When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists have discovered a unexampled species of human sponge that appear to be resistant to common antiparasitic treatments , such as ivermectin .
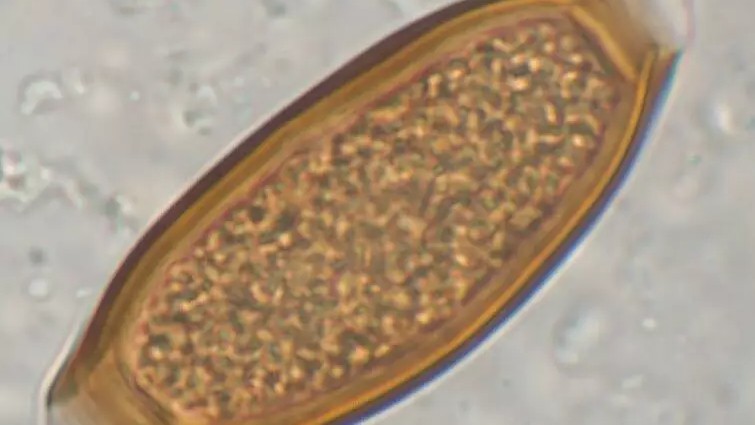
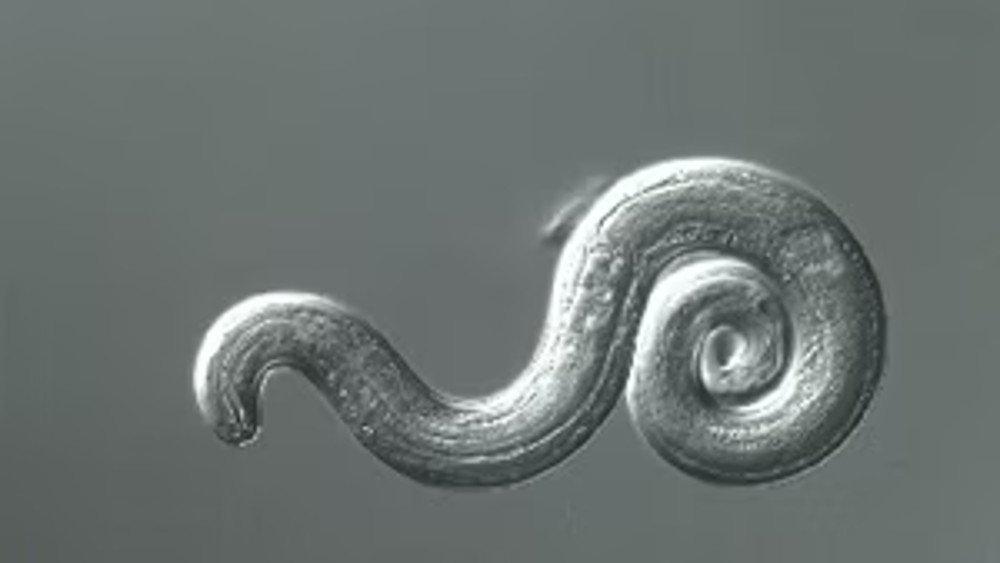
The sponge , namedTrichuris incognita , is a eccentric of intestinal roundworm that is closely come to to the whipwormTrichuris trichiura , which is currently retrieve to taint between 429 million and 508 million citizenry globally , allot to theU.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC ) . So far , the newly identified species has been retrieve only in West Africa — spceifically Côte d’Ivoire .
" The infection tends not to be deadly , but laborious infection can cause serious disease particularly in young children,“John Gilleard , a professor of parasitology and associate doyen of research at the University of Calgary ’s Faculty of Veterinary Medicine , told Live Science in an email .
The newly identified specie was discovered during a wide study into parasitic drug electrical resistance in West Africa . Specifically , researchers were investigate the efficacy of using ivermectin and albendazole in combination . These two antiparasiticsrecommended by the World Health Organization(WHO ) to treat many different enteric parasite .
" There was a suspiciousness of something odd , because the drug combining was substantially less efficacious in a clinical trial in one country relative to others,“Abhinaya Venkatesan , who transmit the inquiry as part of her doctorial thesis , say in astatement released by the University of Calgary .

" Our genetic analysis break the epenthetic worm from Côte d’Ivoire , West Africa , were a unlike mintage to those at the other subject field sites , " Venkatesan say . " In fact , it is a entirely new species and more standardised to a leech that infect hog than those unremarkably found in humankind . "
These results were published Dec. 18 in the January 2025 takings of the journalEmerging Infectious disease .
What isTrichuris incognita ?

Researchers ' understanding of this newly pick up parasite is still in its early stages .
" At present major biological or clinical differences betweenT. incognitaand thehuman Trichuris speciesT. trichiura(other than predisposition to drugs ) are unknown , " Gilleard said . " As far as we know the symptoms will be similar to the unwashed whipworm in humansTrichuris trichiura . "
According to the CDC , infections withT. trichiura — a condition make love as trichuriasis — are often symptomless . However , they can sometimes result in gastrointestinal problems , admit abdominal pain , diarrhea andrectal prolapse , as well as stunted increment in children .

