When you purchase through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
The face of a car - size , millipede - like creature — the largest arthropod ever to endure — has finally been reveal thanks to two well - preserved fossils , a new subject reports .
The arthropod , Arthropleura , live in forests near the equator between 346 million and 290 million old age ago , during the later Paleozoic era . In the oxygen - rich aura at that time , Arthropleuracould develop to a massive8.5 base ( 2.6 time ) long and weigh over 100 Cypriot pound ( 45 kilo ) .
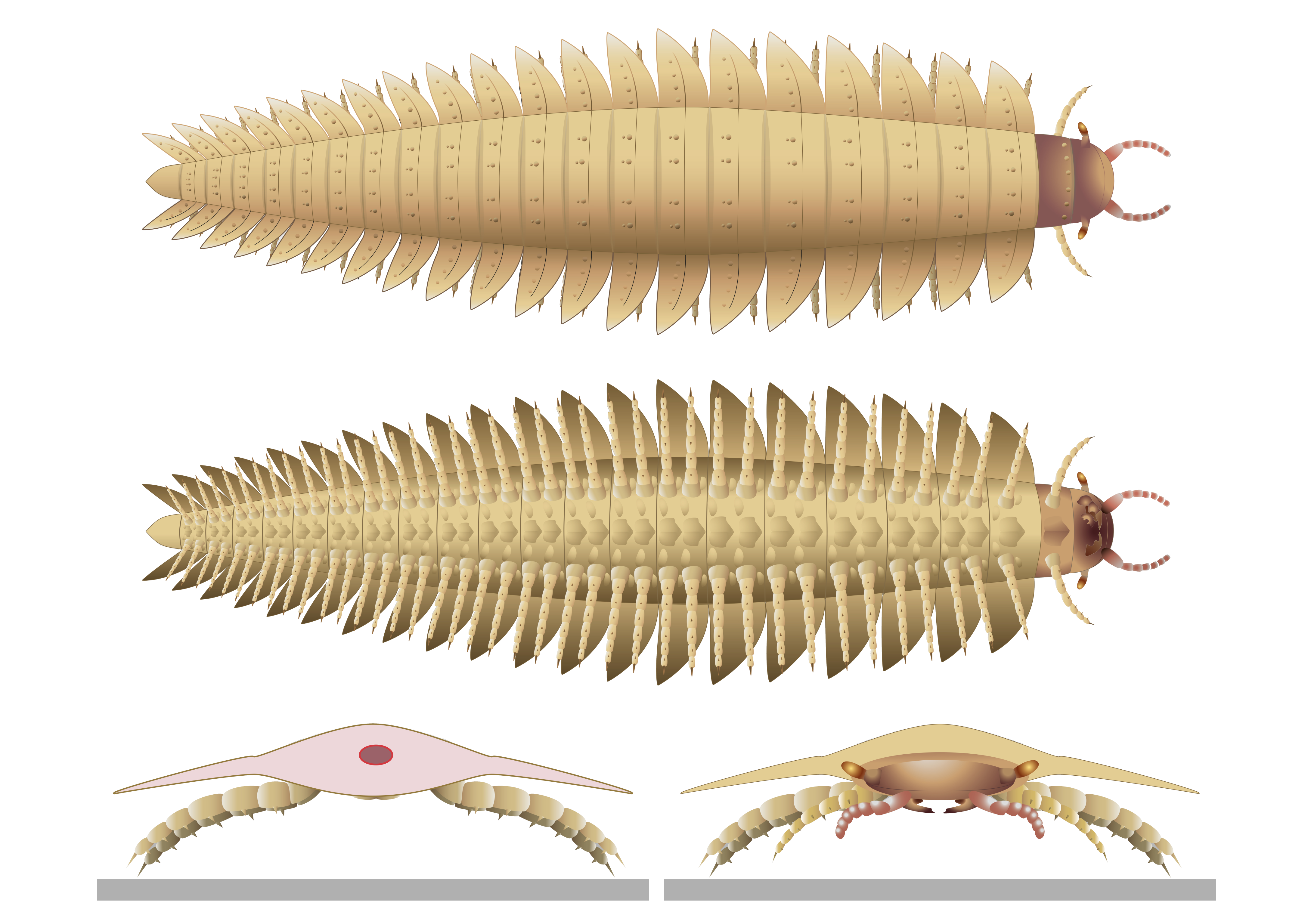
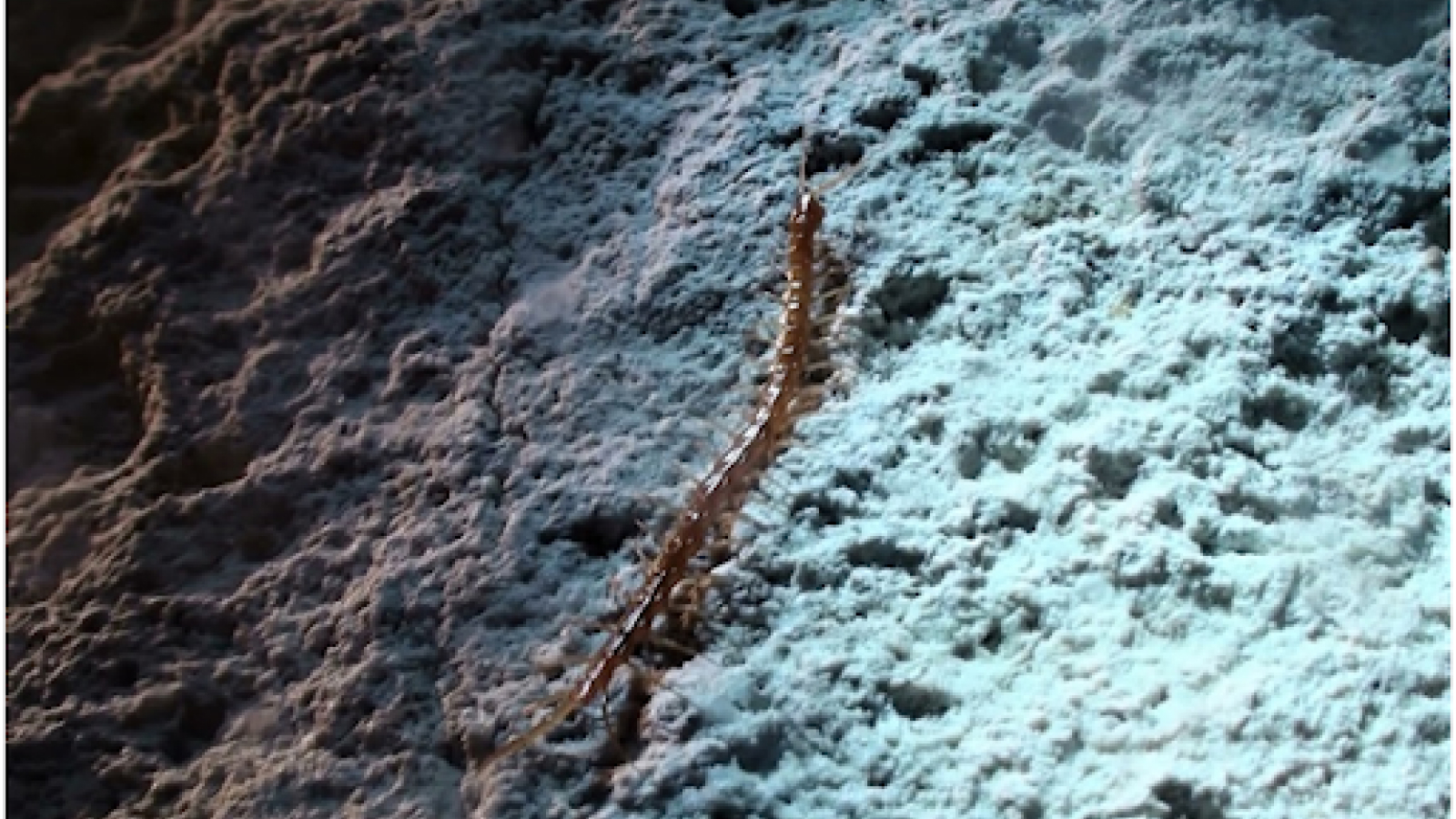
The 6.5-feet-long (2 meter) arthropod’s head has been found for this first time after hundreds of years of uncovering incomplete fossils.
" Arthropleura … has been love since the eighteenth century , over 100 year , and we had n’t find a complete head , " consider first authorMickaël Lheritier , a paleontologist at Claude Bernard Lyon 1 University in France , tell Live Science . " Now with the complete head , you’re able to see the mandibles , the eye , and these equipment characteristic can [ help us understand ] the position of this [ creature ] inevolution . "
The jumbo arthropod had perplexed paleontologists for decades . Arthropleura ’s body had characteristics like a milliped . But without the head , scientists could n’t understand the animal ’s relationship to modernistic arthropods like millipedes and centipedes . While these two modern creatures may look standardised , they actually diverge about 440 million years ago , manner beforeArthropleuracame around . Paleontologists wondered ifArthropleurawas a member of the milliped group or the centipede group .
