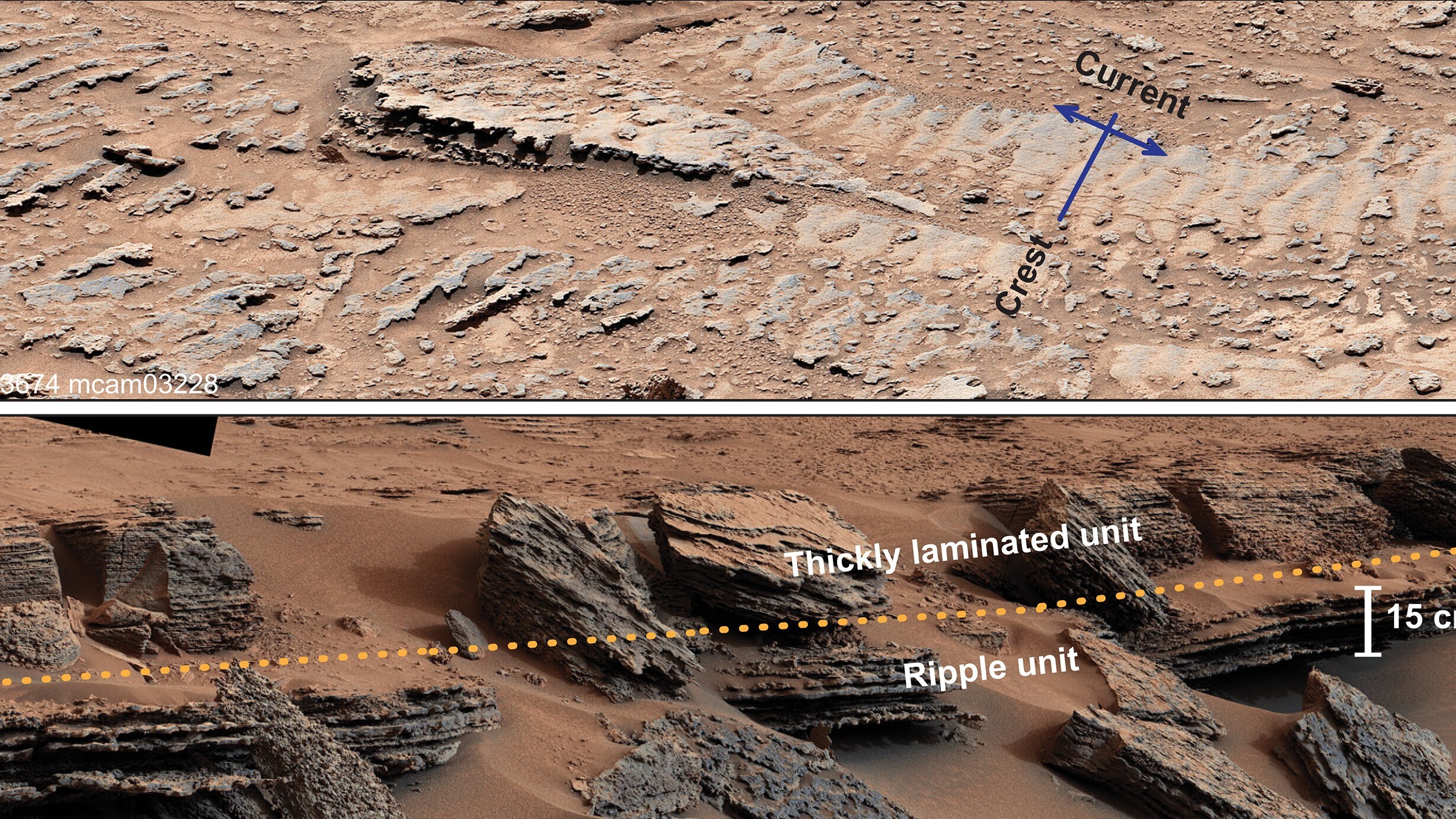
When you purchase through links on our web site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it sour .
Recordings of Martian seism , or " marsquakes , " collected by a automaton on the Red Planet may have finally solved a 50 - twelvemonth - old mystery : why one one-half of Mars is so drastically different from the other .
Since the 1970s , researchers have known that Mars is split into two main areas . The northerly lowlands cover around two - thirds of the planet ’s northern hemisphere , while the southern highlands cover the rest of the major planet and have an average elevation approximately 3 miles ( 5 km ) higher than that of the northern lowlands . Mars ' crust , which sits on top of a mantle of liquified rock interchangeable tothe one inside Earth , is also thicker in the southern Highlands of Scotland . This world-wide asymmetry is known as the " Martian duality . "
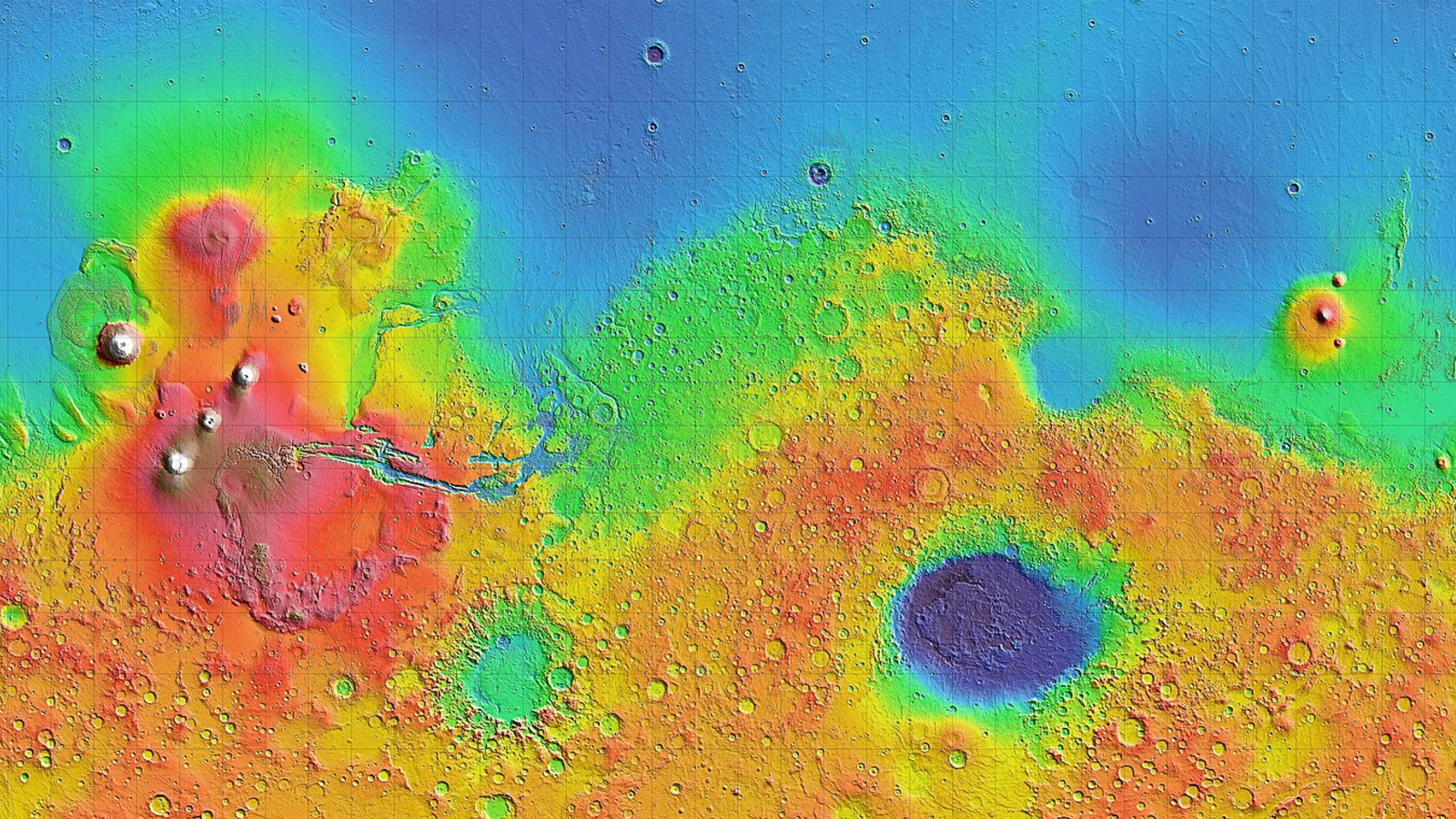
There is a stark difference between the elevation of Mars' surface in the planet’s northern and southern hemispheres. Researchers call this the Martian dichotomy.
There are two main theories for the line of descent of the Martian dichotomy . One is that the divide was cause by some unknown process within the planet ’s interior . The other is that a massive collision with a moon - size object or multiple smaller space tilt reshaped the planet ’s surface . However , the ages of the rocks on the Martian open hint that whatever caused the unbalance happen in the very early twenty-four hours of thesolar system , which makes it backbreaking to specify the exact causal agency .
But in a new study published Dec. 27 , 2024 , in the journalGeophysical Research Letters , researchers analyzed data fromNASA ’s InSight lander , which records how seismic wave from marsquakes reverberate within the planet , to see if they could find any evidence of an interior origin for the Martian duality .
InSight is located near the perimeter between the northern lowlands and the southerly highlands , which allowed the squad to equate how seismic waves moved through the mantel below two sites : one on each side of the water parting .

