When you buy through links on our web site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Archaeologists have unearthed a Roman wind bell call a tintinnabulum — feature a prominent genus Phallus — at an archaeological website in eastern Serbia .
Such objects , which were hung near the doorways of houses and shops , were conceive to service as magical protection for the premiss . This one was come upon on the porch of a enceinte domicile on a main street in Viminacium , an ancient Roman city , the blanket ruination of which now lie near the Serbian town of Kostolac , about 30 miles ( 50 kilometre ) east of Belgrade .
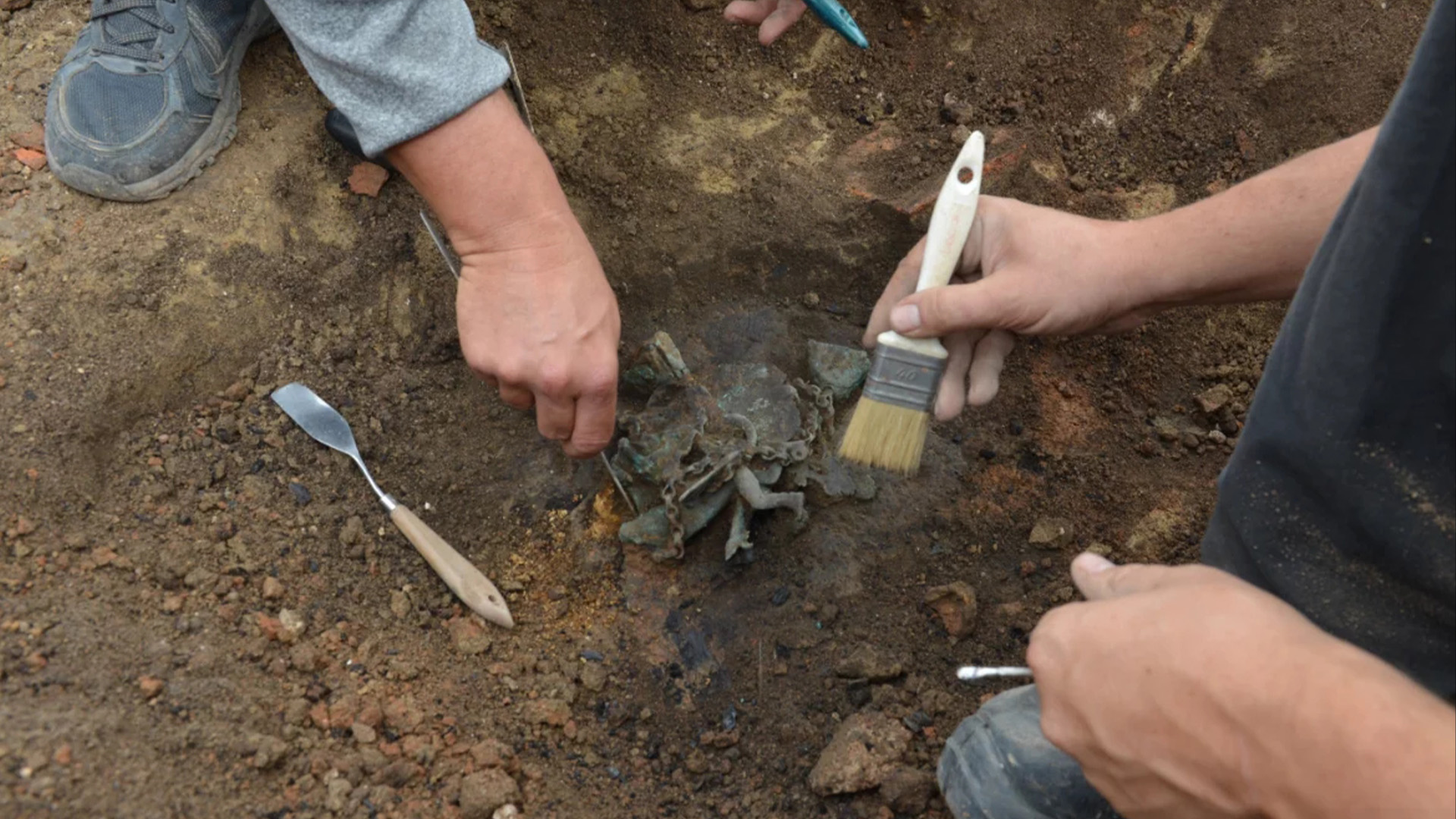

The “tintinnabulum” wind chime was found In debris from a large home in the ruins of the civilian city at the vast Viminacium archaeological site in the east of Serbia.
