When you buy through links on our site , we may realise an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
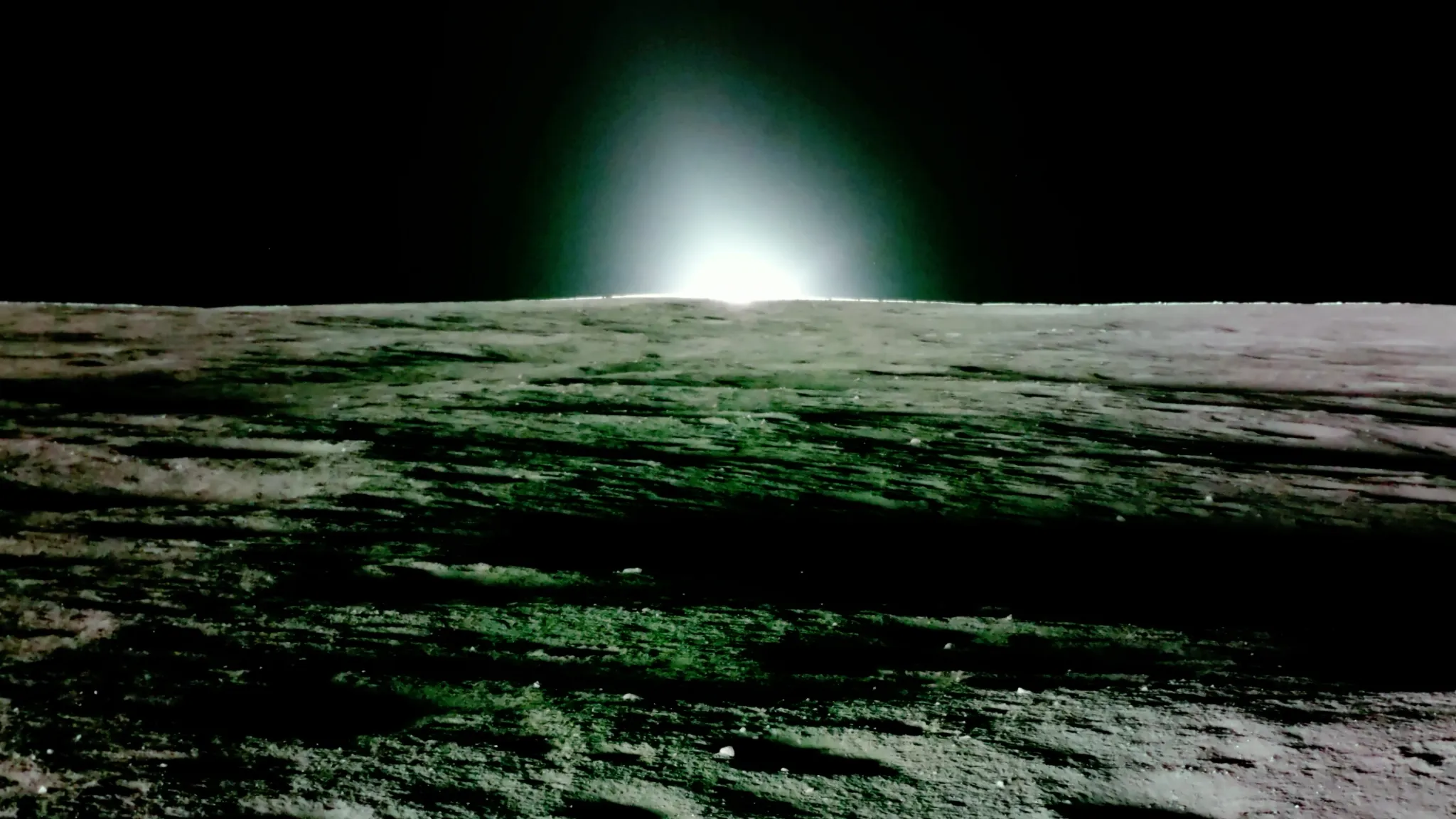
NASAhas successfully bounced a optical maser beam off of an " Oreo - sized " mirror on India ’s historic lunar lander and back to the orbiting spacecraft that fire it . This feat is the first time that such a maneuver has ever been carried out , and it could help facilitate in high spirits - preciseness landing during next charge tothe moon .
