When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate delegacy . Here ’s how it influence .
Scientists have discovered evidence that limpid weewee was once exposed to the melodic phrase in ancient , shallow lakes onMars . The finding is evidence that not all body of water on the Red Planet was covered in ice , as some Martian climate models evoke .
global geologist and astronomers analyze Mars have know for 10 that weewee was once likely present on the planet , afterNASA’sMariner 9mission catch images of dry gully in the 1970s . But there has been on-going argumentation about what form that water took and how long it hold up . Some modelspredict that any fluent water system on Mars ' airfoil must have been cover by sheets of ice before it disappeared .
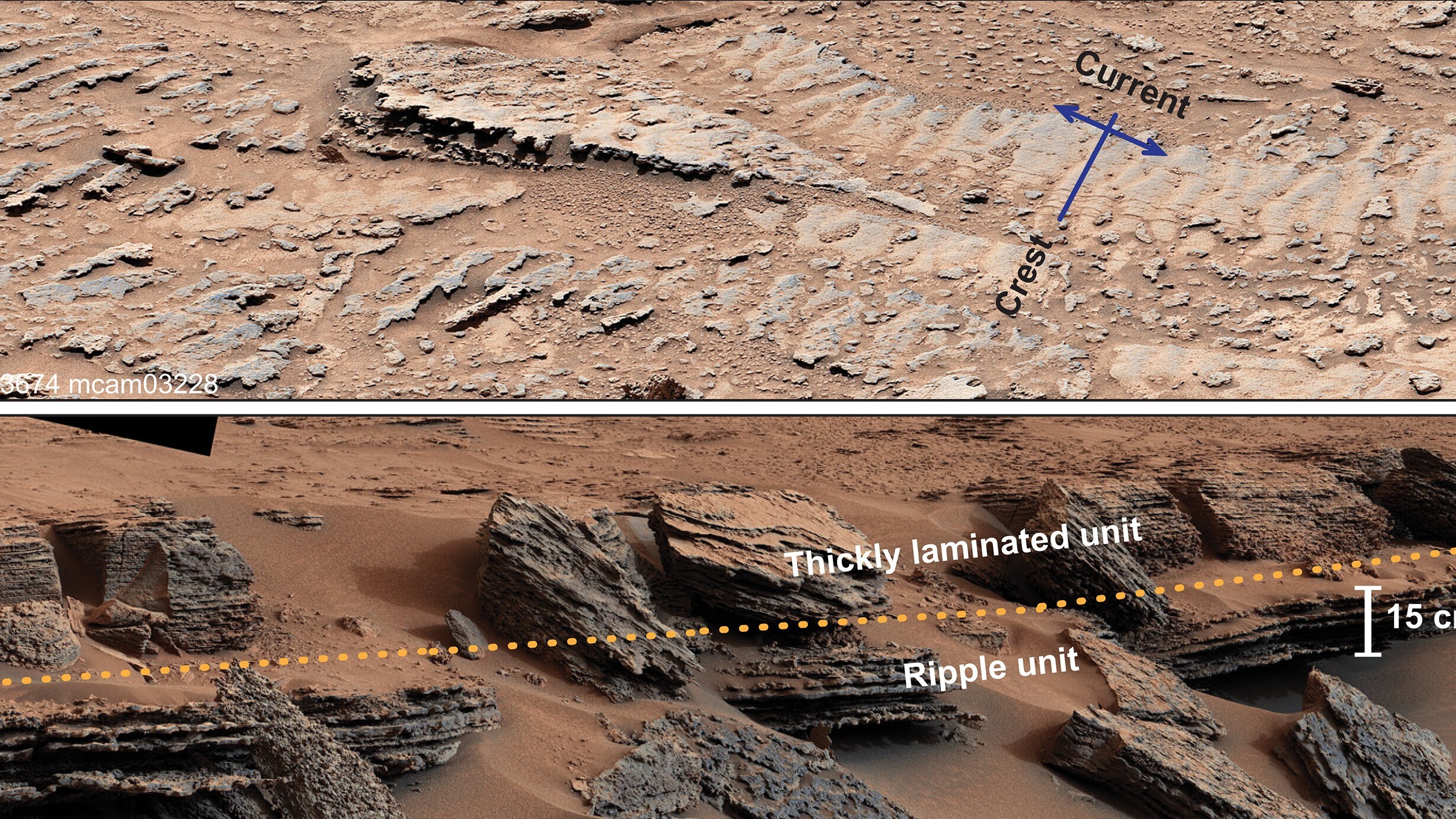
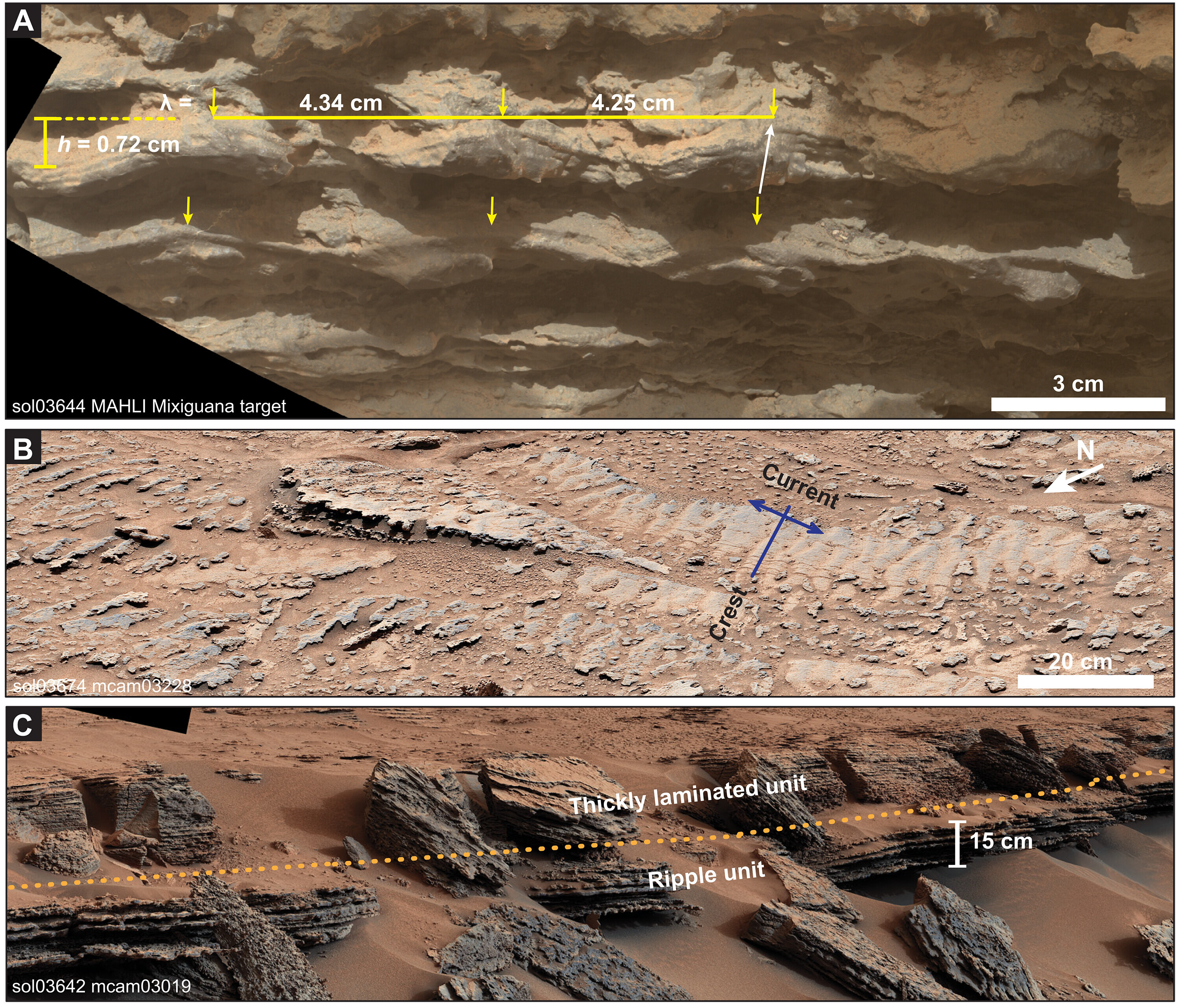
NASA’s Mars Curiosity rover discovered symmetric ripple marks at two separate spots within the Red Planet’s Gale Crater — offering strong evidence that Mars was flowed with open, liquid water.
However , the new determination , which were publish Jan. 15 in the journalScience Advances , , say a different story . The convention , which were photograph by NASA ’s Curiosity rover , are live as undulation ripples — second ridge - like structures that shape along the shores of lakebeds . This means that exposed liquid body of water must have flow across Mars ' surface at some point in its account . The ripples were present in two separate lakebeds in Gale Crater , which Curiosity has been exploring since Aug. 2012 .
" The shape of the ripples could only have been formed under water that was open to the atmosphere and acted upon by idle words , " study first authorClaire Mondro , a sedimentologist at CalTech , said in astatement .
Related:32 things on Mars that front like they should n’t be there
