When you purchase through link on our situation , we may realize an affiliate delegacy . Here ’s how it wreak .
Scientists may have spotted a petite wizard , perchance with an alien humanity in towage , shooting through theMilky Wayaround 500 timesfaster than a speeding bullet train . This would make this the firm world system of rules ever seen . However , there is still doubt about the true nature of the speeding object and its companion .
In 2011 , researcher indirectly spot a pair of mysterious objects in the Milky Way , via a phenomenon bonk as " microlensing " — a low - degree form of gravitational lensing where light get " bended " as it passes throughspace - time that is distorted by big objects . Although the team did not straight off see or measure the pair , the gravitational anomaly let out the large object was around 2,300 time heavier than the smaller aim . One of the lead possibility to explain this was that the dyad consisted of a small star being orbit by a sizableexoplanetlocated somewhere in the " astronomic swelling " of stars near the Milky Way ’s shopping centre .
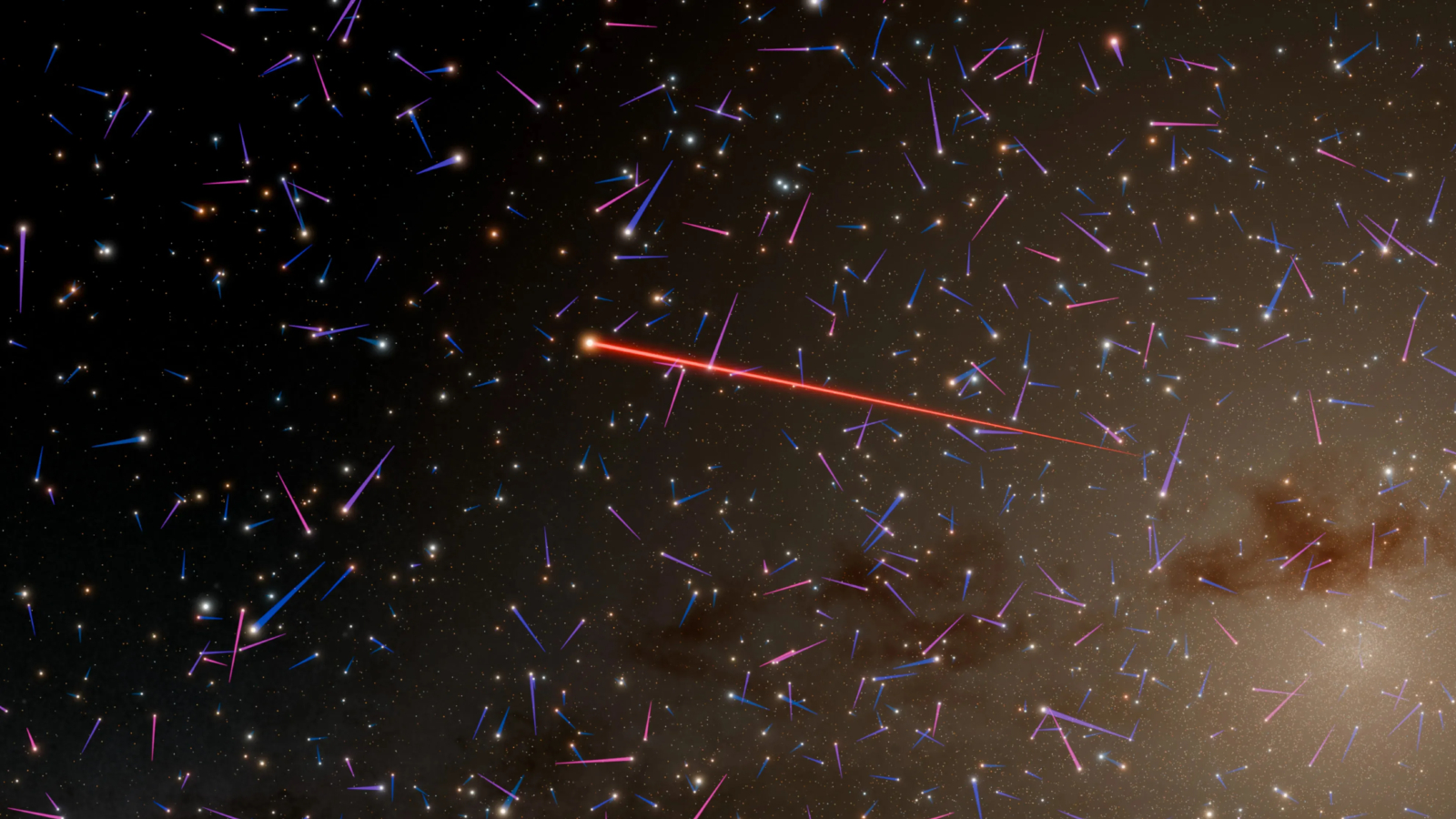

A newly discovered star could be speeding through the inner Milky Way at more than 1.2 million mph. This illustration shows how far it has moved in comparison with other stars during the same period.