In August 2023 , India became the fourth nation to put down a ballistic capsule on Earth ’s prominent satellite when the country’sChandrayaan-3 mission deployed the Vikram lunar landernear the Manzinus crater in the moon ’s south pole part . The lander , which was also carry thePragyan scouter , spent week collecting datum on the moonlight — includingvaluable evidence of moonquakes — butfailed to wake up after a scheduled power downin September . But the defunct lander is still of great pursuit to NASA .
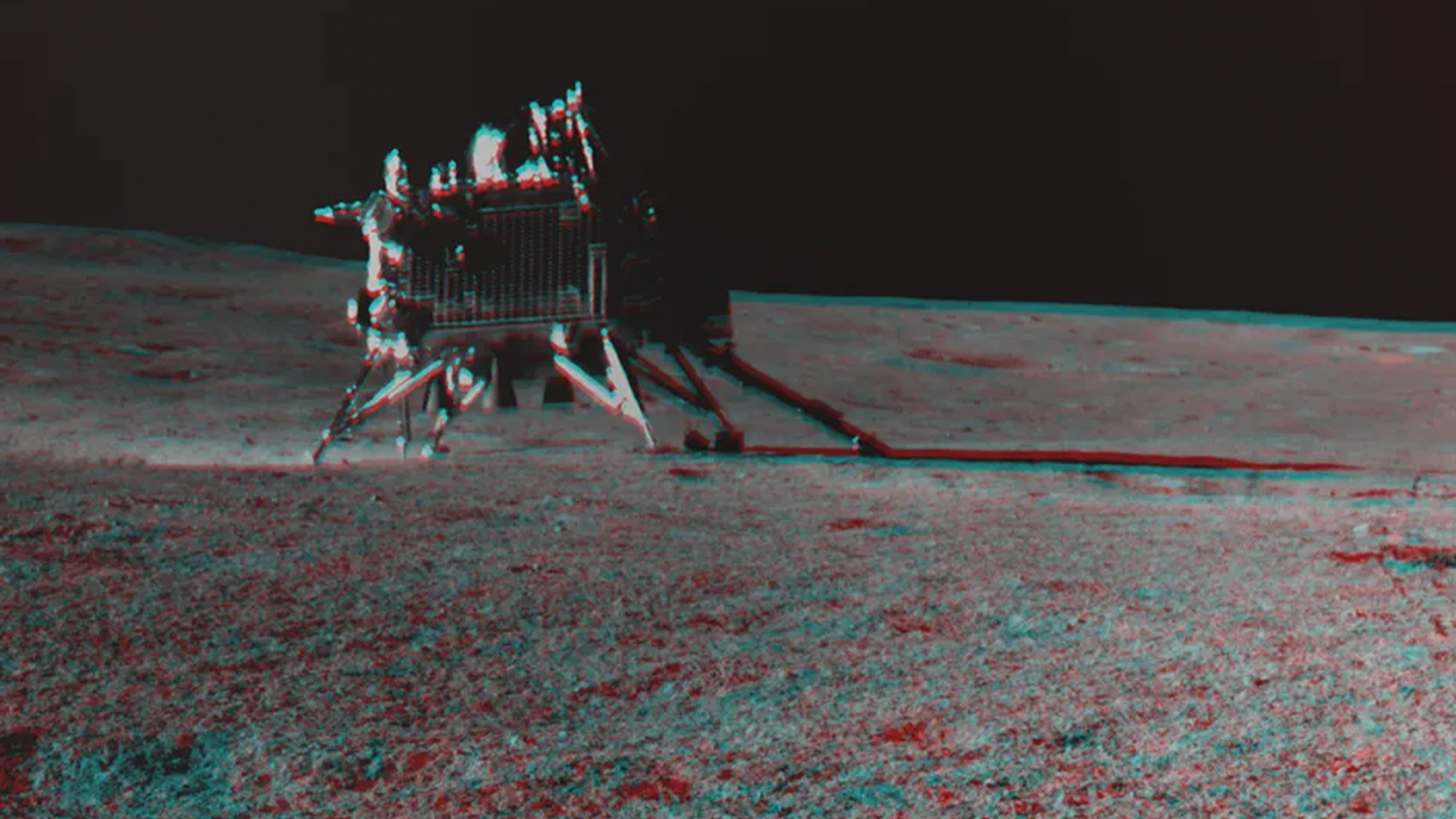

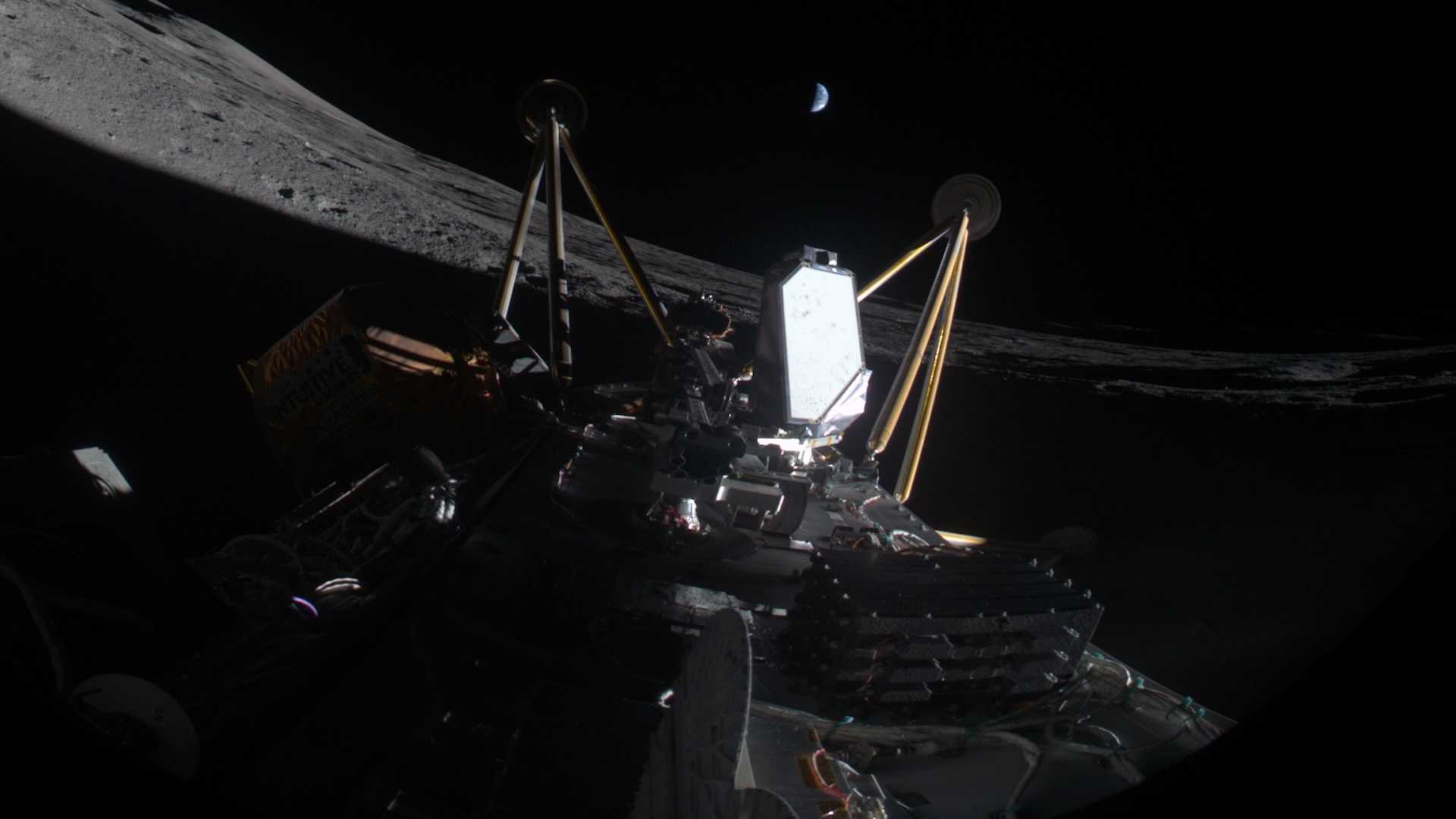
India’s Vikram lunar lander has a small mirror device attached to its exterior, which NASA recently bounced a laser off from more than 60 miles away.
