When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it forge .
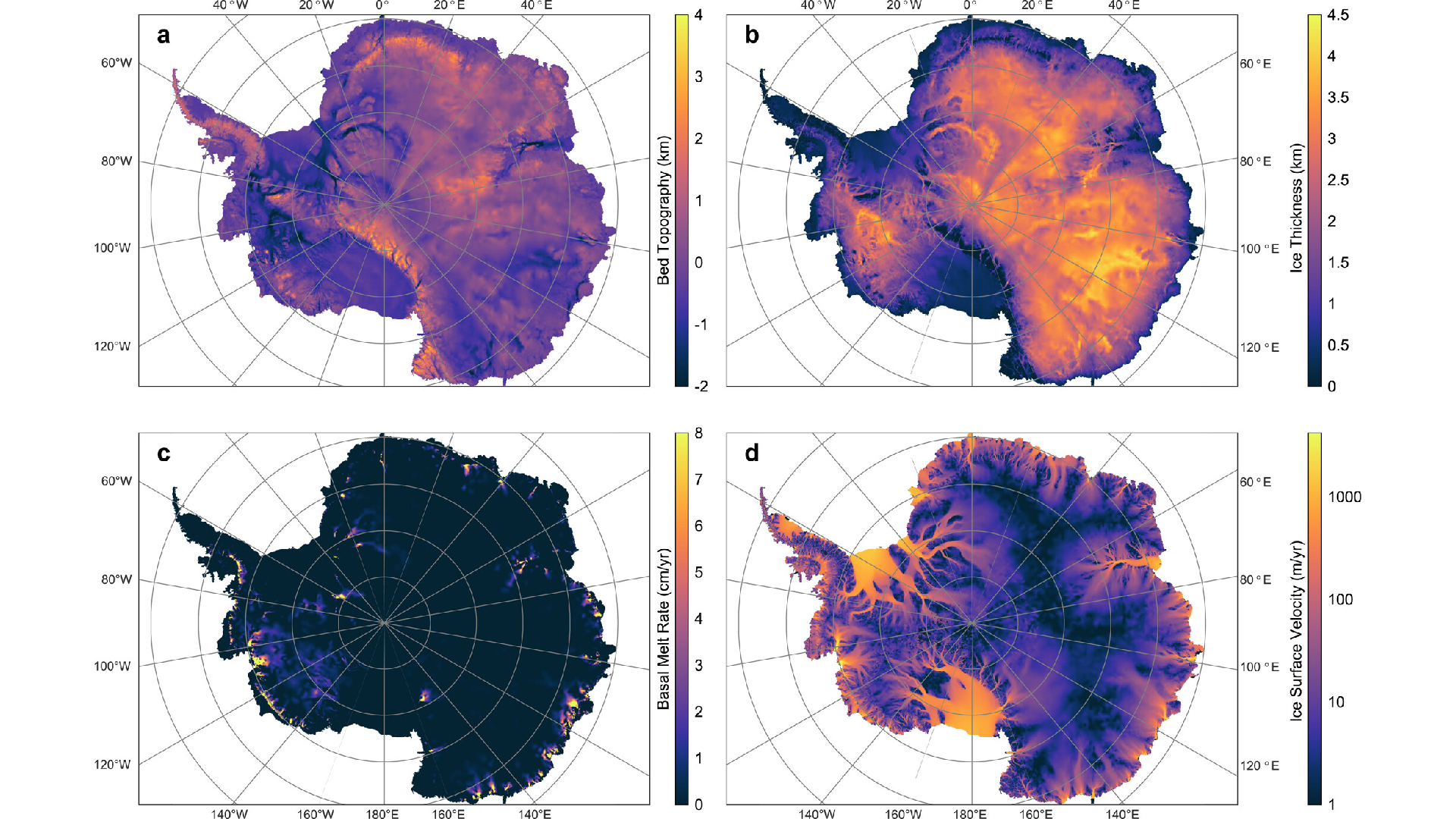
Antarctica has gained shabu in late year , despite increase middling global temperatures and clime change , a unexampled study find .
Using data fromNASAsatellites , researchers from Tongji University in Shanghai chase after change in Antarctica ’s ice sheet over more than two decades . The overall trend is one of substantial ice loss on the continent , but from 2021 to 2023,Antarcticagained some of that lose ice back .