" The edifice was put down in a fire , during which the porch collapsed and pass to the ground,“Ilija Danković , an archeologist at the Institute of Archaeology in Belgrade , narrate the Serbian - linguistic communication website Sve o arheologiji .
Tintinnabulums were plan to take in the wind , supposedly so their randomness and strange visual aspect would frighten off evil spirit and ward off thecurse of the evil middle , which was greatly feared in antiquity .
Viminaciumwas the civil and military capital of Rome ’s Upper Moesia province from the first to fifth 100 , until it was sack by the Huns underAttilain 441 . The city was rebuilt under the Byzantine emperor Justinian , but it was in conclusion destroyed by invading Slavs in about 535 .
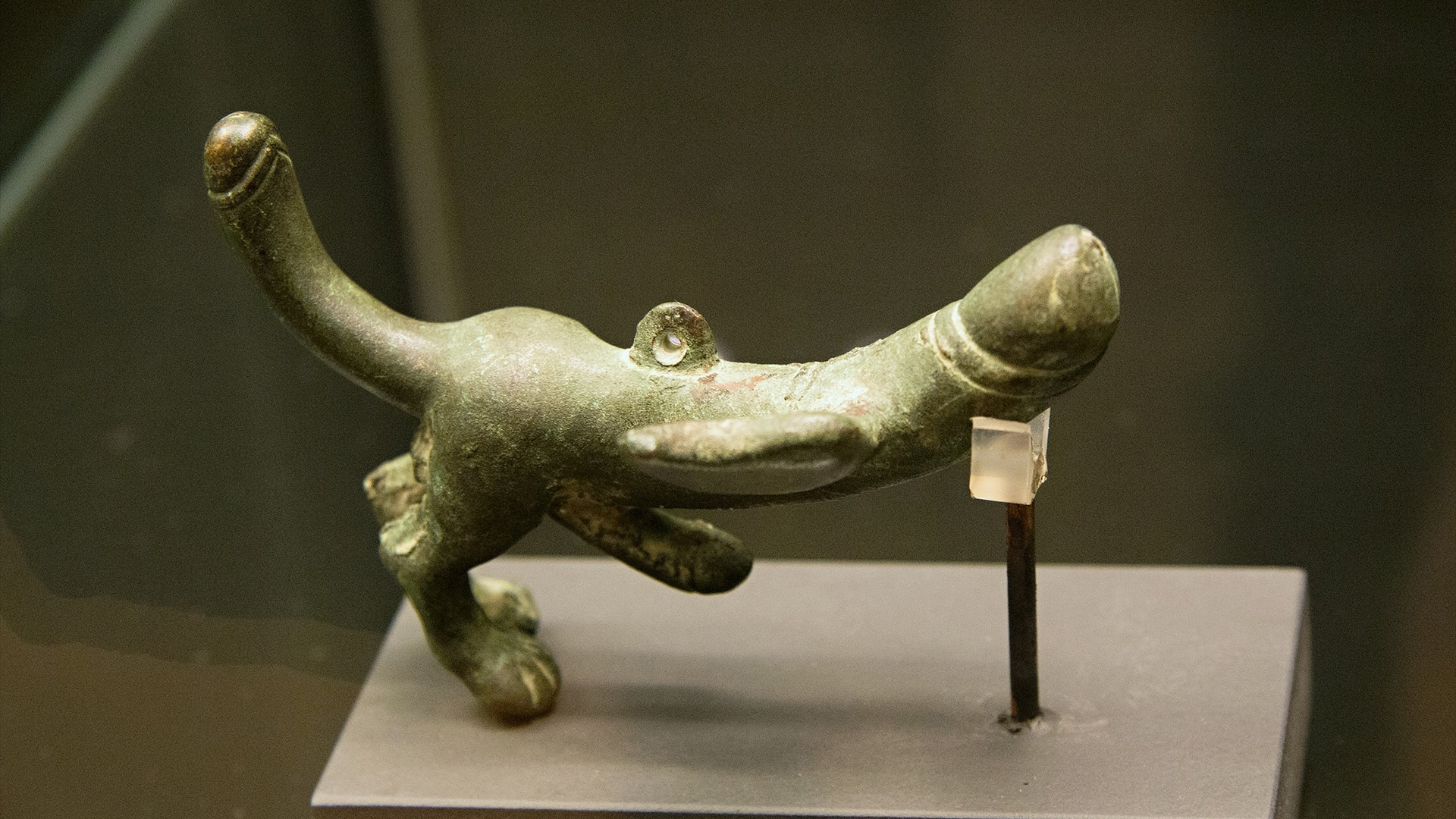

