When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
scientist have pinpoint a familial grounds of an passing rare bone - weakening disease experience in untried the great unwashed .
Idiopathic osteoporosis is a bone disease forecast to affectaround 0.4 mass per 100,000 every year . Like more common shape ofosteoporosis , it weakens people ’s bones , causing them to become brittle . This increases the risk of infection of fractures , even from relatively gentle movement , such as cough or bending over . Most osteoporosis cases move peopleover age 50 , especially postmenopausal women , but idiopathic osteoporosis is unlike in that it ad libitum arises inyoung and otherwise sizable individual .

Disruptions to melatonin signaling may explain why some people develop osteoporosis much earlier than others, new research suggests.
The exact cause of idiopathic osteoporosis is unknown , but it appearsto execute in menage , with many affected role experiencingexcessive bone fracture during puerility . This trend suggests that the disease may have a genetic cause — and now , scientist have describe what that cause could be .
research worker perform a genetical depth psychology that revealed that variation in a specific gene can disrupt the function of a protein called MTNR1A , and this may be partially creditworthy for the development of idiopathic osteoporosis . The scientist put out their findings Oct. 16 in the journalScience Translational Medicine . The protein is a receptor on the surface of cells that melatonin , best cognise as a eternal sleep - kick upstairs appurtenance , plugs into .
Related : scientist uncover raw hormone in strange discovery

Melatonin is a hormone thatregulates the physical structure ’s sleep - wake cycle — the daily rhythm method of birth control that shift the physical structure from sleep to vigilance and back again . But enquiry shows that melatonin may also have other functions , admit the power tosuppress cancerin some contexts , humbled blood pressureandcontrol the outgrowth of making new ivory tissue paper .
In the new study , scientists sequenced the genome of 10 people in the same family , several of whom had idiopathic osteoporosis . ( The squad learned after the bailiwick was completed that the family had Ashkenazi Judaic ancestry . )
In addition to the phratry , the researchers try deoxyribonucleic acid from 75 female patients with the condition who were not related to one another .

