When you purchase through links on our web site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work on .
stargazer have blot a mysterious pair of icy balls in a remote region of theMilky Way , and they ’re unlike anything they ’ve ever take in before .
The peculiar object come along in the same part of the sky but are 13,000 light - years apart and unrelated to each other . They were first tell apart in 2021 lurking in datum taken between 2006 and 2011 by Japan ’s AKARI space telescope .
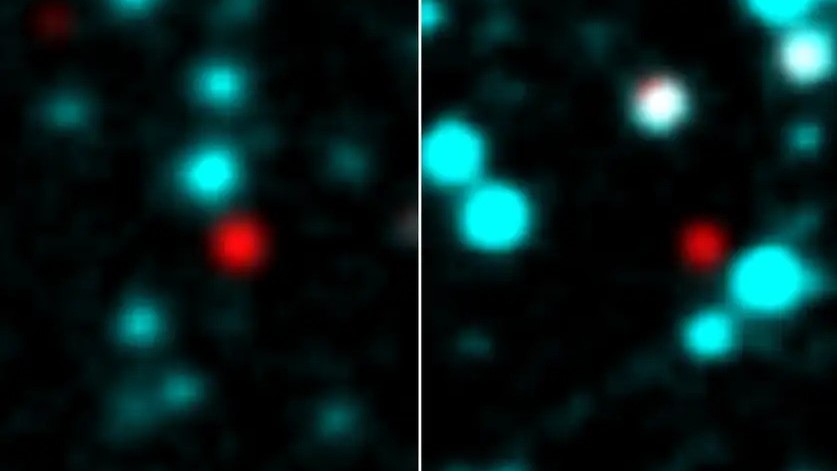
Images of the two icy objects as seen by the ALMA telescope.
Now , new reflexion made using the Atacama Large Millimeter / submillimeter Array ( ALMA ) in Chile have deepened the mystery surrounding the peacock blue object .
They could be dense gaseous state clouds or a never - before - seen character of whizz , but their strange glacial appearance and distance from neighborhood where maven ordinarily form mean they ca n’t yet be explained using known physics . The researchers published their findings Jan 9 . on the preprint serverarXiv , so the results have not yet been peer - reviewed .
Related : Bizarre Modern cosmic physical object is the most charismatic star in the cosmos

" old infrared observations have reported that both object show deep internal-combustion engine and junk absorption features that are often seen in embed new stellar objects ( YSOs ) or background stars sitting behind dense clouds , however , they are locate neither in known champion - work region nor in hump thick cloud , " the researchers wrote in the study . " They may represent a previously unsung type of isolated frosty objects . "
Stars take tens of millions of age to form , growing from slow , billow cloud of turbulent rubble and gas pedal to gently glowing protostars , before materializing into gigantic orbs of fusion - powered blood plasma like our Lord’s Day .
— Ultrabright star objective is shining beyond the ' expiry line , ' and no one can explain it

— Why do some star fail to ignite ?
— Hundreds of ' ghost maven ' haunt the Milky Way ’s centre . Scientists may eventually know why .
Yet these strange grim ball are isolate from these whizz - imprint regions . sit at respective distances of 30,332 light - years and 43,704 lightsome - age from our sun , they each assess up to 10 times the size of oursolar system .
This may seem large , but it ’s petite compared to the scales of other gas clouds , which can load up tomany time the sizing of the entire Milky Way . Infrared reading show that the gas surrounding the objects is chiefly Si dioxide and some carbon copy monoxide — a ratio typically encounter surrounding new superstar . But given their minuscule size of it and icy nature , it ’s improbable the mystery objects are stars .
To investigate the mystery further , the researchers have applied to practice theJames Webb Space Telescope ’s sensitive infrared eye to take an even more detailed flavor at the orbs .