When you purchase through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it knead .
gamey - resolution satellite images have bring out dripping rouge - like convention on Mars that match those found on Earth , according to a new study .
The intimate stain radiation diagram suggest that Mars and Earth were work by similar forces . On Earth , the patterns form on the side of cold , mountainous regions where soils stop dead and thaw throughout the year . IfMarsonce had the same icy , wet condition , then these patterns could be a good place to explore the role that liquid water may have had in shaping the Red Planet and its potential to harbor sign of life .

Mars has wave-like soil patterns that match those found on Earth. This image, taken from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, shows the patterns inside a Mars crater.
" Understanding how these patterns form offers valuable insight into Mars ' clime history , especially the potential for past freezing and dethaw cycles , though more oeuvre is needed to tell if these features formed recently or long ago , " study pencil lead authorJohnPaul Sleiman , a doctoral pupil in the department of Earth and environmental science at the University of Rochester in New York , articulate in astatement .
" at last , this research could help us identify mark of retiring or present environments on other planets that may support or limit possible life , " Sleiman added .
The researcher print their finding online March 26 in the journalIcarus .

The wave-like soil patterns form in cold, mountainous regions on Earth.
Related : NASA rover discovers out - of - property ' Skull ' on Mars , and scientists are baffled
On Earth , ground patterns like this are known assolifluction lobe . They form when a canvass of frozen reason partially thaws and loosens , make soil to creep downhill . The effect creates wave - like traffic pattern on the side of hills in dusty regions . Mars is further away from the sun than Earth , and typically much colder , but the Martian lobes only occur at high latitude .
Some premature studies have indicate that Mars ' high - latitude region may have experienced freeze - thaw conditions in the planet ’s late climate history , which would explicate why it has similar lobes . However , there are many unanswered questions environ the Martian lobes , including why they appear to be significantly larger than those on Earth , according to the study .
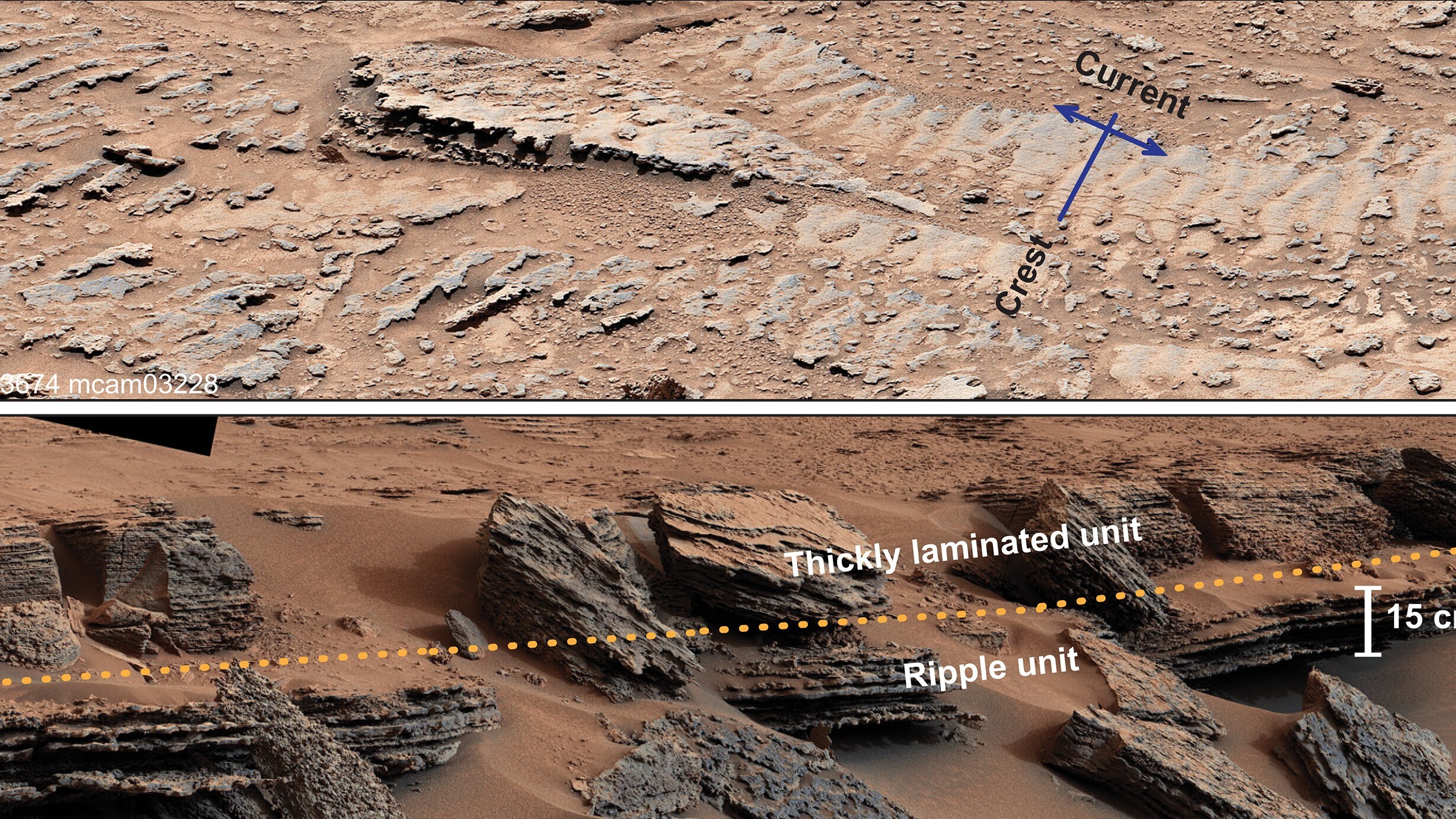
By analyse high - resolution satellite imagery of the Martian surface taken by the HiRISE photographic camera aboardNASA ’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter , the inquiry team saw that the wave - like landforms conform to the same basic geometric pattern as those in Earth ’s Rocky Mountains , Arctic and other cold mountainous regions , according to the statement .
— Life on Mars could survive — so long as you ’re one of these foreign , intercrossed lifeforms
— Curiosity rover see largest carbon chains on Mars from 3.7 billion - year - old rock’n’roll

— scientist discover sign of crucial aliveness - sustaining operation on Mars : ' I eff correctly forth how authoritative this find was '
Study conscientious objector - authorRachel Glade , an adjunct professor in the department of Earth and environmental sciences at the University of Rochester , compare the landforms to patterns see in fluids . These patterns " are large , tardily - moving , granular examples of usual patterns found in everyday fluid , like paint drip down a wall , " Glade said in the instruction .
The team also confirmed that the Martian lobe were larger than Earth ’s — around 2.6 times grandiloquent on average . To explain this , they propose that Mars has taller lobes because itsgravityis weaker , which allows waves of accumulating sediment to grow taller before collapsing , according to the bailiwick .

The findings reinforce previous distrust that Mars ' lobes are — or were — tie to ground water ice , with their patterns resembling what would be expect from fluid - similar instabilities . However , the researchers could n’t be certain that fluid water was involved just from the satellite data point . The authors suggested that succeeding research laboratory experiment could explore whether crank and fluent water are both required for the wave - like patterns to form .
Mars quiz: Is your knowledge of the Red Planet out of this world?
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .