When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Microplastic pollution from industrial dissipation has been contaminate freshwater ecosystems for decades , with evidence place to this run - off starting in the1950sto1970s . Now , though , young evidence indicate the extent of that pollution might be even broader than once think .
In a survey bring out April 25 in the journalScience of The Total Environment , scientists examined the larva of caddisflies , pocket-size insects that work up protective shell around themselves using plant material , grit and small-scale Stone in their environs . These case , gathered in the 1970s and eighties , came from well-defined , saltation - fed stream in the Netherlands that were considered pristine at the sentence .

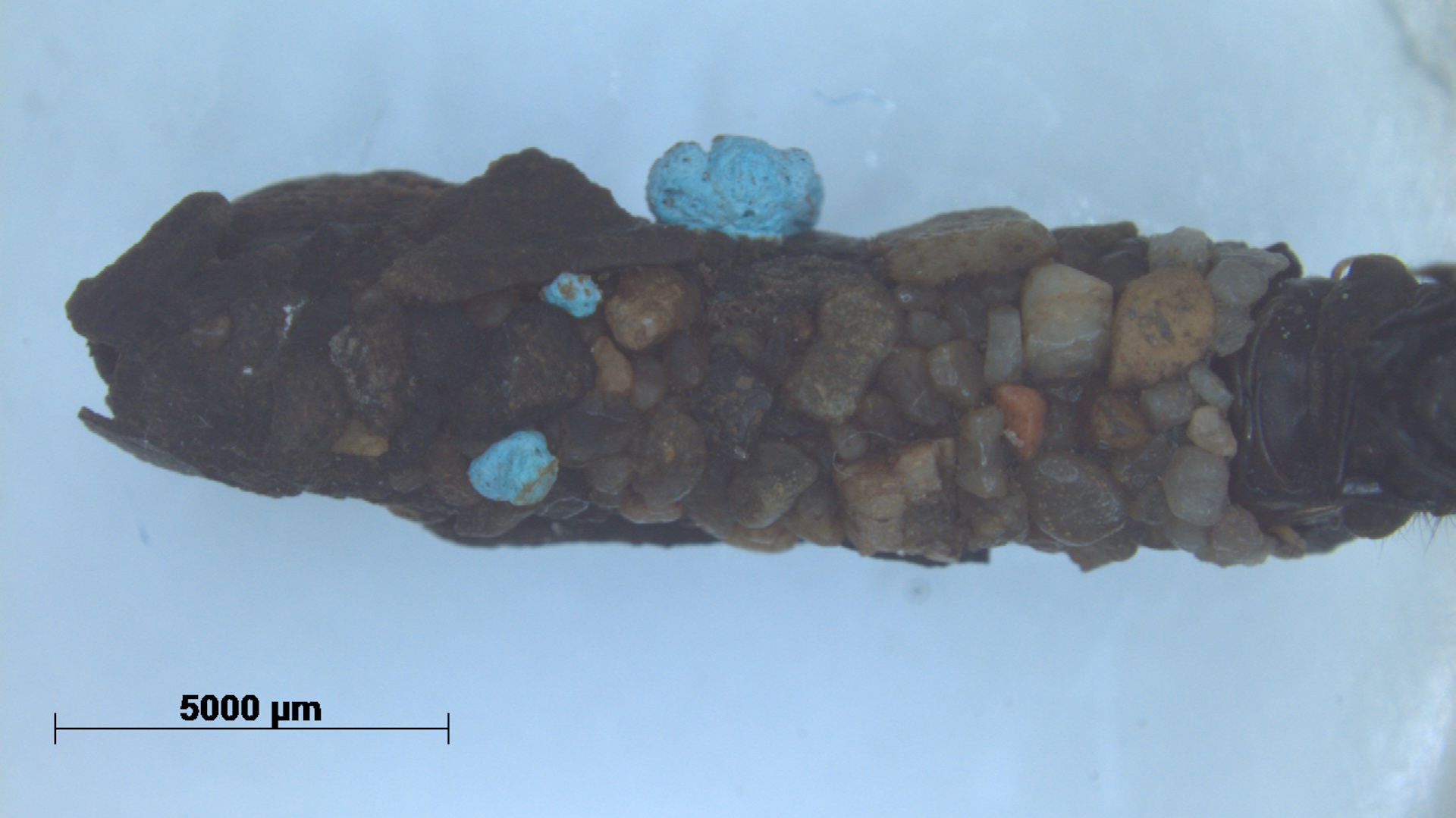
