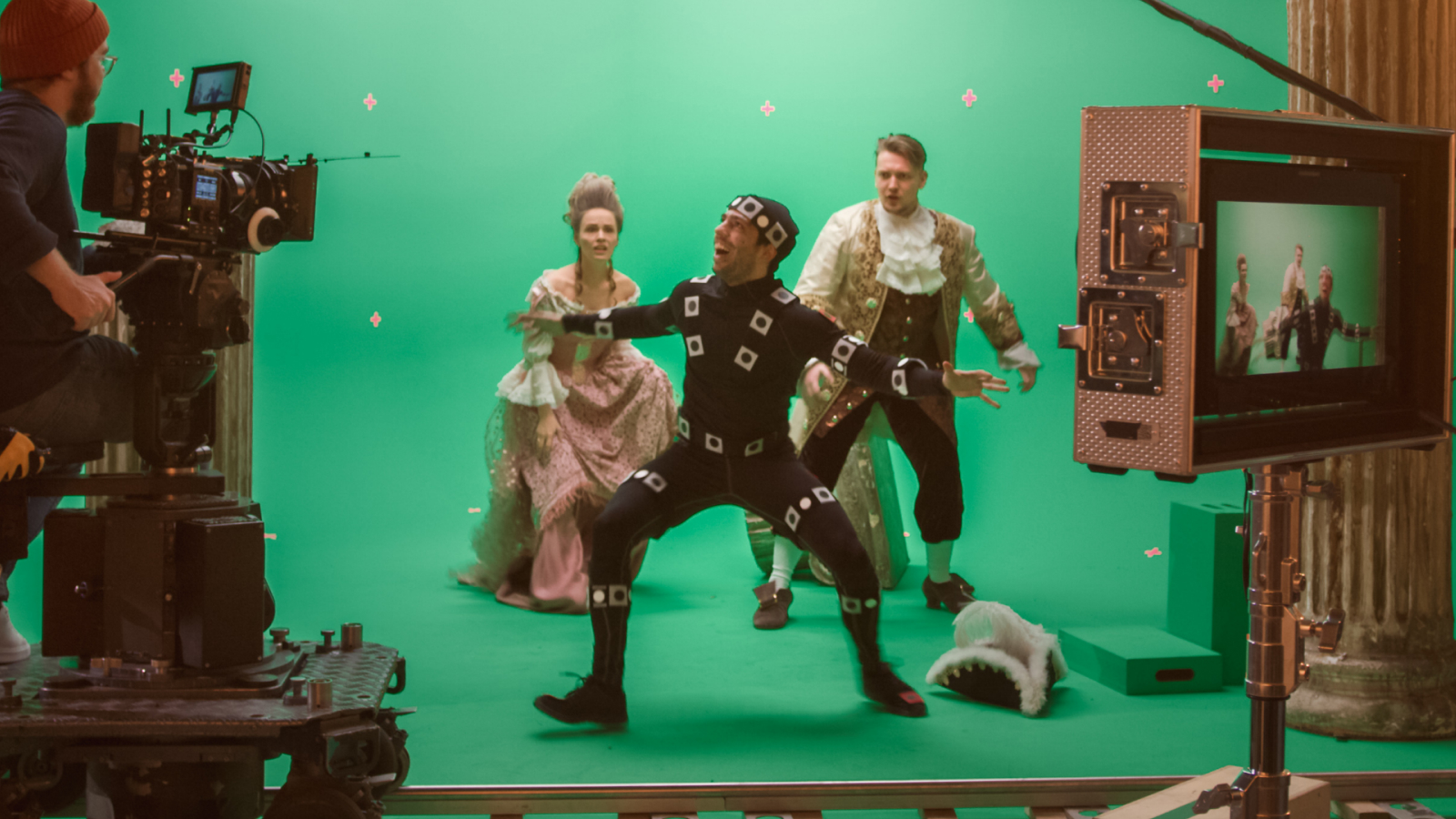

Motion gaining control is often used in the photographic film and video play industries to capture actor ' movements and translate them into estimator - generated quality that look on - screen . Arguably the most famous example of this process is Andy Serkis ' execution as Gollum in the " Lord of the Rings " trilogy . But motility gaining control usually requires specialized room , expensive equipment , bulky television camera and an array of sensors , including " mocap suits . "
Setups of this sort can cost upward of $ 100,000 to run , the scientist say . Alternatives like the discontinued Microsoft Kinect , which relied on stationary cameras to see body movements , are cheaper but not hard-nosed on the go because the action must pass within the photographic camera ’s field of view .
rather , we can replace these technologies with a undivided smartphone app , the scientist said in a unexampled field of study presented Oct. 15 at the2024 ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology .

colligate : Playing with flaming : How VR is being used to train the next generation of firefighters
MobilePower achieves high truth using machine learning and in advance physics - free-base optimization , said bailiwick authorKaran Ahuja , a professor of computer scientific discipline at Northwestern University , said in astatement . This will reach the door to new immersive experiences in gaming , fitness and indoor sailing without specialized equipment .
The team relied on inertial measurement units ( IMUs ) . This system of rules , which is already embed in smartphones , apply a combination of detector — including accelerometers , gyro and magnetometers — to measure the body ’s posture , predilection and movement .

However , the faithfulness of the detector is ordinarily too crushed for accurate movement seizure , so the researchers augmented them with a multistage machine determine algorithm . They direct the AI with a publicly available dataset of synthesized IMU measurement that were bring forth from gamey - lineament movement - capture data . The result was a tracking error of just 3 to 4 inches ( 8 to 10 cm ) . The natural philosophy - based optimizer refines the prognosticate social movement to make certain they match real - life physical structure bowel movement and the eubstance does n’t do out of the question feats — like reefer bending backwards or the user ’s promontory rotate 360 degrees .
— What causes gesture nausea in VR , and what can you do to keep off it ?
— Watch scientists control a robot with their hands while wearing the Apple Vision Pro

— VR headset vulnerable to ' Inception attacks ' — where hackers can mess with your mother wit of realness and steal your data point
" The accuracy is better when a someone is wear more than one equipment , such as a smartwatch on their radiocarpal joint plus a smartphone in their pocket , " Ahuja said . " But a key part of the organisation is that it ’s adaptive . Even if you do n’t have your watch one twenty-four hour period and only have your phone , it can adapt to figure out your full - soundbox pose . "
This engineering science could have applications in entertainment — for case , more immersive gambling — as well as in health and seaworthiness , the scientists said . The squad hasreleased the AI model and relate dataat the spunk of the app so that other researcher can build up on the work .