Before the misssion begin , the authority put to have a small , multi - sided mirror , sleep together as a laser reflector raiment or retroreflector , attached to the lander . The 2 - inch - wide ( 5 centimeters ) equipment , which is made from eight quartz - corner - cube prism arrange into a dome - forge aluminum frame , is designed to reflect lasers to revolve spacecraft from almost any incoming slant .
associate : Humanity ’s future on the moon : Why Russia , India and other countries are racing to the lunar south pole
Ever since the lander get going offline , NASA ’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter ( LRO ) , which is the only optical maser - arm space vehicle currently circling the moon , has repeatedly tried to bounce lasers off the retroreflector with no winner . But on Dec. 12 , 2023 , after eight failed endeavor , LRO finally hit the array from 62 mile ( 100 kilometre ) away and received a laser Ping River in comeback .
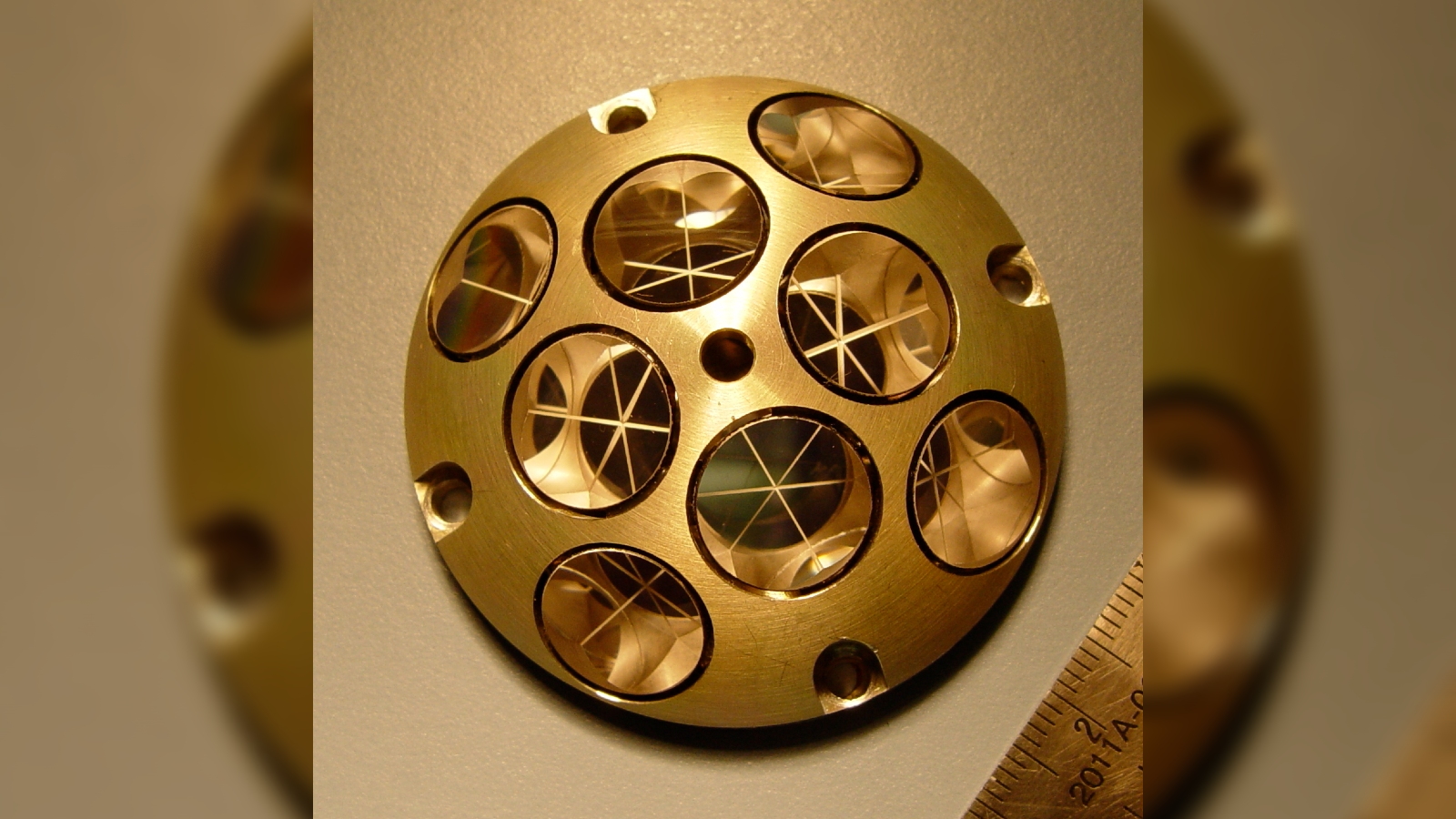

The laser reflector array, or retroreflector, is designed to be able to reflect lasers to orbiting spacecraft from almost any angle.