Tintinnabulums usually featured phalluses, which were a symbol of good luck for the Romans. This tintinnabulum of a phallus with wings and legs was found at Prague.
Magical phallus
This is the second tintinnabulum find in the ruin , Danković told Live Science . The first is now in a individual collection in Austria ; nothing is make love about its discovery , he said .
However , the newly discovered tintinnabulum was unwrap in its full archaeological context . " As before long as we started expose it , we know immediately what we had notice , " he enounce .
The latest tintinnabulum from Viminacium is made of bronze , but it is being kept surround by soil until it can be properly restored . As a result , its exact contour is n’t known . But it is centered on a " fascinum " — a portrayal of a magical penis — with two legs , wings and a tail , he said .
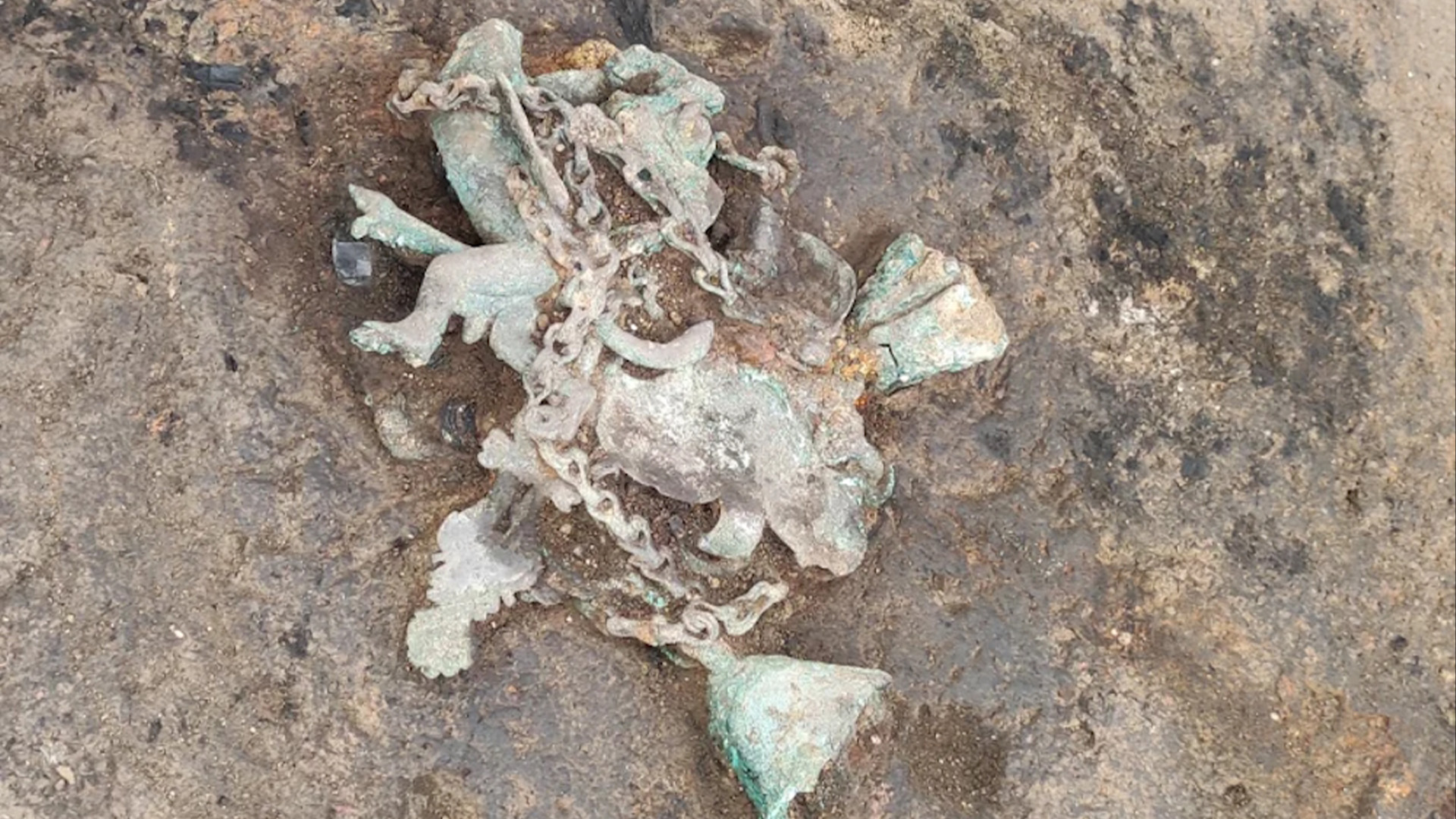

Like many tintinnabulums, this one featured a portrayal of an outsized phallus with wings and legs. They were supposed to frighten off evil spirits with their unusual appearance and the noise they made in the wind.
" pronounce by what can be seen … it had four bells and the chain from which it cling , " Danković said , adding that there also seemed to be other elements to the innovation not seen on other tintinnabulums .
Roman beliefs
The symbolisation of a genus Phallus was n’t always erotic or obscene for the ancient Romans , Danković allege . " It was a bringer of adept fortune and happiness , and an efficient weapon system to combat the evil eye , " he say . " For this reasonableness , penis can be seen everywhere in the Romanic world , from wine cup to the amulets worn by children . "