Antarctica is almost entirely covered in freshwater ice.
However , this is n’t a sign thatglobal warmingand climate modification have miraculously reversed . Picture a long ski slope with a small jump at the end . That ’s what a line through the Antarctic ice sail data looks like when plotted on a graphical record . While there have been some late ice gain , they do n’t even begin to make up for almost 20 years of losses .
Most of the gains have already been ascribe to an anomaly that sawincreased precipitation(snow and some rainwater ) settle over Antarctica , which caused more ice to form . Antarctica ’s ice levels fluctuate from year to year , and the gains appear to have slowed since the study geological period ended at the beginning of 2024 . The levelsreported by NASAthus far in 2025 look similar to what they were back in 2020 , just before the abrupt profit .
relate : What ’s hiding under Antarctica ’s glass ?
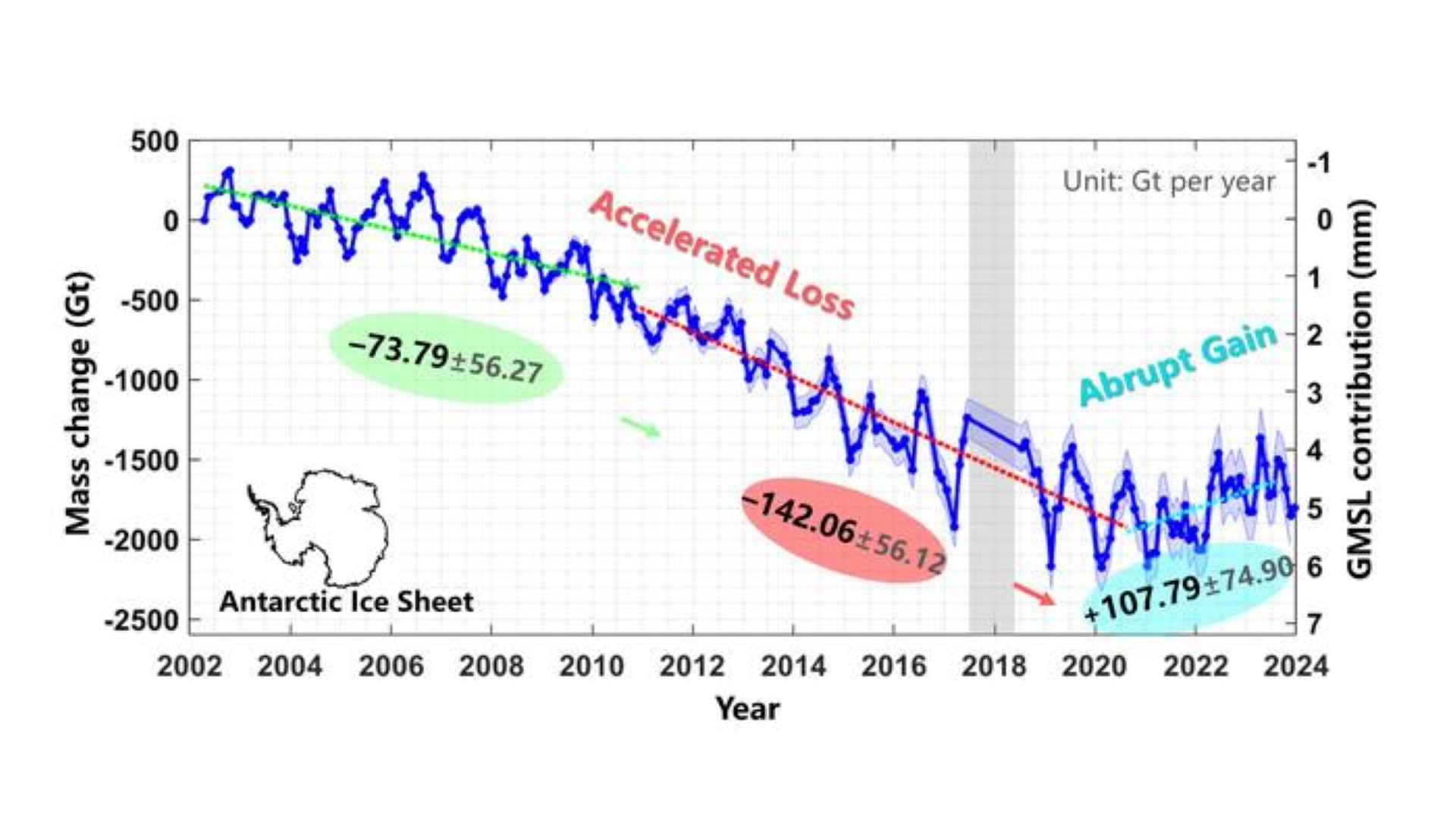
The recent Antarctic ice sheet gain doesn’t make up for the continent experiencing a sustained period of accelerated ice loss.
