When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may take in an affiliate delegacy . Here ’s how it works .
For the first fourth dimension , scientist have created detailed maps of immune mobile phone in the placenta , showing how the cells defend the foetus from invaders during early pregnancy .
Such infections canlead to serious complications , such as gestation going and preterm parturition , so this knowledge could someday be used to grow treatments that halt these problems from arising , the research worker order .
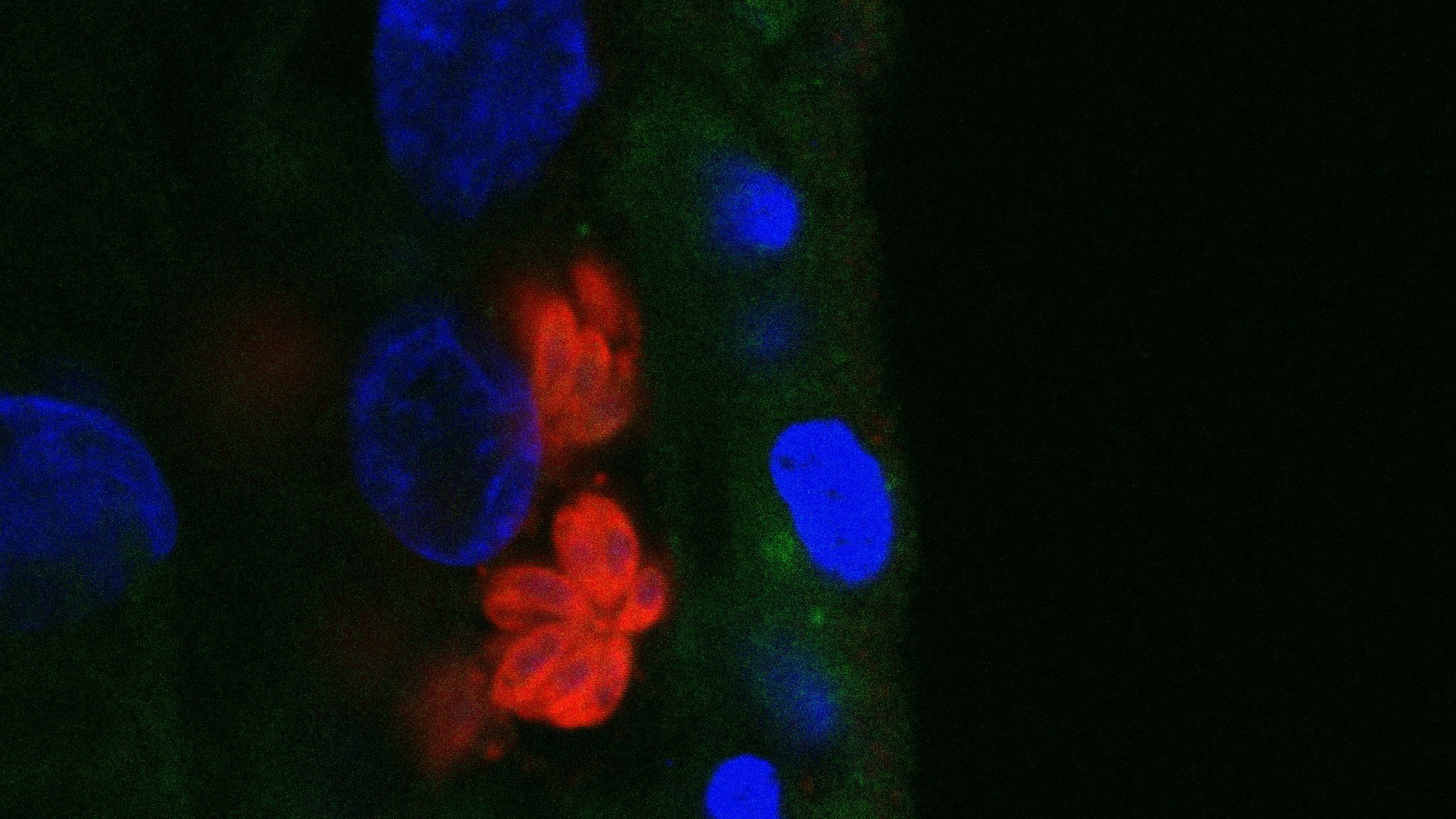
The new placenta model shows how immune cells in the placenta respond to infection from three major types of pathogens. For instance, the parasite that causes toxoplasmosis (red) can be seen infiltrating the nuclei of placental cells (in blue) in the microscope image above.
To create these maps , the researcher used " mini - placentas " arise from 0.15 square inches ( 1 square centimeter ) of placental tissue donate by women who were aroundsix to 14 weeks pregnantat the clock time . These flyspeck version of the placenta were cultured in the research lab using growth - inducing chemicals .
The scientists used the placentas to investigate how three major pathogens infect the electronic organ : the parasitesPlasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii , which causemalariaandtoxoplasmosis , respectively ; andListeria monocytogenes , a bacterium responsible for an infection calledlisteriosis .
Related:‘Mini placenta ' may discover roots of gestation disorders like preeclampsia

The placenta acts as aselective barrierbetween the female parent and develop fetus during pregnancy , meaning it lets some center , such as nutrients , through while blocking others , such as harmful germ and toxins . This is important , as during the early degree of pregnancy the fetus ' resistant system isonly just begin to mature .
However , T. gondiiandL. monocytogenescansneakily crossthe placenta , whileP. falciparumcanattach to it . Scientists still do n’t fully sympathize how these infections finally lead to pregnancy complication , the researchers write in a study published Friday ( May 3 ) in the journalCell Systems .
" While infection during pregnancy have been known to do complications , include miscarriage and stillbirth , very little has been known about the underlie mechanisms,“Regina Hoo , lead study author and a postdoctoral fellow at the Wellcome Sanger Institute in the U.K. , said in astatement .

That ’s where the miniature placentas make out in — they leave a window into early gestation that would otherwise be very difficult to take note .
Using their placenta models , Hoo and colleagues mapped how the organ responds to infection withT. gondii , L. monocytogenes and P. falciparumat the horizontal surface of individual cells . They divulge that resistant cells calledHofbauer cells — fetal versions of pathogen - gobble cells calledmacrophagesseen in adults — activate in reply to all three infections . However , different molecular switches jell them off .
All three pathogen can also infect Hofbauer cells , the team found . For example , T. gondiican hide in them as a path to evade the immune system and travel around the foetus ' body .

Across the circuit board , the infections triggered inflaming in the placenta that disrupted of import functions , such as communication between cellular phone . This implies that some pregnancy ramification could be a knock - on event of this inflammatory response , the team reported .
" Infections during maternity can have devastating encroachment , and there are circumscribed pregnancy - specific handling options that can help,“Roser Vento - Tormo , co - fourth-year study source and a group loss leader in cellular genetics at the Wellcome Sanger Institute , said in the argument .
— ' Zombie cells ' in the placenta may cause heart nonstarter in gestation

— ' reed organ - on - chip ' shows how womb sweet-talk conceptus to implant in early gestation
— How COVID-19 might affect a pregnant fair sex ’s placenta
Although an resistant response is still " essential " to combat infection , the writer suggest that new drugs could theoretically be developed to quell this uncontrolledinflammationand thus forbid to-do in fetal maturation .
By charting a extremely detailed atlas vertebra of the immune organization of the early placenta , " we hope that our research can be used by the research community worldwide to help rise young ways to understand and handle gestation complications that impact billion of lives every yr , " Vento - Tormo said .
Ever wonder whysome people build muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckle add up out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human torso works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject argumentation " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answer on the website !