When you purchase through link on our site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it ferment .
An indispensable Atlantic Ocean flow that regulates the planet ’s climate is dampen much quicker than antecedently thought , harmonise to a new study .
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation ( AMOC ) , which admit the Gulf Stream , stabilizes climate in the Northern Hemisphere and beyond .

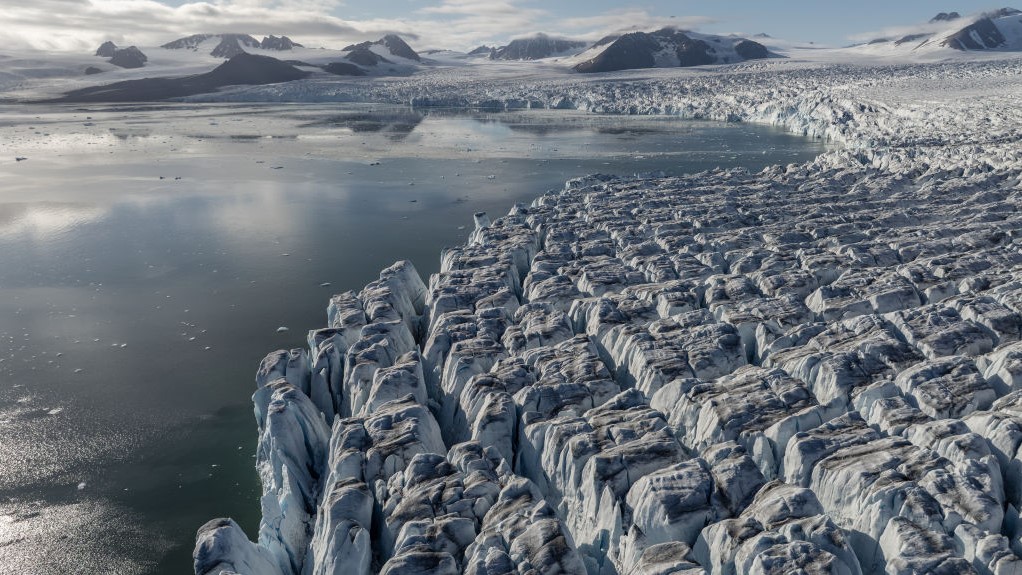
The Ilulissat Icefjord in Greenland on July 3, 2024. The glacier is calving enough ice daily to meet New York City’s water needs for an entire year.
But a young climate model that factors in freshwater melt from Greenland ’s glass sheet has suggested that , at the current rate of ball-shaped carbon paper dioxide emissions , the current could weaken by as much as one - third in the next 15 years . The researchers issue their finding Nov. 18 in the journalNature Geoscience .
The AMOC acts as a global conveyor swath , fetch nutrients , atomic number 8 and estrus north from tropical waters while moving cold water south — a balancing act that keeps both sides of the Atlantic 9 degrees Fahrenheit ( 5 degree Celsius)warmer than it would otherwise be .
But inquiry into Earth ’s mood history shows that the current has switched off in the past , and a growing number of studies have hinted that climate change is make the AMOCto slow . Worst - case scenarios indicate the current maycollapse .
