When you buy through nexus on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists have captured magnetic signatures from Earth ’s sea tides in the finest detail yet .
These faint signals , which sure satellites can discover when flying at very lowly orbits , may hold clues about magma distribution beneath the seabed , according to astatementfrom theEuropean Space Agency(ESA ) .
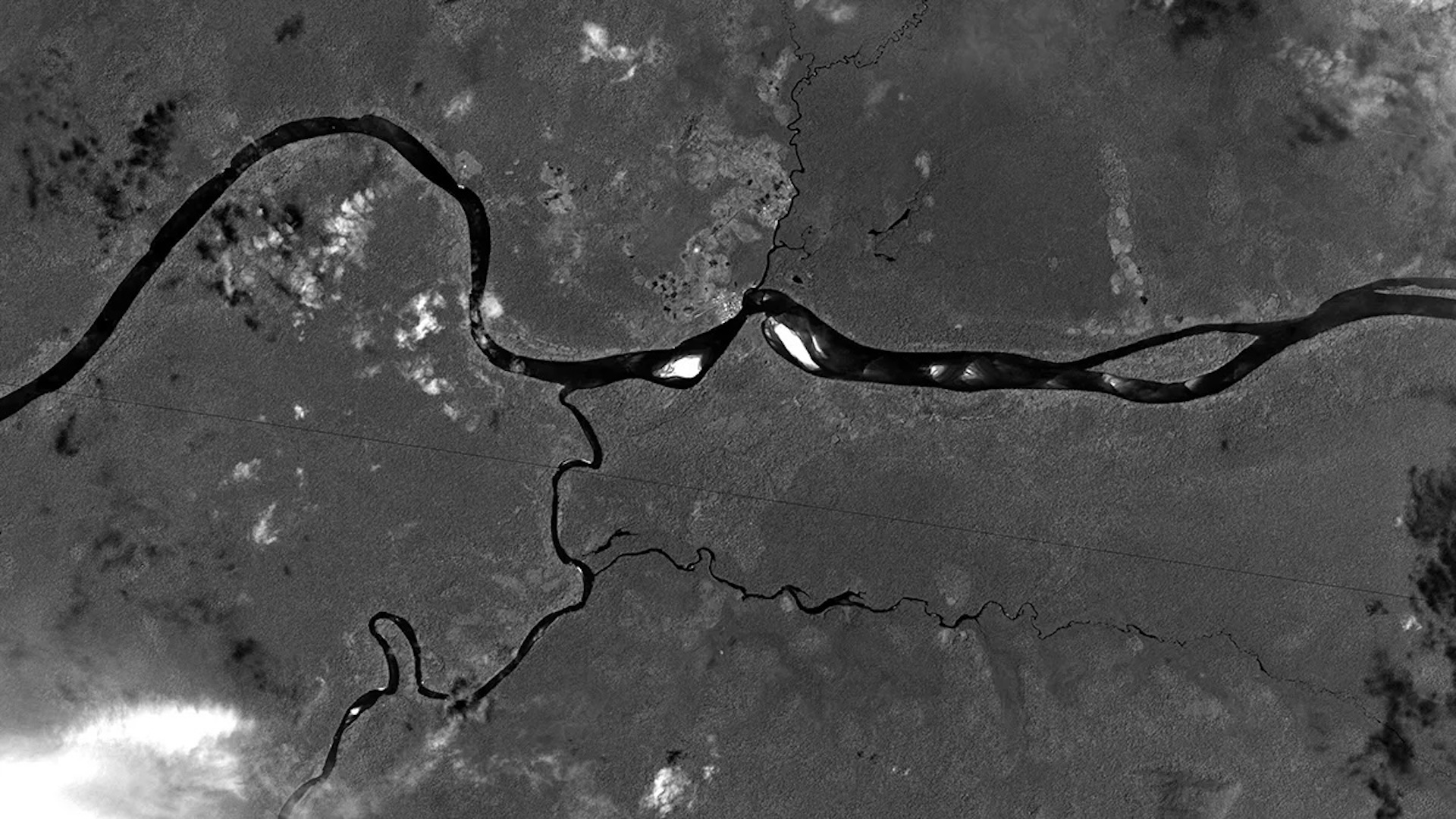
Satellites orbiting Earth have detected faint magnetic signatures resulting from ocean tides.
As seawater wavelet over our planet ’s magnetized subject area , it generates weak electric flow that in turn produce magnetic signal perceptible from distance . In a new study , published Dec. 2 , 2024 in the journalPhilosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A , researcher decipher these signals using data from ESA ’s ongoing Swarm charge , which constitute three satellites that measureEarth ’s magnetic bailiwick .
" These are among the smallest signals notice by the Swarm mission so far , " sketch lead authorAlexander Grayver , a geophysist and older lecturer at the University of Cologne in Germany , said in the statement .
Earth ’s magnetic field of operations results from a purl ocean of electrically charge molten branding iron in the planet ’s outer core . heating system currents and Earth ’s spin both fuel the movement of this fluid iron . The core group ’s movement make agiant , bipolar envelopethat extend into space , shield us from cosmic radiation and charged particles emitted by the sun .

Related : Listen to haunting sound of Earth ’s magnetic field flipping 41,000 year ago in eery new spiritedness
Swarm launch in 2013 and has been collecting selective information about Earth ’s magnetic field ever since . But cleared signals created by ocean tides are unmanageable to obtain , because they are so faint they hardly ever kick downstairs through the widespread " noise " in space , according to the statement .
In the late 2010s , several factors adjust that enable Swarm to record the magnetised signatures of sea tide in unprecedented detail . One of these agent was a spectacular reduction in the sunshine ’s activeness , and another was the closeness of Swarm satellites to Earth .

" The data are peculiarly good because they were gathered during a period of solar lower limit , when there was less noise due to space weather , " Grayver said .
The sun keep up a approximately 11 - twelvemonth cycle that prescribe the level of action at its surface . At thesolar maximum , the Dominicus emit Brobdingnagian waves of electromagnetic radiation and charged particles that obscure measurements of magnetic signals from Earth . Activity dies down during the solar minimum , making it easier for satellites to peck up these signals .
— ' A force more sinewy than gravity within the world ' : How magnetism locked itself inside our planet

— The position of the charismatic north pole is officially modify . Why ?
— Earth ’s magnetic field of view formed before the planet ’s Congress of Racial Equality , study suggests
ESA initially design to end the Swarm mission in 2017 , but its valuable consequence prompted the way to stretch forth it . Over the years , drag has pulled the satellite closer to Earth , enabling the instrument on board to pick up faint signal that they could not have detected in their original , higher cranial orbit .

" This is one of the benefits of flying mission for longer than originally planned , Anja Strømme , ESA ’s Swarm missionary post manager , pronounce in the statement . " you could tackle scientific interrogative sentence that were n’t in the first place envisaged . "
The new study shows that satellite can peer through the depths of Earth ’s oceans and extract utile information , Strømme said .
drove could stay operational until 2030 , when the next solar lower limit is due . scientist hope that this will leave another rare opportunity to discover secret ocean signal .