In a new work , published Monday ( Feb. 10 ) inThe Astronomical Journal , a dissimilar grouping of research worker has identified a unexampled star that could be the larger objective from this mysterious dyad . The star has a mass roughly one - twenty percent that ofthe sunand is located around 24,000 light - years from Earth in the astronomical interior . Based on its location comparative to the 2011 sighting , the research worker cypher that the star is traveling at least 1.2 million mph ( 1.9 million km / h ) .
No alien world was spot during the young observation , which is unsurprising given that it can take years of constant monitoring to detect an exoplanet circling a genius . However , based on the size of the larger object , the researcher could foreshadow the mass of the potential exoplanet and its aloofness from its home hotshot .
" We believe this is a so - call off topnotch - Neptune world [ roughly 30 time more monolithic than our planet ] revolve a low - mass star at a distance that would lie between the orbits of Venus and Earth if it were in oursolar system , " study trail authorSean Terry , a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Maryland and NASA ’s Goddard Space Flight Center , said in astatement . " If so , it will be the first major planet ever found orbiting a hypervelocity asterisk . " ( devote the star ’s small size , the planet would almost for certain be uninhabitable , the squad add . )
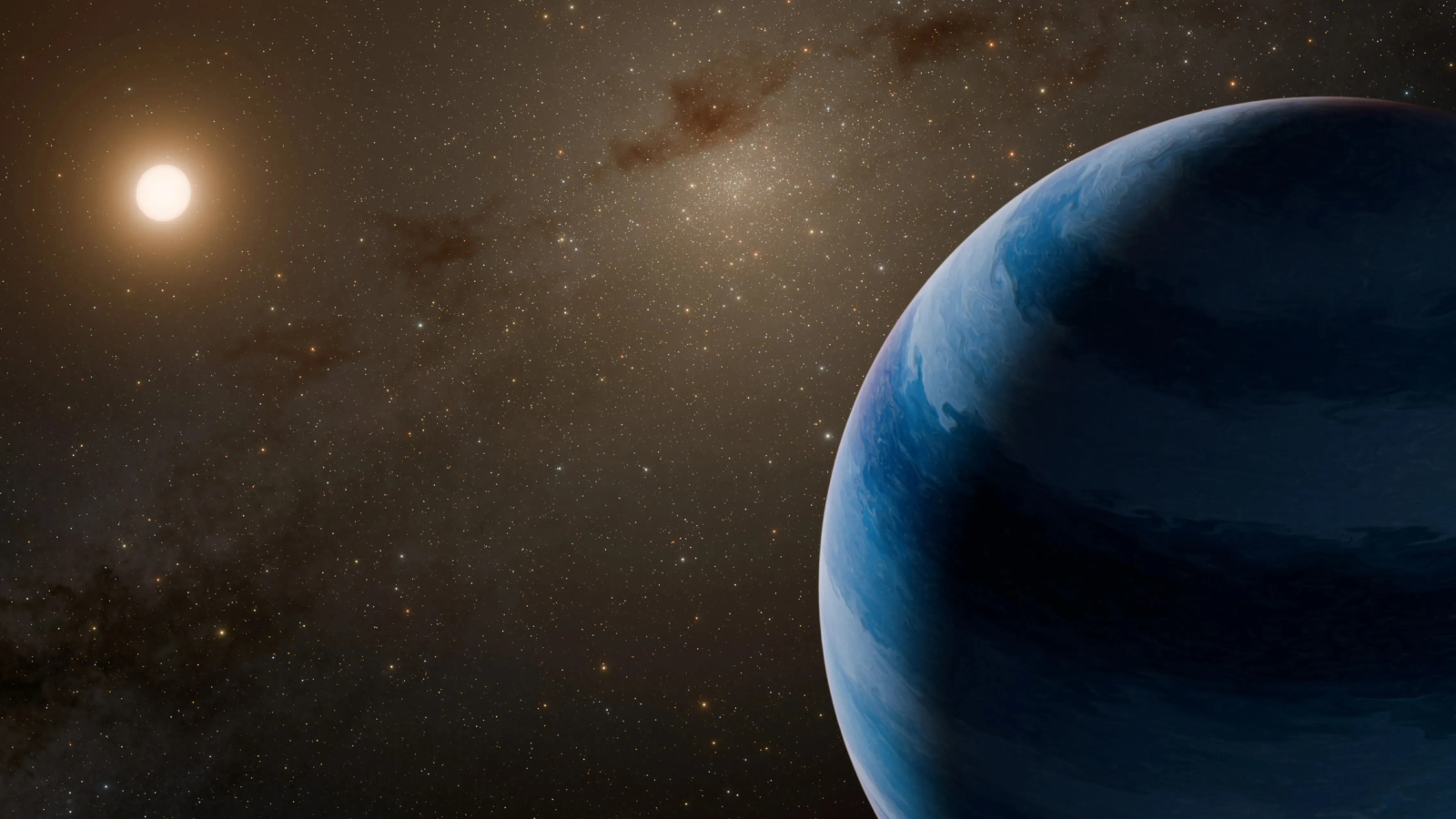

The pair of objects spotted in 2011 could be a small star orbited by a super-Neptune gas giant exoplanet. The larger object is 2,300 times heavier than its counterpart.
Related:32 alien planets that really subsist
At this speed , the potential planetary system would be move through the Milky agency roughly twice as tight as the solar system . However , it could be traveling even faster , because the new observations do not take into account its direction proportional to our system , the researchers wrote .