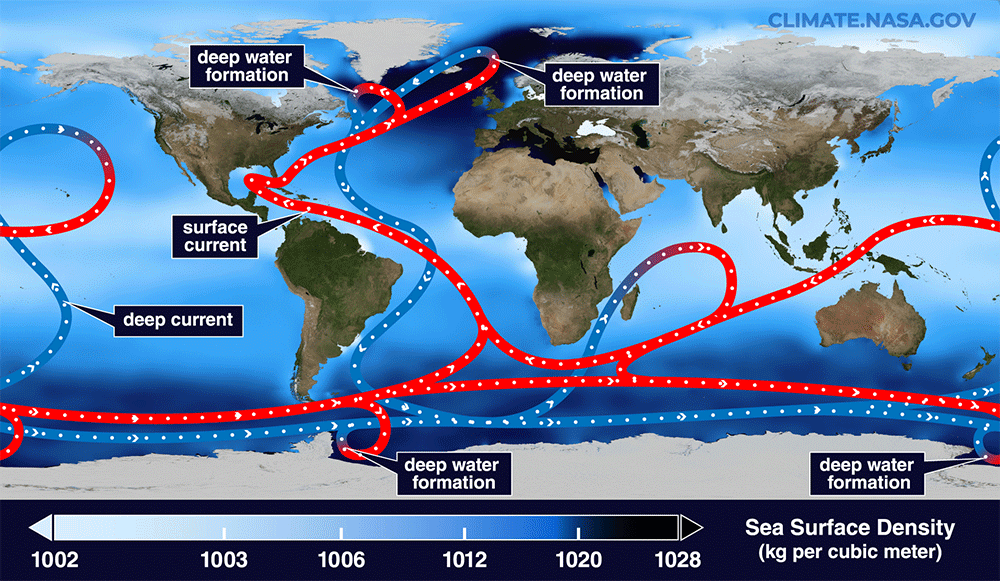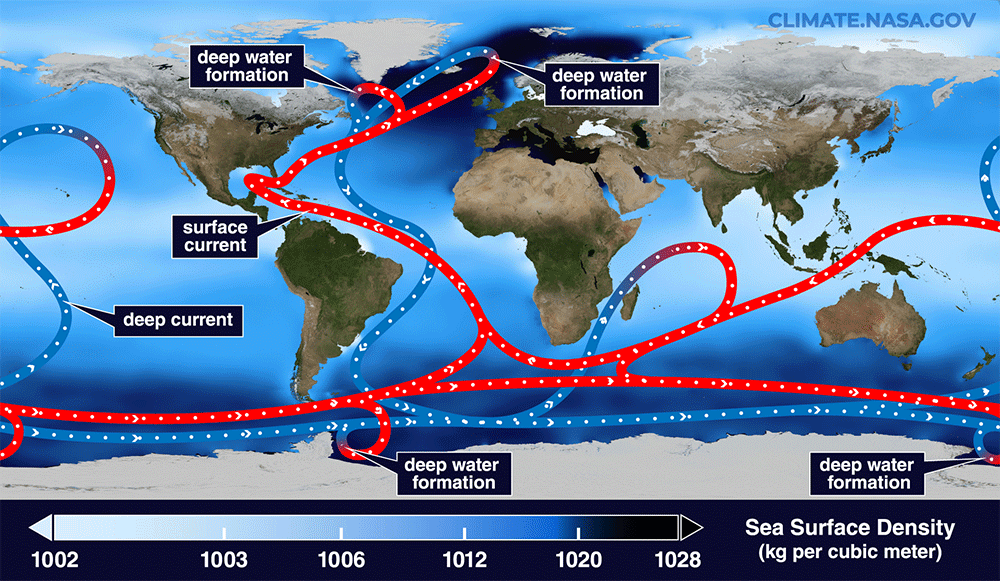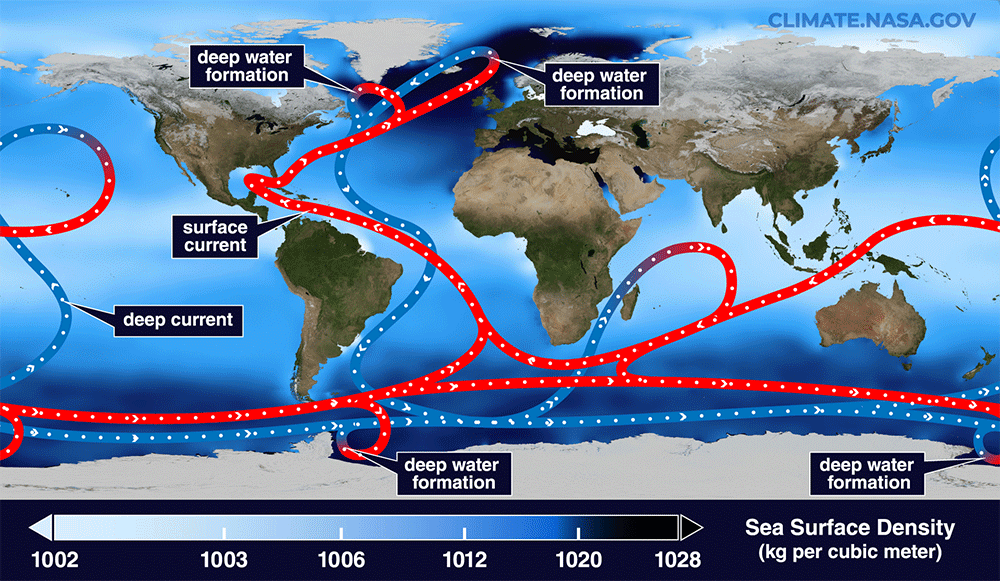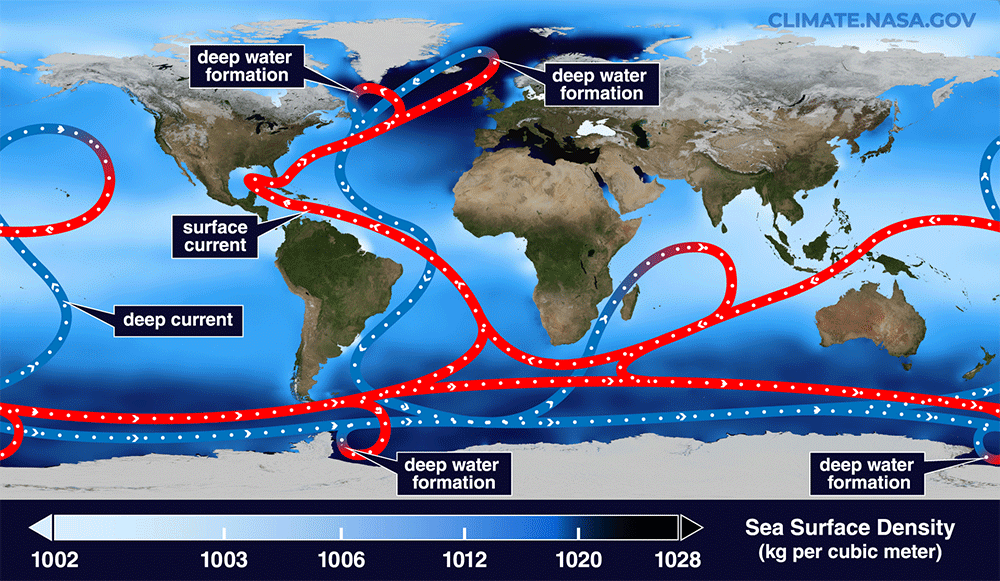
A simplified animation of the global AMOC “conveyor belt”, with surface currents shown in red and deep sea ones in blue.
If the stream were to break whole , it would seed chaos across the globe , make temperatures to plummet across Europe , storms to proliferate at the equator , and other unanticipated effects to impact tipping points in the Amazon rainforest and other regions .
Related : Earth is racing toward climate circumstance that break up fundamental Atlantic flow before the last ice years , subject area finds
However , while many clime models predict a temperate slowdown in the AMOC before 2100 , the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC)has estimatedthat the probability of the system pass over a tipping point this century is less than 10 % .

Yet this is only the beginning of the story . Other exemplar have suggested that the current couldcollapse soon , stirring up disagreement among scientists , and some have suggest that the peril of the current weakening have been underestimated anddemand pressing natural action .