The long - expect success is an significant proof - of - conception for NASA , which is planning to use more retroreflectors in future mission to the moonlight , include theupcoming Artemis delegacy .
" We ’ve showed that we can settle our retroreflector on the Earth’s surface from the Moon ’s orbit,“Xiaoli Sun , a inquiry scientist at NASA ’s Goddard Space Flight Center who led the mission , read in astatement . " The next gradation is to improve the proficiency so that it can become unremarkable for missions that want to apply these retroreflectors in the hereafter . "
This is not the first time scientist have bounce optical maser off the moon . In the past , NASA has successfully ponder Earth - fired optical maser off contemplative board that were left behind on the lunar aerofoil during the Apollo mission . This has divulge that the moon isslowly move away from Earth by about 1.5 inches ( 3.8 centimeters ) every year .
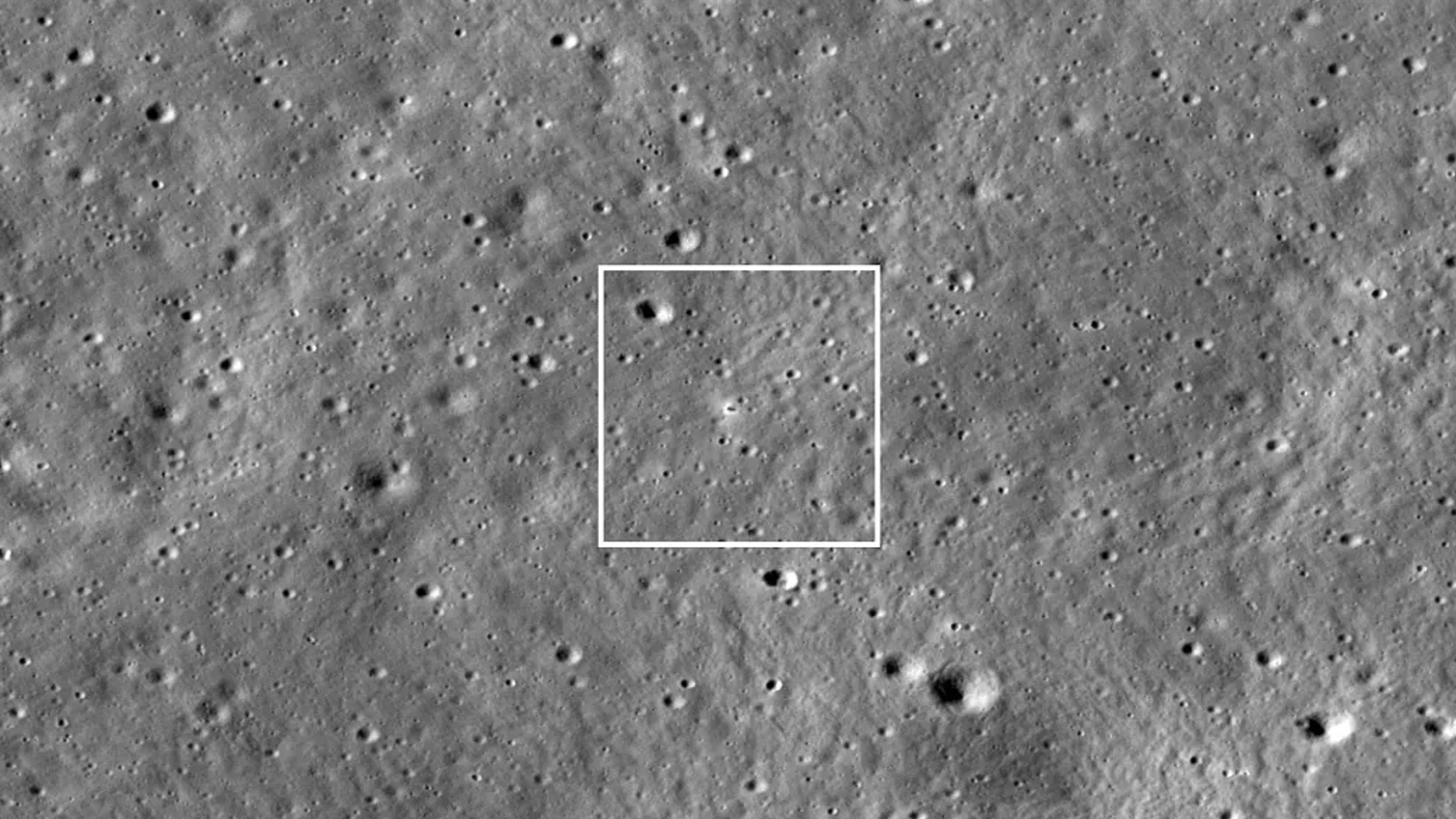

LRO orbits the moon at an altitude of 62 miles, which makes it difficult to spot the Vikram lander.
However , the new retroreflectors were plan with a more hardheaded use in brain . NASA plans to habituate the devices to help remote-controlled ballistic capsule land next to be objects on the Sun Myung Moon by being able to measure exactly how far away they are from the surface ( based on how long it select for the laser to bounce back to the ballistic capsule ) .
This would be important for build next lunar bases and could also allow astronaut to set down in complete iniquity on the far side of the moon . Similar " precision marker " aid incoming astronaut capsules and cargo pods to dock with theInternational Space Station ’s airlocks .
Related:15 incredible figure of speech of Earth ’s moon