Caddisfly larvae built protective casings around themselves using materials available in the environment. This casing, from 1986, has blue microplastic in it.
However , the written report revealed that the larvae were incorporate plastic particles into their protective casing as early as 1971 — in other discussion , microplastics had infiltrated even these apparently untouched ecosystems .
" The inclusion of plastic in the casing of a caddisfly signify charge plate is come in the nutrient range of mountains , " said lead study authorAuke - Florian Hiemstra , a doctoral prospect in evolutionary ecology at the Naturalis Biodiversity Center .
" Many birds and fish consume these caddisfly larva , and some withdraw them including their casing , " Hiemstra told Live Science in an email . " If caddisflies have been affect by microplastics for over half a hundred , that means the panoptic ecosystem is affected too . "
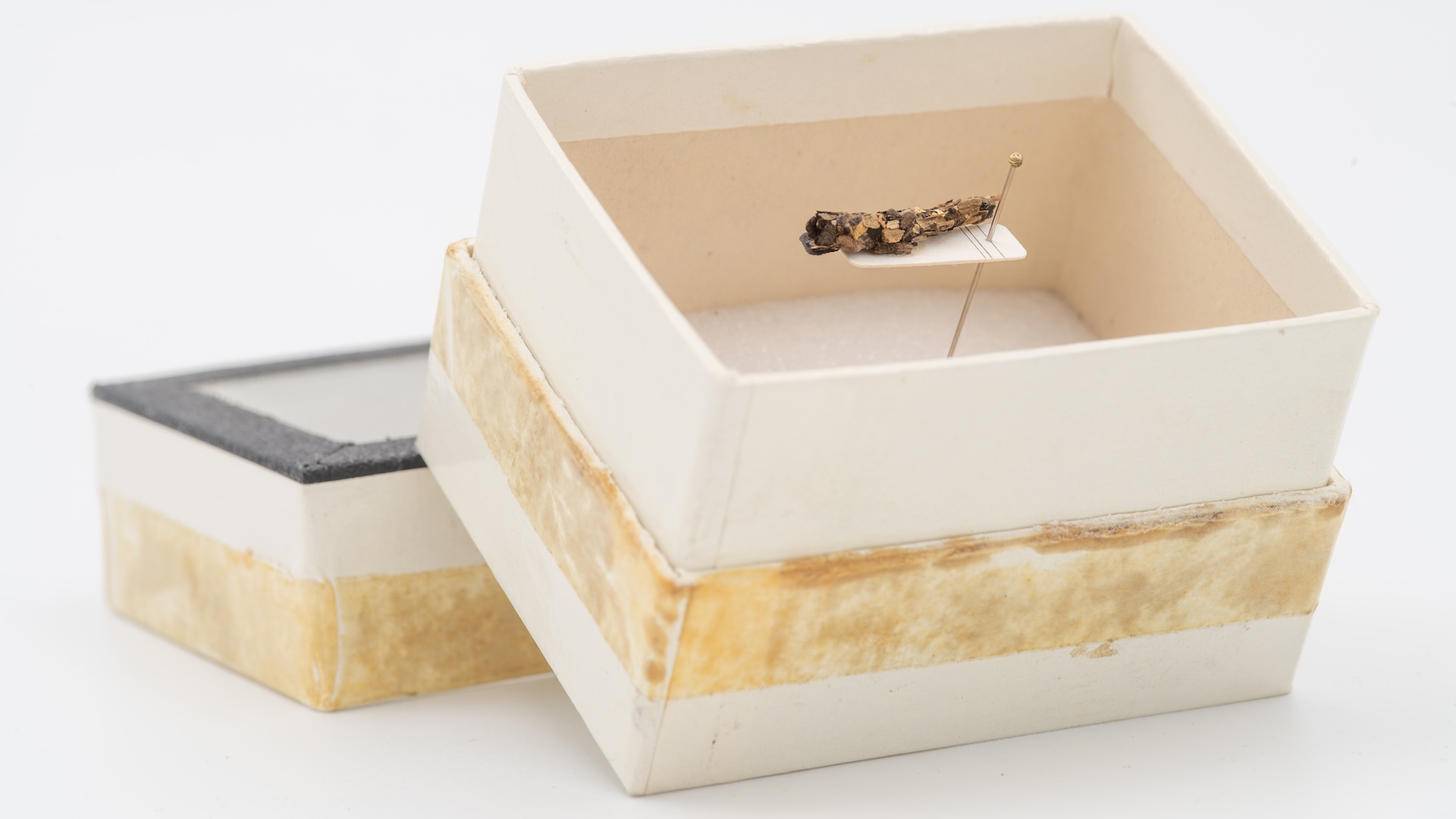

