risk lurks behind every corner on the vane : phishing , fake Websites , stolen digital identities — it ’s all mighty there on the cyberspace , waiting for unwary exploiter to lower their guard and be take for a ride .
Despite the cottage industry that has sprouted up with the exclusive purpose of protect us from the evil of New living , all it take to relish a secure relationship with the Digital Age is nothing more than the lowly onetime web browser app , coupled with a spot of knowledge about the way the Web works . Let ’s take a look at the basic security feature article used by most Web browsers . understand how these features work can make the Web a little safer .
Learn how to protect your privacy when using your internet browser
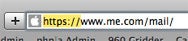
Secure Websites have address that start with “https://”.
A matter of trust
A normal connection between a web internet browser and a site engage place completely “ in the decipherable , ” with all the information get over — unchanged and unprotected — the various nodes that make up the Internet , until the data turn over its destine receiver . Obviously , this is no way to conduct a transaction that involves any form of individual information — be it your quotation wit bit , revenue enhancement data point , or even just the password to your Twitter account statement .
For these design , Websites trust instead on asecureconnection , which establishes trust between your web browser and the waiter to which it talks . good connections , which are name by the use of the “ https ” prefix in the Website ’s savoir-faire , postulate two factor : privacy and identification .
good Websites have speech that start with “ https:// ” .
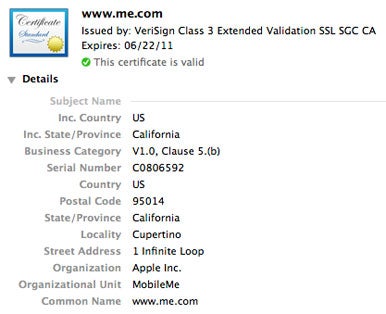
Clicking on Safari’s lock icon displays information about the owner of a digital certificate—the perfect to check that you’re not falling prey to an imitator.
Privacy is guaranteed by means ofencryption : browser app and server agree on a way to transfer data point in a way that makes the data point look like gibber to everyone else . This manner , there is no way for someone who happens upon the datum interchange to gain access to any selective information that you do not need to share .
A private conversation , however , is not secure unless you also lie with who you ’re talking to — and this is where recognition comes into dramatic play . Browsers rely on a tool known as adigital certificateto square up that the Website ’s destination is being used by its rightful proprietor . Digital certificates , in turn , are issued by so - calledcertificate authorities , which typically do so after corroborate sure aspects of a business , like its legal condition , internalization papers , domain ownership , and so on .
It ’s important to translate that have a digital credential does n’t automatically make a Website safe . It just mean that the entanglement computer address you ’re call is being operated by the entity that owns it .
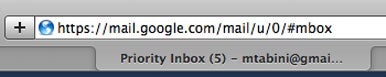
Because e-mail is often used to reset the password of other services, it’s a good idea to use a secure a connection when visiting web apps that, like GMail, support one.
This note is essential , because the web browser app ’s ability to allow a strong environs is merely a technical one ; for obvious reasons , it can not make judgment call — which means that you’re able to not look wholly on your browser app to ascertain whether a web site that is good is also safe .
How browsers help us
select Safari ’s ringlet icon expose information about the owner of a digital certificate — the perfect to check that you ’re not light quarry to an emulator .
Nonetheless , the process of establishing a dependable connexion gives us several utile tools to check that that we are not about to fall target to an net cozenage . The first one is simply watching for warnings : if the browser app complains about some possible security measure issue , it ’s always a sound idea to give attention and essay to figure out what has happened .
Typically , however , the internet browser will only actively complain under very specific circumstances — for example , if the digital certificate used by a Website is invalid , or has expired . Under normal conditions , the visual cues that distinguish secure and insecure connection are much subtler , which intend that you must actively reckon for them .

Safari displays the owner’s name of Websites that use an Extended Validation Certificate in green on the address bar.
Therefore , the exclusive and most of import thing that you may do to protect yourself from chiseler is to discover when you should ask a secure connection ; these include some obvious scenario , such as when you ’re doing your banking , or when you are on the payment page of an e - commerce store , but even other activities that one would n’t normally consider crucial , like accessing an online e - mail organisation such as GMail .
Most browser app have some other variety of visual indicant that a connectedness is secure ; Safari , for example , exhibit a curl in the top - right corner of its window . If you select the lock , the browser app pops open up a dialogue corner that shows who the owner of the digital certificate is , give you an extra opportunity to ensure that you are , indeed , visiting the veracious place .
Because e - mail is often used to readjust the password of other services , it ’s a good idea to use a strong a connectedness when bring down web apps that , like GMail , support one .
Ultimate protection
alas , scammers have gotten quite skillful at play tricks even the most heedful users by choosing addresses that are only subtly different from the existent affair . Nobody would consider a banking website whose address is “ www.joesfishmart.com , ” but even the good can be fox into trusting a arena like “ yourb4nk.com , ” or “ your-bank.com . ” And , while watch the information confiscate to the digital certificate will tell you who you ’re dealing with , it ’s not always a hard-nosed thing to do .
To whelm this problem , some Websites use what is known as anExtended Validation Certificate , which is only issued if a tight solidification of establishment criterion are met . When they encounter one of these certificates , most web web browser will volunteer additional ocular cues — in Safari ’s case , you will see name of the site ’s owner come along in green inside the address bar .
Safari displays the possessor ’s name of Websites that use an Extended Validation Certificate in green on the address saloon .
As you may see , the security of WWW pages is a complicated — and sometimes mussy — function . A little aid and some unsubdivided tricks , however , can go a long agency towards providing a safe surf experience without the penury for any especial ( and often expensive ) package — except , that is your old , close internet browser .
[ Frequent Macworld contributor Marco Tabini is based in Toronto and can be found on Twitter as@mtabini . ]