If you ’ve been using a Mac for any length of fourth dimension , you know that it ’s more than just a pretty point - and - click , window - and - icon interface . Beneath the surface of the operating organisation is an integral human beings that you could get at only from the command line of reasoning . Terminal ( in your /Applications / utility leaflet ) is the nonpayment gateway to that mastery line of descent on a Mac . With it , instead of pointing and clicking , you typewrite your command and your Mac does your command .
Why would you want to do that ? For almost all of your computation needs , the regular graphical user user interface is enough . But the statement line can be handy when it comes to troubleshooting your Mac , to turn on “ obscure ” preferences , and other sophisticated job . It ’s a good idea for anyone who is n’t an pure tiro to be familiar with it .
If you are n’t already familiar with your Mac ’s command - line interface . First up : How to voyage the file system from the command - line command prompt .

The prompt
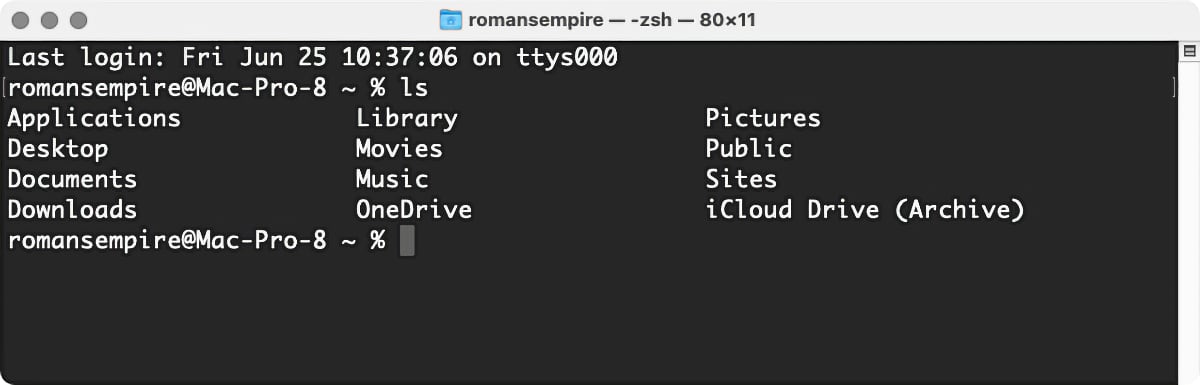
By default , when you afford Terminal , the first thing you ’ll see is something like this :
Last login : Fri Jun 25 10:37:06 on ttys000romansempire@Mac - Pro-8 ~ %
Here ’s what you ’re see :
How to see what’s in a folder
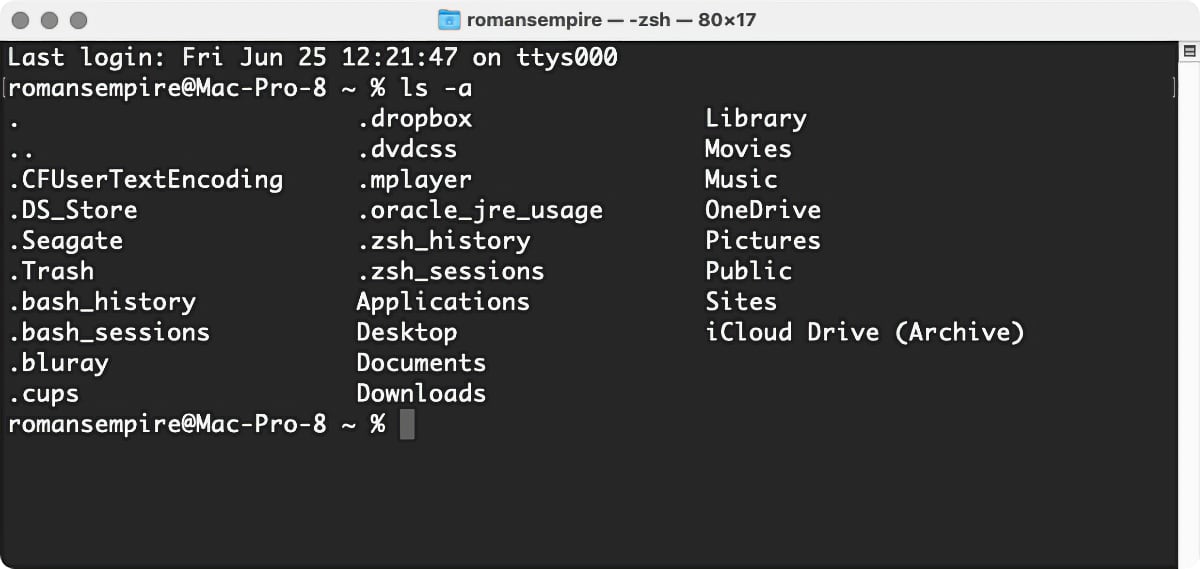
When you first get to the bid billet , you ’re in your home folder . While you ’re there — or when you ’re in any folder ( directoryin Unix - speak)—you might require to know what ’s in it . To do that you use thels(orlist ) program line . Typelsand compress the Return key , and you ’ll see the folder ( and/or files ) in the current directory .