Arthropleura ’s family - tree disputation " feature fierce debates about its affinities,“James Lamsdell , a paleontologist at West Virginia University who was not involved with the study , write in anaccompanying perspectivepublished in the same journal . But with the breakthrough of an intact head , " the enigma ofAnthropleuranow appears solved . "
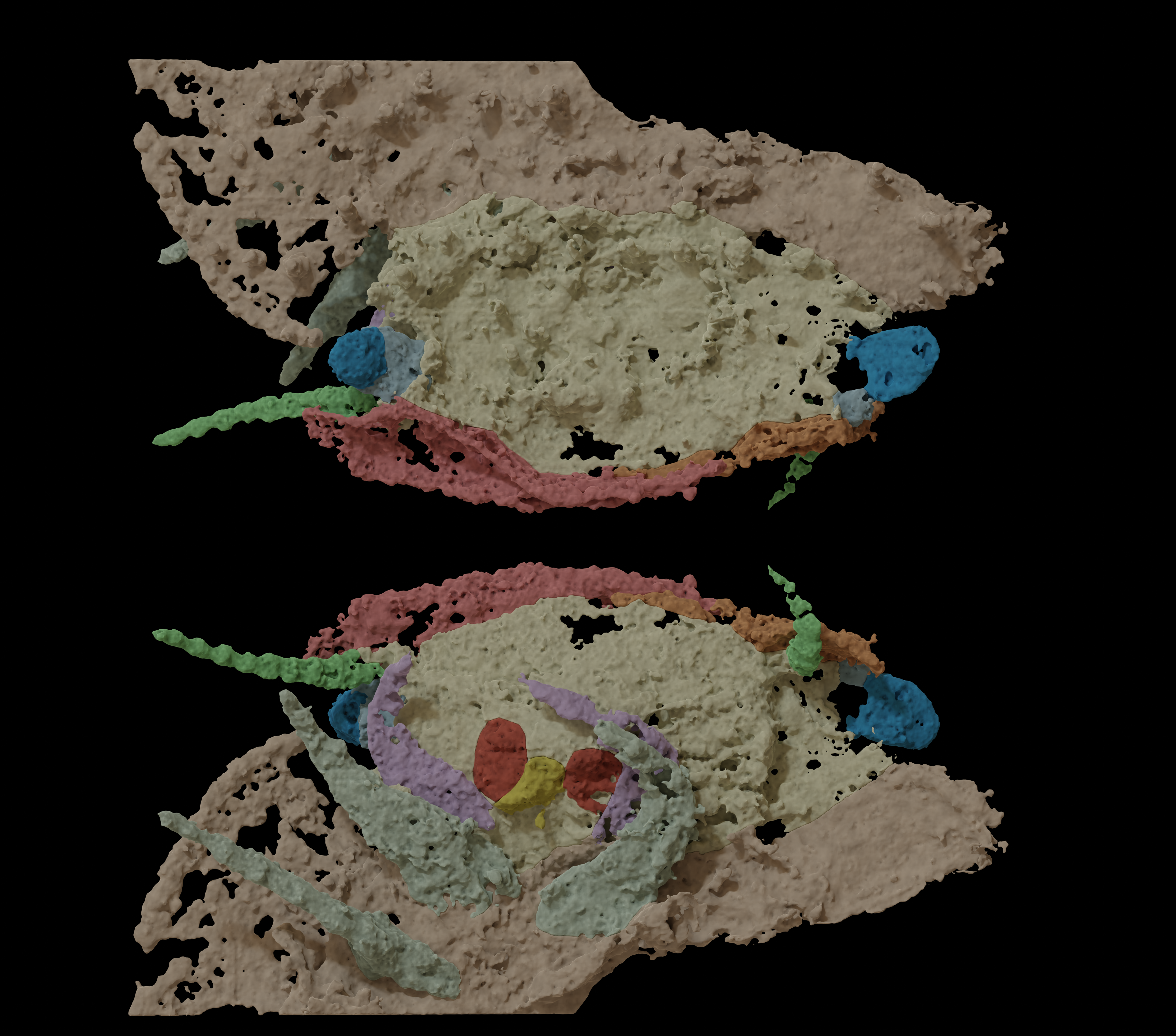
The stalked eyes ofArthropleura, in blue, may suggest that juveniles spent time in the water before becoming adults that lived on land.
Related:7 - base - long arthropod commanded the sea 470 million years ago , ' exquisite ' fossils show
The CT scan virtually bring out the fossilised head of two juvenileArthropleuradiscovered within stone in the Montceau - les - Mines Lagerstätte fossil site in France . The CT scan discover singular stalked eye jutting from the side of the head ; gently curved antennae ; and small , centipede - like mandibles . Together , these traits made up a confusing amalgamation of centipede- and milliped - like characteristic .
" These detail , together , may appear to leaveArthropleuraas much — if not more — a puzzle than before , " Lamsdell tell . " But the ostensibly chimeric nature ofArthropleurais really important grounds that may help answer a fundamental question regarding the [ evolution of these metal money ] . "

— My jaw just overleap ' : 500 million - year - old larva fogey come up with brain preserved
— Swiftie scientist names millipede mintage after Taylor Swift
— Ancient and bizarre ' invention crab louse ' from China had heart on stalk , spike - studded arm and a fanny full of ' blades '

Based on anatomical characteristic , paleontologists ultimately groupedArthropleuraas most closely related to the millipede folk . However , the haunt orb have never been realize in the milliped or centipede folk . Arthropleurahas been wide considered terrestrial , but eyestalks are typically found in semiaquatic or fully aquatic animals , likecrustaceans .
Because the headspring belongs to a juvenile person , the account might lie in the animal ’s life stage , Lamsdell suggested . As juveniles , Arthropleuramay have spent more clip in the water , before losing the stalked eyes in maturity . " The stalk centre persist a braggart mystery , because we do n’t really make love how to explain this , " Lheritier said .