It hold LRO multiple effort to successfully speculate lasers off the Vikram lander because the artificial satellite was not design with such exact tactical maneuver in mind . The ballistic capsule , which is currently operating 13 years past its original foreign mission parameters , was designed to represent the lunar surface . To do this , it firesbursts of fragile laser linestoward the moonshine and measures how long it take for them to bound back to the spacecraft . But because these lines are spaced far aside , it made it hard to accurately hit such a pocket-size butt .
Future ballistic capsule that target the retroreflectors will have more precise lasers and in all probability be firing them from much faithful distances . So , in possibility , they should be able-bodied to hit their diminutive targets every metre , according to NASA .
— NASA ’s 1st successful 2 - way of life optical maser experiment is a gargantuan bounce for moon and Mars communication

— South Korea ’s lunar orbiter bring out jaw - degenerate images of Earth and the Sun Myung Moon
— Earth receives laser - beam content from 10 million sea mile away in new NASA experimentation
NASA is plan to put more retroreflectors on the synodic month to run similar experiments in the future . However , their last few attempts have not gone well .

One of their proposed retroreflectors was onboard the in private - owned Peregrine lunar lander , whichrecently burned up in Earth ’s atmosphereaftersuffering a ruinous propellant leakshortly after launching on Jan. 8 . Another was attached to Japan ’s SLIM lander , which successfully landed on the moon on Jan. 19 butmay already be dead after a trouble with its mogul source . ( It is presently ill-defined if the retroreflector on the SLIM lander could still be used by NASA . )
These issue may have set up back NASA ’s enquiry into retroreflectors . But since the first man Artemis missionhas been delayed until 2026 , they will likely get several more chance before those mission come around .