When you buy through linkup on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Earth ’s electron orbit is clogged with all kind ofspace junk : defunct satellites , pieces of space vehicle , and even maculation of paint from these human - made technologies .
Now , a novel method acting show hope for track the smallest bits of space bedding material , down to about the sizing of a piece of pencil confidential information — and it relies on " lighting - same energy burst " that can be observe from the ground when multiple objet d’art of space junk collide , according to the research worker . The new inquiry was lay out Dec. 5 at the Second International Orbital Debris Conference in Sugar Land , Texas .

A computer-generated image of trackable objects in low Earth orbit. Each dot represents an object, and around 95% of them are debris. The trackable objects are already beginning to form a cloud of debris around Earth, but there are millions of smaller pieces that can’t be tracked from the ground.
Eventiny bits of space rubble can cause unbelievable equipment casualty . TheInternational Space Station(ISS ) fudge a large part of space litter about once a twelvemonth , accord toNASA . Space agencies presently track orbital detritus using ground - establish radar , but piece under 3 millimeters ( about 0.12 inch ) ca n’t be discover by these methods . That intend about 99 % of space debris ca n’t be tracked from Earth — leaving the ISS and other operable ballistic capsule vulnerable to possible collisions .
" Right now , we detect outer space detritus by looking for objects that think over Christ Within or radar signals,“Nilton Renno , a professor of climate and space scientific discipline and engineering and aerospace engineering science at the University of Michigan who lead the new study , tell in a argument . " The pocket-size the object get , the harder it becomes to get sun or radar signals strong enough to detect them from the primer coat . "
Related : Sci - fi inspired tractor beams are existent , and could solve a major space junk problem
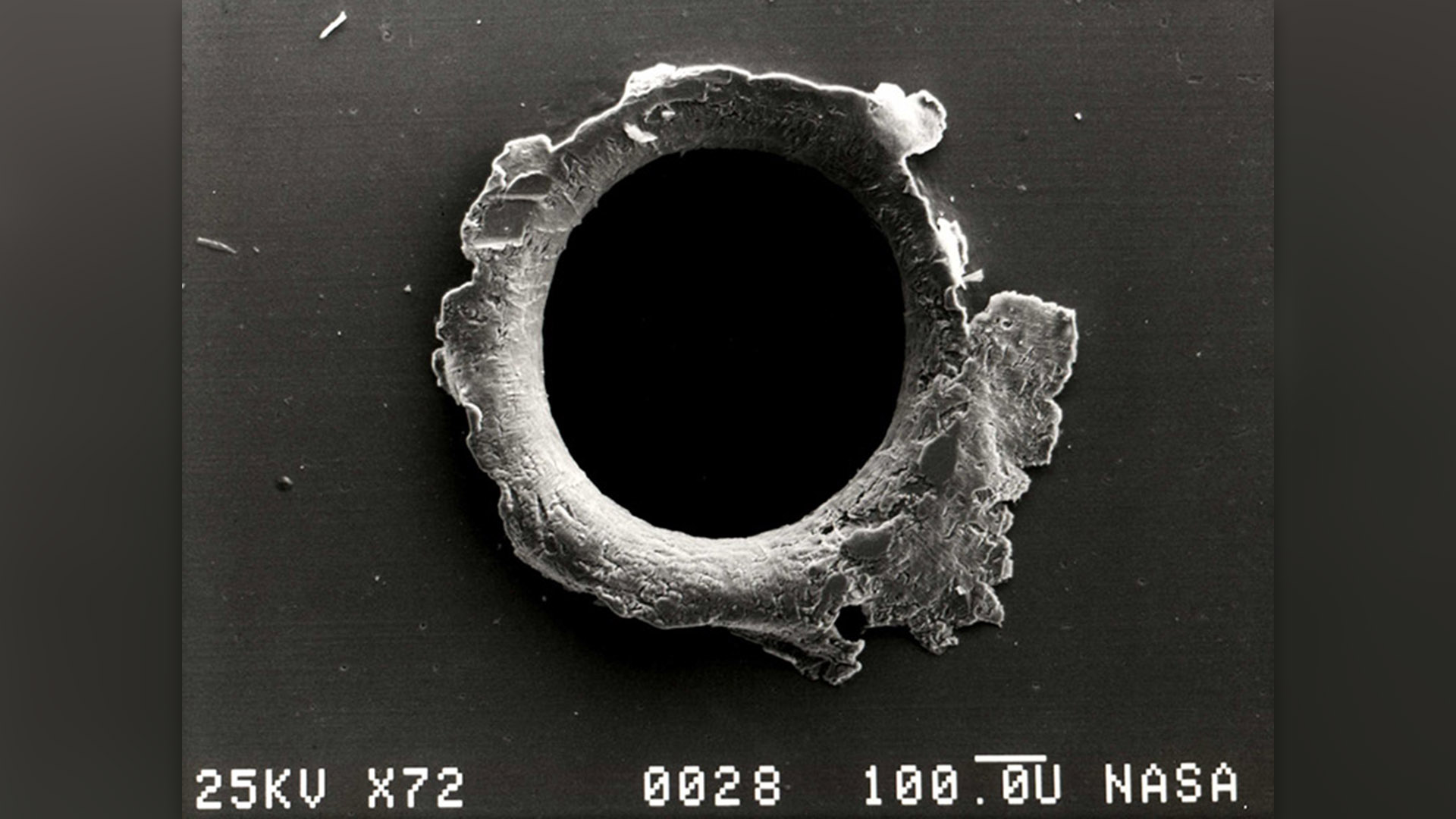
A piece of space junk punched this hole into the hull of NASA’s Solar Max spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA Orbital Debris Program Office.
Renno and Yun Zhang , a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Michigan , rein in the power of the hit between petite pieces of debris to dog the petite fragment of distance junk . harmonise toNASA , the middling collision speed between pieces of space rubble is 22,370 mph ( 10 kilometers per second ) and can make 33,554 mph ( 15 km / s ) .
Because of this dizzying speed , even collisions between crumbs of debris expect a lot of energy . Upon impact , helping of the detritus are vaporized into charge gas , unloosen bursts ofelectromagnetic radiation therapy . These electromagnetic pulses can be notice by 85 - animal foot - diam ( 26 meters ) ground - base satellite saucer , which are plebeian in arrays around the world , Zhang and Renno reported .
More sensitive transmitting aerial , such as those in NASA ’s Deep Space internet , should be able to detect these orbital collisions as well , according to the researchers . The sketch was conducted with computer simulations , so more work is needed using actual data from Earth orbit .

— US government issues 1st - ever space dust fine , excite artificial satellite TV company whopping $ 150k
— Falling alloy space debris is changing Earth ’s upper aura in ways we do n’t fully see
— Sci - fi inspire tractor beam are material , and could resolve a major space rubble job

ground - bound experiments at theU.S. Naval Research LaboratoryandNASA ’s Ames Research Centercan collide materials at orbital speeds and measure the electromagnetic outcomes , and those data could help the research team expend these electric impulse to determine what type of junk is being observed , concord to study co - leaderMojtaba Akhavan - Tafti , an assistant inquiry scientist in climate and outer space sciences and engineering at the University of Michigan .
" We need to lie with if an object is surd or sonant because that will impact how it orb and how detrimental it can be , " Akhavan - Tafti said in the statement . Knowing this in advancement may allow vulnerable ballistic capsule to divert their course away from the junk , if necessary .