Hope for life?
The researchers also analyse the peak and spatial arrangement of the ripple waves to fix the size of the lake that formed them . The structures are approximately 0.2 inch ( 6 millimeters ) tall and about 1.6 to 2 inches ( 4 to 5 centimeters ) apart , indicating they were go forth by small waves . establish on these dimension , the researchers believe the Martian lake must have been less than 2 meters ( 6.5 fundament ) rich .
— New NASA images reveal jumbo hole in Curiosity rover ’s wheel after 12 days of ' ill-treatment ' on Mars
— Giant ' kidney beans ' spotted in Mars satellite images could charge to sign of weewee and life

— Space pic of the week : Dry ice ' geysers ' erupt on Mars as spring hit the Red Planet
Both dry lakebeds seem to have formed around 3.7 billion class ago , indicating that Mars had an atmosphere thick and ardent enough to support liquid water for longer than previously thought — which could have challenging implications . " Extending the length of time that fluid H2O was present extend the possibilities for microbial habitableness later into Mars ’s history , " Mondro said . In other words : livelihood organism may have had a longsighted window in which they could have evolved on the Red Planet .
Most of Mars ' atmosphere and aerofoil piddle were later stripped aside over billions of old age . scientist conceive this occurred because the planetlost its magnetic field , lead it vulnerable to solar radiation . As the powerful solar wind bombarded the Martian atmosphere , most of the planet ’s C dioxide and water evaporated into quad , leaving behind the gelid desert we know today .

Mars quiz: Is your knowledge of the Red Planet out of this world?
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be incite to enter your show name .