If the stellar contender is traveling at more than 1.3 million mph ( 2.1 million kilometer / h ) , it will have a sufficient escape velocity to one day leave the Milky Way and cart its global companion with it into intergalactic space , NASArepresentatives wrote in the statement .

However , the squad is still unsure about the object ' truthful sizes and speeds — or even what they really are .
Multiple uncertainties
Even if the larger objective from 2011 is a star , there is no guarantee that it is the same principal fleck in the new study , or that it is move at the upper the researcher estimate , because they have not really see it move yet .
" To be certain the newly identified star is part of the system that caused the 2011 signal , we ’d wish to look again in another twelvemonth and see if it travel the right amount and in the correct centering to confirm it come from the peak where we observe the sign , " report co - authorDavid Bennett , a senior research scientist at the University of Maryland , College Park and NASA Goddard , say in the statement .
— Scientists discover the immobile star ever see in the Milky Way

— Enormous planet discovered around tiny star could break our understanding of solar system organization
— The fastest - moving stars in the galaxy may be aviate by healthy noncitizen , young paper advise
There is also an alternative explanation for the 2011 sighting : that the pair of objects is actually agiant rogue exoplanetbeing orbit by a monolithic exomoon . In this scenario , the duo would also be located much closer to Earth .
If succeeding observations show the hotshot does not move , " that would mean the rogue planet and exomoon model is favored , " study co - authorAparna Bhattacharya , a research scientist at the University of Maryland and NASA Goddard , said in the statement .
Milky Way quiz: How well do you know our home galaxy?
Take anotherscience quiz :
— ignominious hole quiz : How supermassive is your knowledge of the population ?
— Solar system quiz : How well do you know our cosmic neck of the woods ?
— James Webb Space Telescope quiz : How well do you know the mankind ’s most muscular scope ?
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to accede your video display name .