He add that the symbol was often publicly displayed to muster prosperity and discourage thief .
The discovery of the tintinnabulum is evidence that Viminacium was " in every good sense a part of the Roman world , " Danković aver .
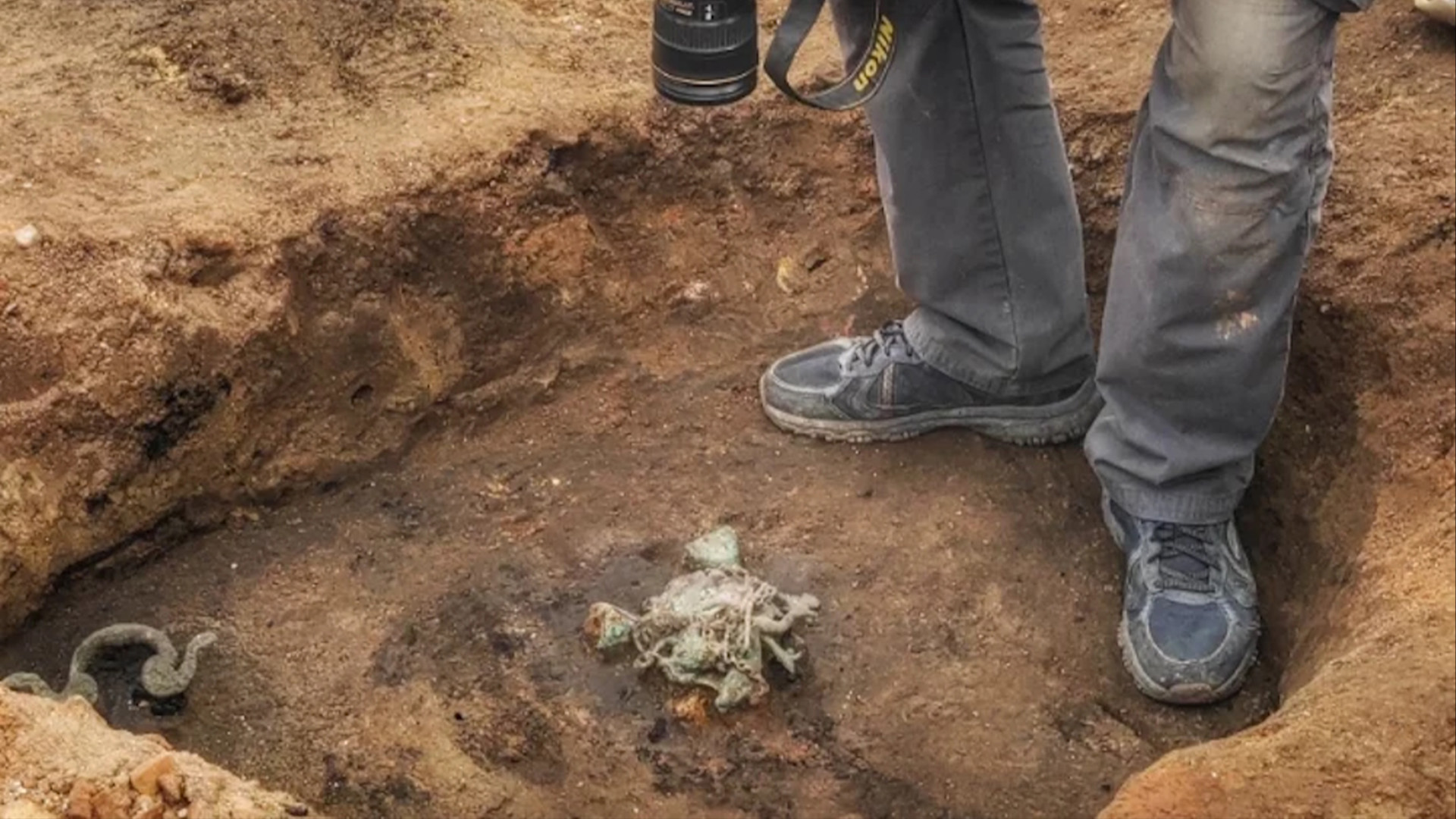

Archaeologists say the discovery of the tintinnabulum at Viminacium shows the social elites of the provincial city shared the same beliefs as people in the heart of the empire in Rome and had money to spend on imported objects.
Not only did its hoi polloi share many papist beliefs , he enjoin , but it ’s potential that the tintinnabulum was import from elsewhere in the empire , showing that there were social elite at Viminacium who were willing to pay off a substantial amount of money for such an aim .