The sparkler canvass covering Antarctica is the big mass of internal-combustion engine on Earth . Bigger than the whole of the U.S. , the sheet holds 90 % of the world ’s fresh water , grant to theAntarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition , an environmental non - governmental organization . Antarctica is also surrounded by ocean ice ( frozen ocean H2O ) , which expands in the winter and retreat to the south-polar coastline in the summertime .
The planet data bring out that the tack know a sustained geological period of ice loss between 2002 and 2020 . The internal-combustion engine deprivation accelerated in the latter one-half of that period of time , increasing from an mediocre passing of about 81 billion slews ( 74 billion metric tons ) per class between 2002 and 2010 , to a loss of about 157 billion rafts ( 142 billion metric rafts ) between 2011 and 2020 , according to the study . However , the trend then wobble .
The ice canvas gained mass from 2021 to 2023 at an average pace of about 119 billion ton ( 108 metrical oodles ) per year . Four glacier in eastern Antarctica also flipped from accelerated ice going to significant aggregated gain .

" This is n’t particularly unknown , " saidTom Slater , a inquiry fellow in environmental science at Northumbria University in the U.K. who was n’t involved in the study . " In a affectionate climate the air can hold more wet — this produce the likeliness of extreme atmospheric condition such as the gravid snow which get the recent mass profit in East Antarctica , " he told Live Science in an e-mail .
A2023 studydocumented Antarctica ’s unprecedented mass gain between 2021 and 2022 . That study , written by many of the same authors behind the new study , found that a high precipitation anomaly was responsible for for the amplification in ice . The latest study suggests that the trend continued until at least 2023 .
Slater noted that researchers expect the ice gains to be temporary .

" Almost all of Antarctica ’s grounded ice release come from glacier elsewhere which are speeding up and flowing into the thaw ocean , " woodlouse say . " This is still happening — while the late snowfall has temporarily offset these losses , they have n’t stopped so it ’s not expected this is a long - term variety in Antarctica ’s behavior . "
A warming world
mood variety does n’t think that everywhere on Earth will get hotter at the same charge per unit , so a unmarried part will never tell the whole chronicle of our thaw reality . Historically , temperature over much of Antarctica haveremained relatively stable , peculiarly compared to the Arctic , which has cookedfour times fasterthan the rest of the globe . Antarctica ’s ocean ice has also been much more stable congeneric to the Arctic , but that ’s been transfer in late years .
— Antarctica ' pyramid ' : The oddly symmetrical mount that sparked a major foreign conspiracy hypothesis
— ' We did n’t have a bun in the oven to find such a beautiful , thriving ecosystem ' : Hidden earth of life discovered beneath Antarctic berg

— Massive Antarctic icebergs ' rent from glaciers may be unrelated to mood variety
In 2023 , Antarctic ocean crank score record low gear , which researchers close wasextremely unlikelyto pass off without climate change . Meanwhile , globalsea ice coveris consistently dropping to record first gear or near - criminal record first , whileglobal temperaturesare consistently at criminal record or penny-pinching - disk highs .
In 2015 , world leadership sign theParis Agreement , an international accord promising to limit global heating to preferably below 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit ( 1.5 degrees Anders Celsius ) and well below 3.6 F ( 2 atomic number 6 ) . However , that first promise is on the blood line : April 2025 was the 21st out of the last 22 calendar month to gap the 2.7 F limit , according to theEuropean Union ’s Copernicus Climate Change Service .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your video display name .