This caddisfly casing from 1971 has microplastic in it, the researchers found.
link : reprocess pitch-dark plastic can hold flame retardants , viral subject area found . That ’s still true — but their mathematics was off
Thecasing specimensin the study are part of the natural chronicle accumulation at the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in the Netherlands . The researchers used a technique yell energy dispersive X - re analysis to reveal chemical substance elements and additive commonly associated with plastic inside the casings .
This provided a rare snapshot into the shock of microplastics on freshwater systems , which correspond less than 4 % of current studies on microplastics , Hiemstra say . Generally , the presence of microplastics in the 2000s iswell documented , but the historical timeline of microplastic pollution has remained vague . This lack of historical data has made it difficult to assess how long ecosystems and human populations have been exposed to microplastics , thus refine risk assessment andepidemiologicalstudies .

A close-up of a caddisfly casing from 1986.
So , how might this study deepen our intellect of the history of microplastic exposure and its potential impacts on human health ?
Microplastics in nature and the body
Microplastics are midget fragments of synthetic polymer that can take anywhere from hundreds to M of years to degrade . They’re defined as beingbetween 1 micrometer caliper and 5 millimeters long . Today , they seem to be recover virtually everywhere : inclouds , theairwe breathe , food , drinking water , andhuman bloodandbreast Milk River . These atom stem from the breakdown of larger plastics , and in some cases , they are advisedly manufactured for use in certaincosmeticsandcleaning intersection .
Research suggest that the human bodyclears out some larger microplasticsmeasuring up to 150 micrometer caliper long , while fragments smaller than 10 micrometer may be absorb into tissues . But recent enquiry suggests that some plastic in our bodies are even tinier than that .
While whatqualifies as " nanoplastic"is still under debate , these ultrasmall corpuscle are typically considered to be any credit card fragments smaller than 1 micrometer ( or 1,000 nm ) in diameter . A human hair , by equivalence , is around 80,000 micromillimeter wide . Nanoplastics are small enough to potentiallypass through cell membranes , studies suggest .

Matthew Campen , a toxicologist at the University of New Mexico , recentlyled a studythat sharpen to the presence of nanoplastics in human tissue . Using forward-looking , mellow - settlement imaging techniques , his squad distinguish charge card fragments measuring no more than 200 nanometer in distance — thin enough that they were semitransparent — in brain tissue paper from a few dozen organ donors .
After its issue , some of the analytic techniques used in the study were criticized , so the accurate measure of dissimilar types of plastic may be off , expert told Live Science . But by detecting nanoplastics , the finding expand upon old employment that trust on microscope that could only detect particles up to 25 fourth dimension larger .
That study , which included sample collected between 2016 and 2024 , also suggest that subsequently samples carried higher concentrations of plastic , and that the brains of individual who died with dementedness contained more plastic than healthy wit . These results raised interrogative about whether the public ’s formative picture has been increasing over time .