This analysis revealed that specific mutations in the gene that codes for MTNR1A — named rs374152717 and rs28383653 — may be tied to the disease , as these mutations were only found in masses with the condition .
The squad then flourish their investigation to include genomic data point from large , in public useable databases . They found that these rare mutant were more normally found in Ashkenazi Judaic people than in the worldwide population and also marry to idiopathic osteoporosis .
The rs28383653 mutant was particularly rife in the distaff participants with idiopathic osteoporosis , carried by around 4 % of masses in this universe . That ’s compare to 1.7 % in the Ashkenazi population overall , and 0.9 % of the general population . The rs374152717 variant , on the other hand , was find oneself in 40 % of the sept members , 0.9 % of the overall Ashkenazi population and 0.04 % of the general population . This suggests that people who transmit these mutations are at a bang-up risk of formulate idiopathic osteoporosis .
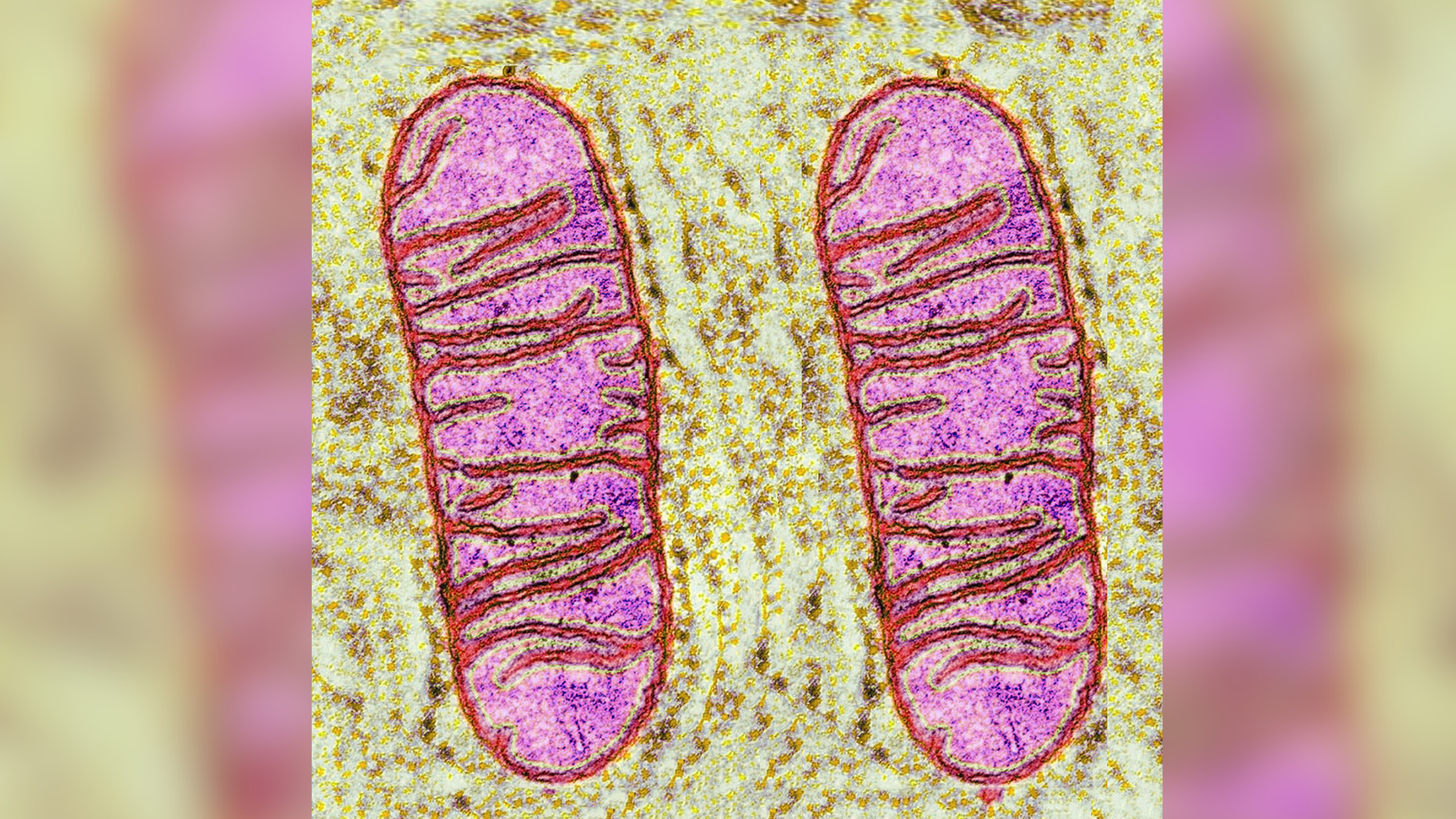
In separate experiment , the researchers used the genome - editing toolCRISPRto inclose the rs374152717 mutation into human bone cells , as well as lab mouse . The mutant caused the bone cellular phone to make a defunct melatonin receptor , disrupt melatonin signaling . In the mice , the mutation spurred the activity of cells know asosteoblasts , which make ivory tissue . This caused the cellphone to age faster and resulted in a simplification in bone mass .
fill together , the bailiwick findings support the idea that melatonin could potentially be used to treat idiopathic osteoporosis , the squad concluded .
" It is potential that by find oneself means to mend activeness of this pathway of melatonin signaling [ in these patients ] , we could forestall further osseous tissue deprivation and fractures or restore ivory defect , " saidStavroula Kousteni , study co - author and a prof of physiology and cellular biophysics at Columbia University .

— New drug could prevent bone loss on lengthy distance deputation , study in space - get along mice suggests
— ' Who are we to say they should n’t live ? ' : Dr. Neal Baer on the scourge of CRISPR - drive eugenics
— CRISPR ' will leave cures for genetic diseases that were incurable before , ' says illustrious biochemist Virginijus Šikšnys

However , " these possibility will need to be tested by experimentation , " she told Live Science in an email .
Variousclinical trialshave already demonstrate that melatonin can improve off-white density and prevent os loss , they noted . At this peak , the study does n’t point to a direction to even off the inherited mutation that may lead to the disease .
Ever wonder whysome people build muscularity more well than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? Send us your question about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the internet site !