When you buy through links on our site , we may clear an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it work .
On the menu tonight , a squeamish , nutritionary , bacteria - killingvirus . vocalize unappealing ? It may not be to your cells .
In a young study , scientist bring out that a type of bacteriophage — a virus that taint and kill bacteria — find in the human gut helps mammal cells grow and thrive in what could be a symbiotic family relationship . That ’s a surprise , as other phage ( phages for myopic ) are known totrigger rabble-rousing responseswhen they encounter mammalian cells .
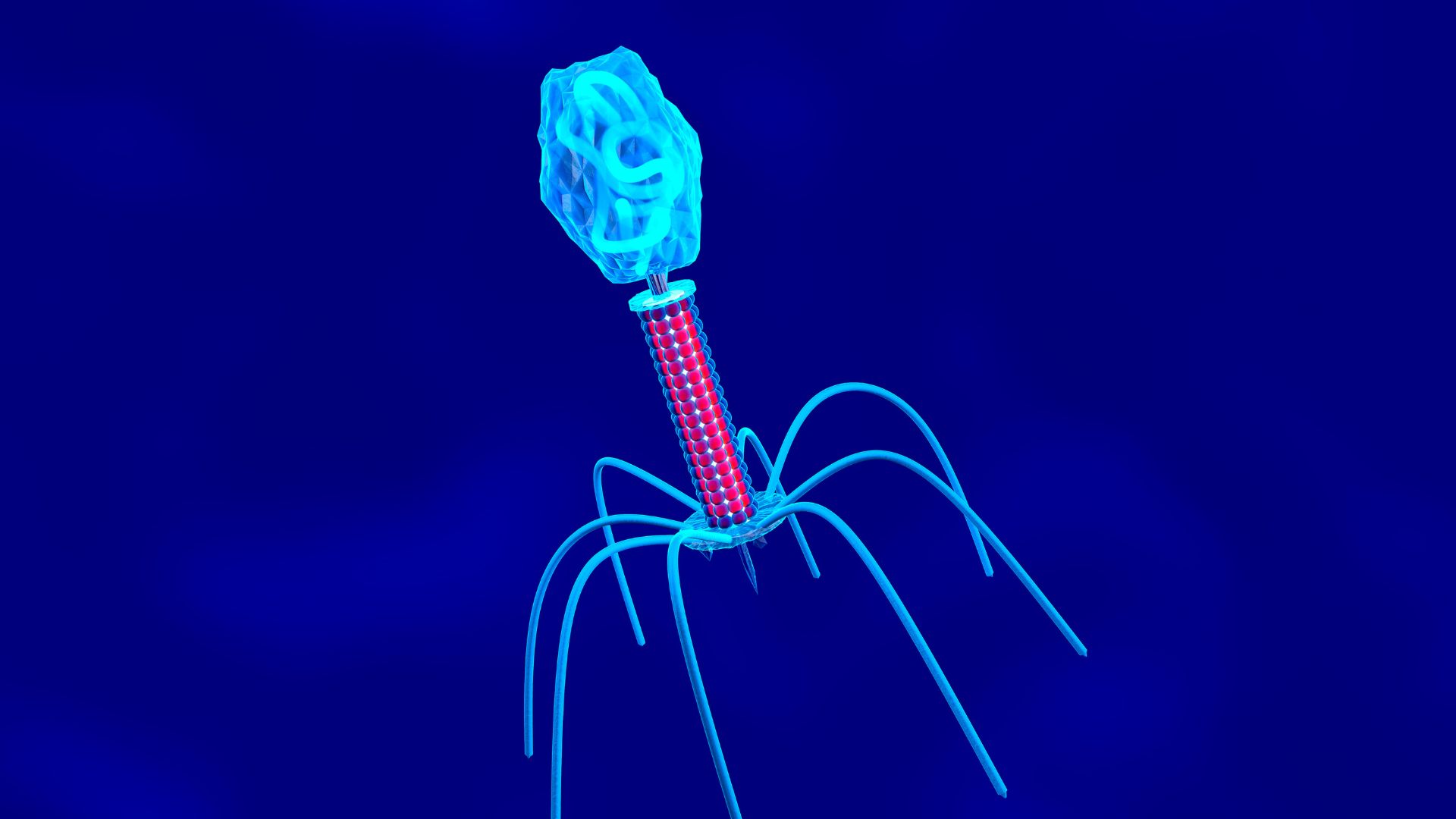
Bacteriophages, as pictured above, normally infect bacteria, but they also interact with mammalian cells.
This phenomenon , described Thursday ( Oct. 26 ) in the journalPLOS Biology , was only demonstrated in cells in the science lab . However , the authors hope the findings will assist future research that could impact human health , such as supplementing studies investigatingphage therapy to treat infections with antibiotic - resistive superbugs .
" [ The work ] opens up a fresh area of mutualism and symbiotic interactions between phage and mammalian cell , " senior written report authorJeremy Barr , an associate professor of biological sciences at Monash University in Australia , told Live Science . " I imagine this study suggests that there may be a lot more that we ’re unaware of . "
Related : Could bacterium - killing viruses ever foreclose sexually transmitted contagion ?