IDG
The output of the plainlscommand is pretty thin ; it shows you the names of file and folder contain in the current directory ( including some familiar ones such as Movies , Music , Pictures , and so on ) . as luck would have it , you could add a numeral of optionalswitchesto thelscommand that allow you to see more entropy . For instance , typels -l(that ’s a low - character L ) , then press Return . You ’ll see something like this :
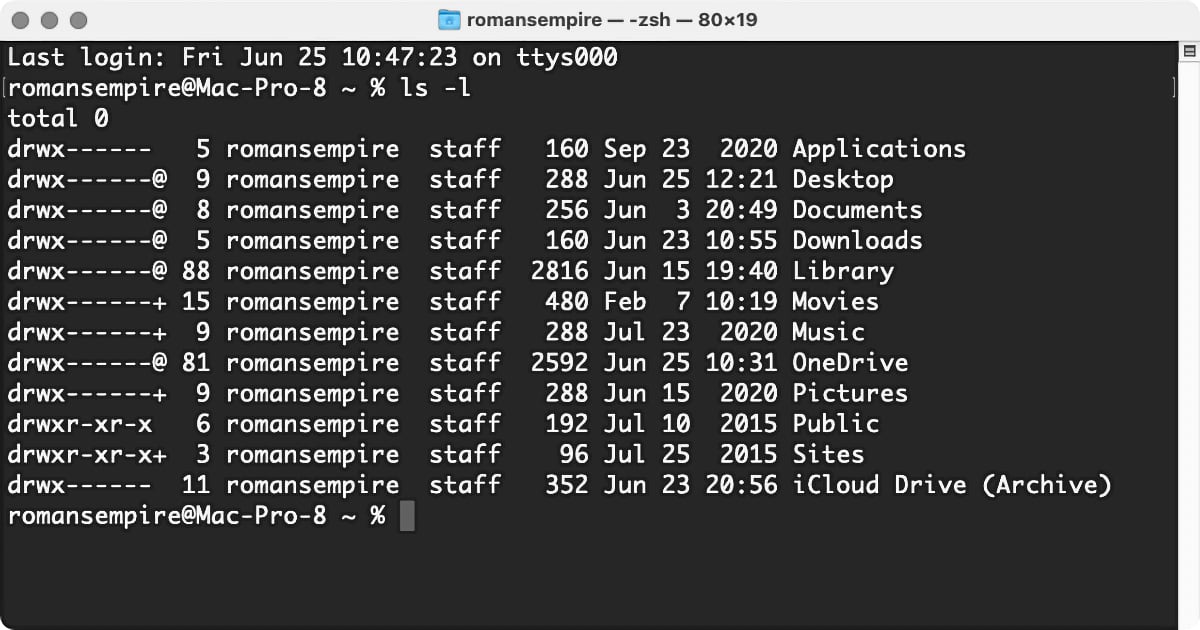
Do n’t worry too much about what all that mean powerful now — we’re just receive our feet wet . The full point is thatlscan cater additional entropy about files and folders , depending on the options you define . In this case , that extra information includes the name of the user whoownseach item in the directory . ( That ownership is part of the Unix organization ’s file - license authorities . ) Theromansempire staffnext to most of those item above means that each one is owned by the userromansempire , who is in the groupstaff . The other understandable bit of information next to each file and booklet is the engagement and time each one was last modified .
One other ready to hand option : you may viewinvisiblefiles — ones that the Finder does n’t normally show you — by typingls -a . ( These concealed files all have dots ( . ) in front of their names . )
How to access other folders/directories
When you ’re in the Finder and you desire to move to another pamphlet , you find oneself that folder and double - click it . From the command line , you use thecd(orchange directory ) instruction instead . So let ’s say you ’re in your nursing home folder and require to peek inside the Downloads leaflet . To do that , you ’d typecd Downloads . ( call back to always type a space after any command that has an additional argument , such as the name of a directory in the old model . ) Once you ’ve done that , lswill show you the mental object of your Downloads folder .
Here are a match of warm tricks for moving around in your Mac ’s file cabinet system .
To get wind more Terminal commands , see our article on how tocopy and move foldersas well asdelete files and foldersusing the control line andget help when you want it from human being pages .