Theparasite ’s egg are pass in infect people ’s ordure ; the eggs can end up contaminating soil if a person defecate outside or use an inadequate sanitisation adeptness . extra citizenry may then get infected if they exhaust food or water contaminate by the ground .
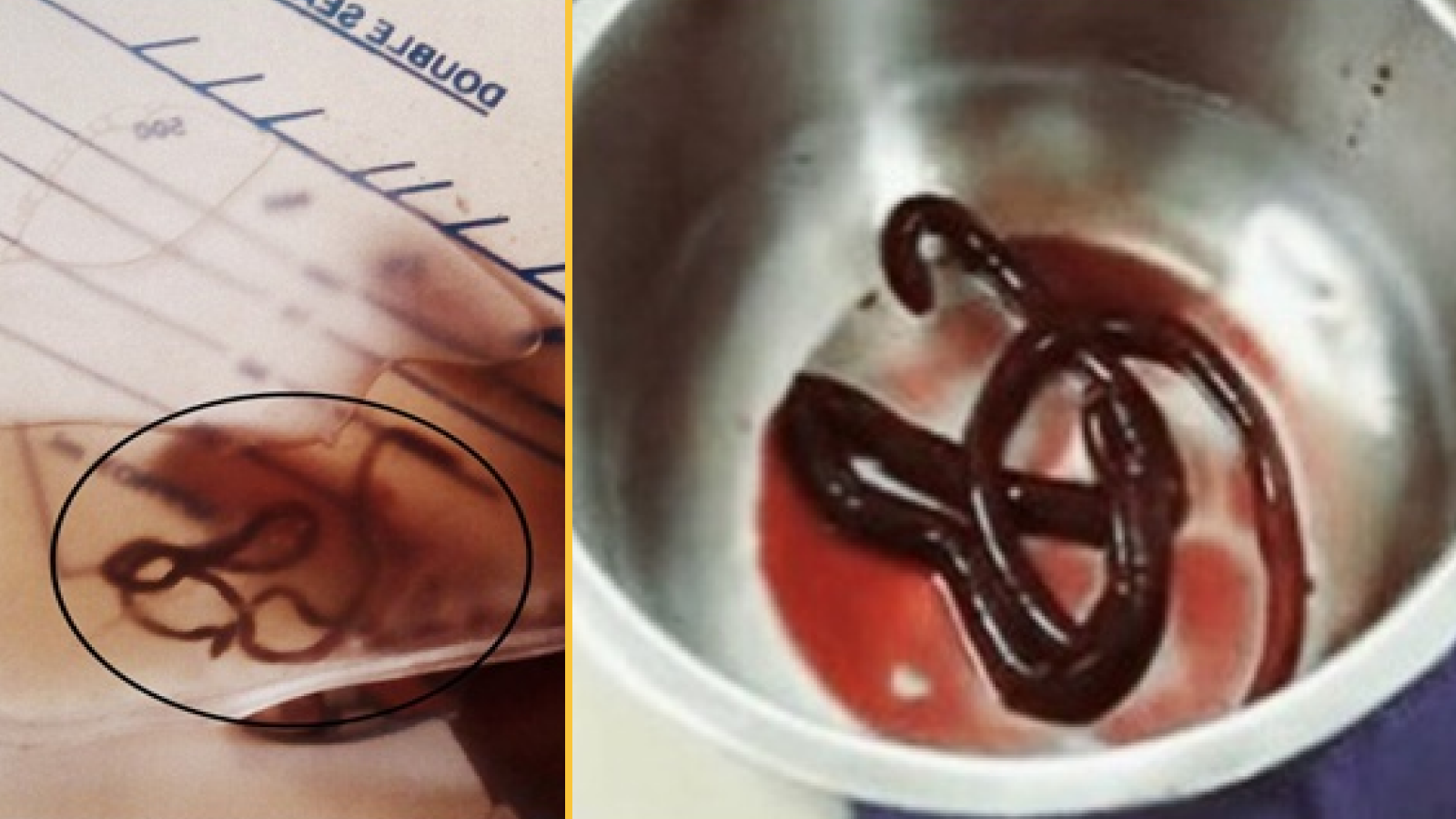
The eggs then hatch in the person ’s small gut , releasing larvae that ripen and establish themselves as adults in the affected role ’s colon . The adult worms , which grow to approximately 1.5 in ( 4 cm ) in duration , live for about a yr , with female worms exuviate up to 20,000 bollock per Clarence Shepard Day Jr. .
interrelate : material body - eating human parasite sweeping across Central America is raise concerns in US — what to experience
Why wasn’tTrichuris incognitarecognized rather ?
Although trichuriasis is fairly far-flung and defined as a major neglected tropical disease by WHO , it may be that unlike species of the parasite have been dominate , Gilleard said . " The challenge is that most diagnosis and surveillance is establish on microscopic examination of feces and the recognition of classical Trichuris character orchis in human ordure and not molecular tests that could discern the species , " he explained .
As a effect , we do not yet bonk how widespreadT. incognitais globally , but Gilleard said " it is likely present in other places in west Africa . "

We also do n’t yet know why the newfangled mintage is resistant to common antiparasitics .
" Different sponger species show different sensitivities to drugs for all sorts of complex biological reason , " Gilleard sound out . It may be that this drug - resistant species has been overlooked , or thatT. incognitais actually an come forth species whose phylogeny is being driven by drug pic . Perhaps being drug - resistant is givingT. incognitaa selection reward overT. trichiura , Gilleard speculate .
However , he added that more enquiry is needed to determine this .

WillTrichuris incognitabe a problem in the U.S. ?
— What ’s the good means to down norovirus , the ' stomach bug ' ?
— Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among minor in China — what is it ?

— How does E. coli get into food for thought ?
" I do n’t anticipate this leech being present in the U.S. , " Gilleard said . " It is really a disease of poorness and prevalent in areas with pitiable public health and sanitization . “T. trichiurais present in some southerly U.S. commonwealth , but compared to other countries , the U.S. has very low rate of the disease .
Although this is improbable to be an effect in America , Gilleard add together that the discovery foreground the ever - changing nature of infectious diseases and the need for extend surveillance efforts .