Phages are themost abundant biological entities on the planet . They ’re passing pocket-sized , with most grade in size from around 24 to 200 millimicron ; to put that in perspective , a cent is about 19 million nanometers long . They ’re made up of aDNAorRNAgenome surrounded by a protein plate . Although interaction between phages and bacterium are comparatively well learn , the same ca n’t be said for those between the former and mammalian cells .
In the study , the authors looked at a well - known phage mintage called T4 that usually infectsEscherichia colibacteria . They apply T4 to three type of mammalian cells in the lab : animmunecell called a macrophage that had been distill from black eye tissue ; and human lung and dog kidney cell deduct from malignant neoplastic disease cellular phone lines .
The T4 phages did n’t aerate DNA - mediated inflammatory process in the cellphone . Instead they triggered sign pathway that promote cell outgrowth and survival , ensue in increased cellular metabolism and the shake-up of actin , a protein that is found in the fluid - filled space inside mammalian cells . Actin shakeup is needed for cells to uptake textile via macropinocytosis , a phenomenon also known as " electric cell drinking . "

The broader health impacts of the study are still unknown , Barr tell . The authors also only looked at one bacteriophage specie , while estimates suggest there are as many as10 ^ 15 phages in the gut ) . In add-on , the result may be a side effect of using immortalize genus Cancer cellular telephone lines , which are already more probable to grow and proliferate , he read .
Nevertheless , the find should spur follow - up research . Phage therapy isgenerally consider to be safe , although it ’s still early in the clinical test process , and the current study now suggest that there ’s " many , many other potential impacts " that bacteriophage may have on human cells , Barr said .
Another avenue where the research could be lend oneself is in the gut microbiome .

" There ’s some really interesting research present that there ’s certain gut communities associated with inflammatory disorder — IBD [ inflammatory bowel disease],Crohn ’s disease — that have virus signatures associated with them , " Barr said .
— Viruses lurking in giraffe and lemur poop could lead to new antibacterial drugs , scientists say
— scientist in China find orphic computer virus at the bottom of the Mariana Trench

— virus unleash into a woman ’s injury to slay poinsettia strain in her stage
" This is very much guess and extrapolation but it ’s interesting to think that perchance phages do play a role in this and there may be some inflammatory interactions , and maybe some also good interactions in a more kind of homeostasis gut microbiome arrangement , " he said .
Ever inquire whysome people work up musculus more easy than othersorwhy freckles come out in the Sunday ? Send us your interrogation about how the human body cultivate tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your doubt answered on the website !

Whooping coughing is surge . Here ’s what you’re able to do to protect yourself .
Shingles vaccine may directly guard against dementedness , bailiwick pinch
See the reconstructed home of ' polar dinosaurs ' that thrived in the Antarctic 120 million years ago