— Battered Roman - era skull with sign of the zodiac of violent trauma and a possible brain tumor unearthed in Spain
— Rare 2,100 - year - one-time aureate coin bear name of dark ruler from pre - papistical Britain
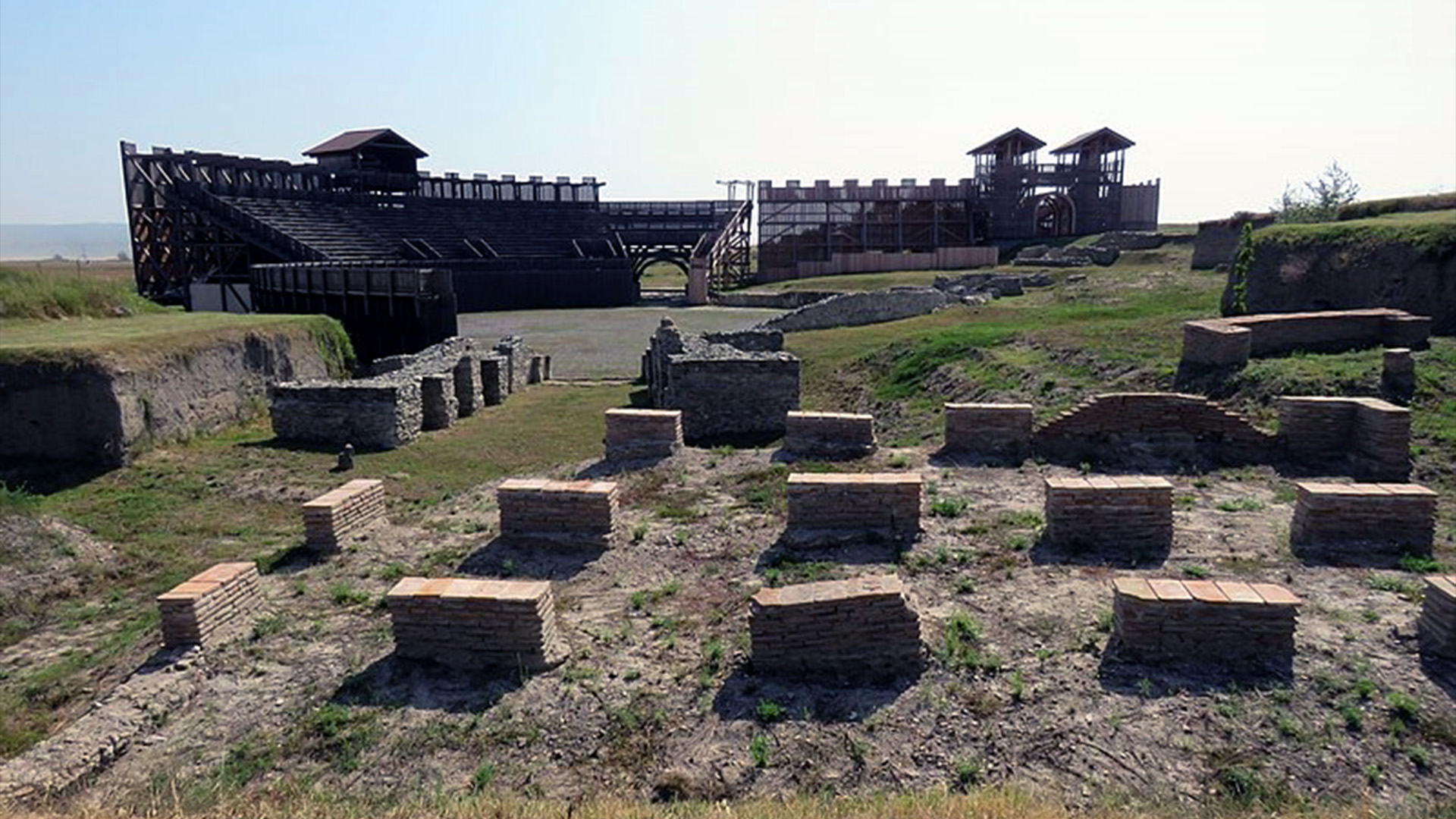

Viminacium was the military and civil capital of the Roman province of Upper Moesia from the first until the fifth centuries, when it was destroyed by invading Slavs. It is now one of the most important Roman sites in Europe.
— 2,000 - year - old decorated R.C. sandal unearthed in Spain
Ken Dark , an archaeologist and historian at King ’s College London who was n’t involve in the breakthrough , said the Viminacium tintinnabulum was a type of " apotropaic " amulet that was design to ward off evil influences and give protection to citizenry or their property .
Such talisman " were vernacular in the Roman humans , and these sometimes took forms which would seem very strange — or even amusing — to us today , " he say Live Science in an e-mail .