Martian dichotomy has been one of the biggest mysteries surrounding the Red Planet over the past 50 years.
Related:10 amazing things we line up on Mars in 2024
" compare these two [ site ] designate that the wave lost energy more quickly in the southerly upland , " the study author write inThe Conversation . " The most likely explanation is that the [ molten ] rock ‘n’ roll beneath the southern highlands is hot than in the N . "
" This temperature difference between the two one-half of the dichotomy supports the idea that the split was induce by internal force on Mars , not some external impact , " they sum .

Internal origin vs. external impact
The study team thinks this temperature deviation can be explain by ancient architectonic activity that has since disappeared from Mars .
" At one point , Mars had movingtectonic plateslike Earth does , " the researchers write . " The movement of these collection plate and the molten rock beneath them could have created something like the duality , which was then immobilise in office when the architectonic plates stopped moving to form what scientists call a " stagnant eyelid " on the planet ’s liquefied interior . "
In this scenario , the magma beneath the South is constantly being press up against the crust , while the magma below the North is go down toward the planet ’s core . This would also explain why the major planet ’s crust is stocky in the South , the researcher bring .

— Giant ' kidney bean ' spotted in Mars satellite image could orient to signs of water and aliveness
— unearthly ' zebra rock music ' on Mars is unlike anything seen before on Red Planet , NASA says
— Ancient volcanic ash tree on Mars could volunteer new clue in lookup for extraterrestrial life

However , it may be too other to prevail out the external impact scenario , which somerecent studieshave shown to be potentially feasible .
" To conclusively serve the question of what cause the Martian dichotomy , we will need more marsquake information , as well as detailed models of how Mars formed , " the researchers compose . " However , our discipline uncover an important fresh objet d’art of the puzzle . "