Hiemstra ’s new findings tip into that unsubtle discourse and may have significance for how we realise the health risks of microplastics . If the pollutant have been present throughout the environment — not only near industrial sites — since the seventies , that might reframe our understanding of where hoi polloi have been expose and for how long . Plastics not only accumulate in the environs , but also in the body , so well sympathise the timeline and extent of pic can facilitate scientist unpack its retentive - term wellness consequence .
As Hiemstra ’s study was focused on only the Netherlands , though , other work will call for to be done to understand the story of microplastic pollution on a global weighing machine .
Related:‘Very concerning ' : Microplastics can accumulate in genus Cancer cells and may aid them spread , work hint

What do microplastics do to our bodies?
Scientists arestill function to understandexactly how microplastics and the chemicals within plastics — such as phthalates andper- and polyfluoroalkyl substance ( PFAS ) — might dissemble our bodies , Tracey Woodruff , a professor at the University of California , San Francisco ( UCSF ) who studies how pollutant affect generative and developmental health , told Live Science .
other research has linked plastic exposure to the risk of exposure of various health experimental condition , includingheart disease , lung disorder , cancerand Alzheimer ’s disease . In each of these cases , the data link is correlative , so it ’s not clear if or how the plastics might be contributing to the diseases . In addition , in lab - dish studies , some type of plastics appear to be relatively harmless , whileothers have been shownto drink down human cellsin vitro .
In 2024 , Woodruff and her team at UCSF’sProgram on Reproductive Health and the Environmentpublished asystematic reviewof about 2,000 studies on the wellness effects of microplastics as part of a California state - commissionedreportaimed at guide insurance policy decisions . The review identified likely health effects on respiratory , digestive and generative health , and particularly on sperm .

" While a link between chemicals in plastics and continuing disease is unmortgaged , it ’s hard to separate the essence of the microplastic from its chemical substance additive , " Woodruff note .
Our intellect of the possible harms of microplastic exposure is very preliminary at this degree .
She tot that , " with rising genus Cancer pace among young citizenry and increasing exposure [ to microplastics ] from early life , the possible foresighted - terminal figure health peril — specially for those exposedin utero — remain a major concern , " Woodruff allege . Exposure to pollution isone of several competing theoriesfor why the pace of sealed Cancer the Crab are rising in people under 50 .

" More data point will aid come up to the uncertainty in the findings , but we ’re being exposed to [ microplastics ] right now , so it would be prudent to reduce exposures , " Woodruff tell .
While it ’s mistrust that microplastics have negative impacts on human health , the World Health Organization underline that the grounds for these effects is stilllimited and inconclusive .
" Our understanding of the potential harms of microplastic exposure is very preliminary at this phase , " saidBernardo Lemos , a professor of pharmacology and toxicology at the University of Arizona and an accessory professor of environmental epigenetics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health . Lemos has led enquiry to document the effects of microplastic exposure in homo and in example organisms , such asfruit fly , miceandfish .
" I am certain there will be many more written report documenting an abundance of microplastics in historical sample distribution , " Lemos told Live Science in an email . " It will be interesting to document how microplastics ' abundance and caliber change over decades . " The Organisation for Economic Co - operation and Development , an intergovernmental organization , predicts that plastic production maytriple by 2060 .
Related : Humans inhale a stupefying amount of microplastic every hebdomad . Here ’s where it ends up
Is it possible to avoid microplastics?
While Woodruff note it would be prudent to decoct microplastic pic , it ’s unclear what levels of micro- and nanoplastics we ’re realistically taking in on a day-after-day footing . " Plastics can put down into smaller fragments , but they endure , so we ’re buy the farm to be expose to them for a very longsighted time , " Woodruff articulate .
She suggested that , at the individual stratum , people canreduce their exposureto microplastics and the chemical in them by consuming fewerultraprocessed nutrient , which are more likely to come into contact with credit card than whole or less - processed foods . She also suggested that it may help to avoid charge plate container , bottles and packaging where possible .
— Microplastics may be entering the clouds and regard the atmospheric condition , scientist say

— Boiling hydrant water can absent closely 90 % of microplastics , raw subject field finds
— chemical substance in plastics and cosmetics tied to preterm nativity risk
" There is still so small known about the chronicle of microplastics , " Hiemstra suppose . But thanks to collections that admit specimens like the caddisfly case , we may have unknowingly compile more grounds than we mean about the early days of this pollutant .

Other lifelike account collections around the world may harbour even older case with microplastics , he suggested , highlight the untapped note value of such collection as tools for environmental science . They may offer a way of life to give historical baselines of microplastic pollution , which are still largely miss from the record and could assist us trace the true wellness shock of plastics .
This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to go in your presentation name .