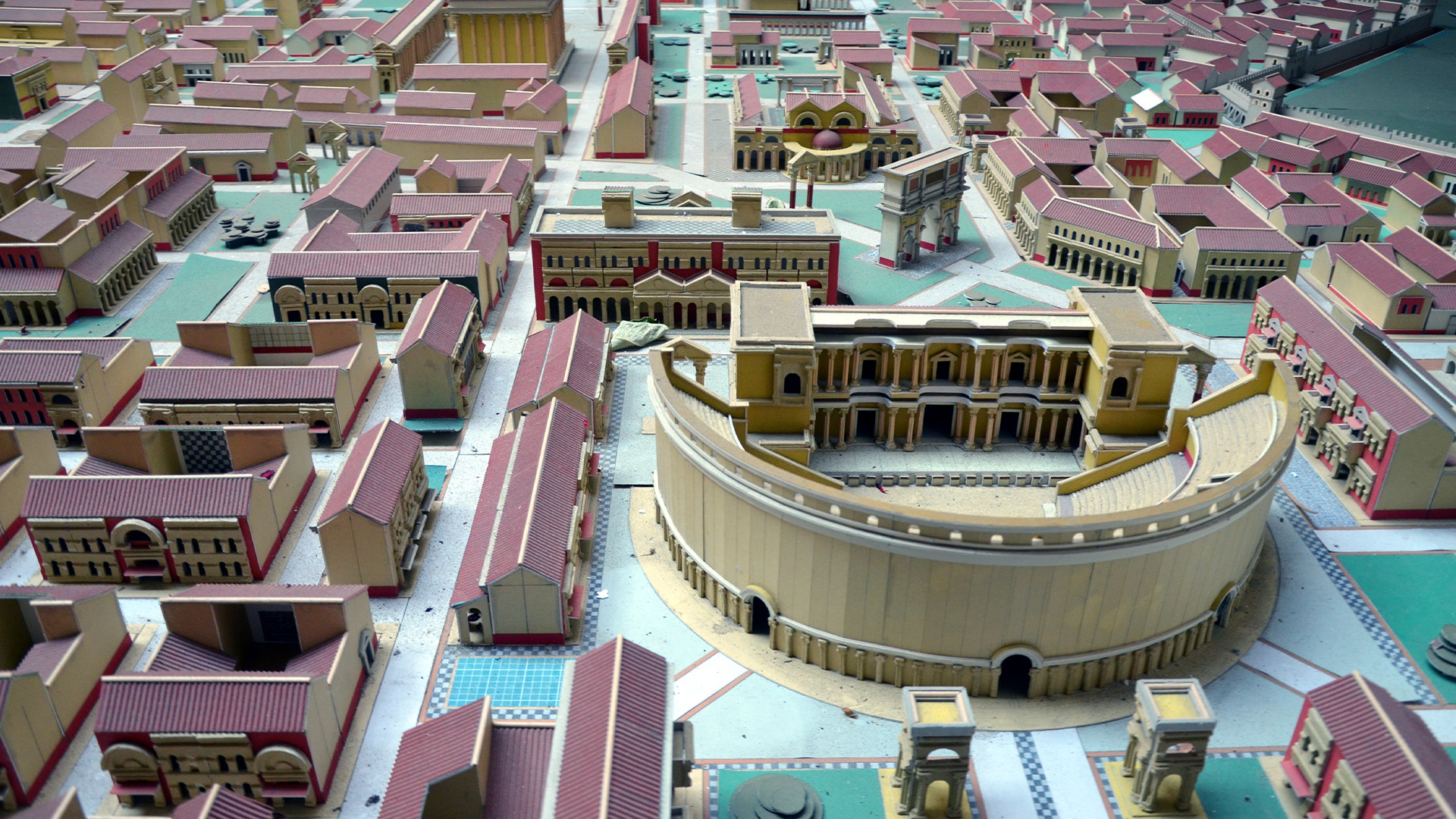
At its height, Viminacium was home to up to 40,000 people, including legions of the Roman Army. This model at the site shows how it looked after the third century A.D., with an amphitheater, temples, public baths and other buildings.
2,000 - year - onetime bed roadblock unearth in Pompeii house — likely a family ’s last effort to break loose Vesuvius ' eructation
1,800 - class - erstwhile warhorse cemetery view as remains of a beloved knight — and a man considered an ' foreigner ' to popish society
The invariant surveillance of modern spirit could worsen our brain function in way we do n’t fully understand , disturbing study advise