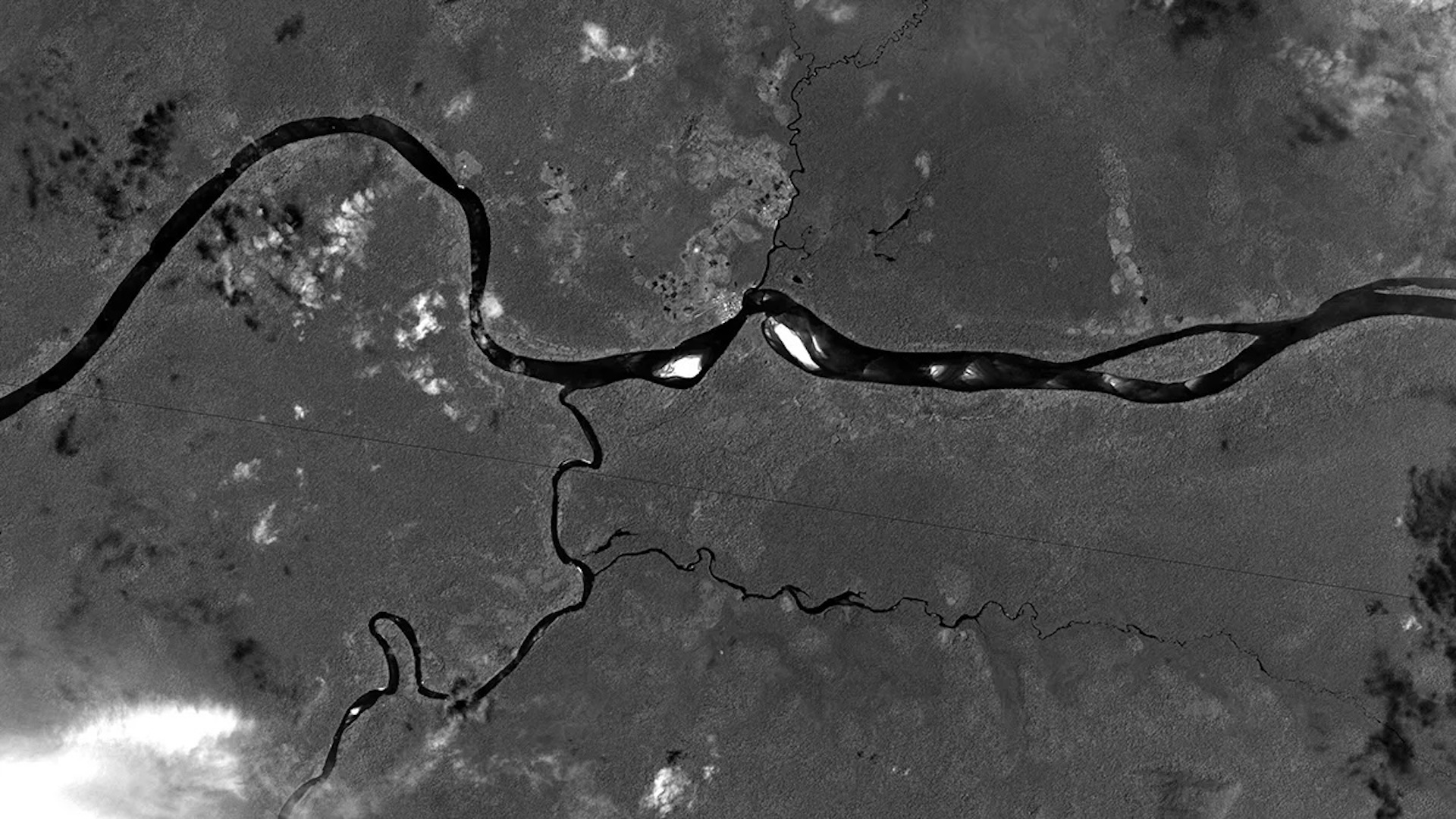
One important piece of the mystifier is meltwater stream into the Atlantic from Greenland and the Canadian Arctic . The AMOC figure out like a giant engine , taking fond water from the South ( which are saltier and denser ) northward . As it moves north , the piquant water cools and becomes denser , and thus sinkhole . This conveyor belt ammunition of water also releases heat into the atmosphere before it returns to the south .
But the inflow of lighter fresh weewee from fade glaciers is displace some of this piquant sea water , stimulate it to stop sinking so deep and slowing down the AMOC . Yet until now , this meltwater had n’t been factor in into the model .

— ' We do n’t really consider it low chance anymore ' : Collapse of key Atlantic stream could have ruinous impacts , says oceanographer Stefan Rahmstorf
— ' We are go up the tipping point in time ' : Marker for the collapse of key Atlantic current find
— Gulf Stream ’s fate to be decided by climate ' jerk - of - war '

" The scientific community is still very disunited on that topic,“Laurie Menviel , a paleoclimatologist at the University of New South Wales ( UNSW ) in Sydney , told Live Science . " The first look is that getting precise estimate of extra meltwater and ice-skating rink electric discharge is unmanageable . There was also a notion that the flux was too belittled to affect the organisation . "
To look into the potential superintendence , Menviel and her colleagueGabriel Pontes , a enquiry scientist at UNSW , create a new poser that factor out in the estimated meltwater outflow .
The yoke ’s model suggests that the AMOC has been slowing at a charge per unit of 0.46 Otto Neumann Sverdrup ( a sverdrup is 1 million three-dimensional meter of water per second ) every decade since 1950 , and that if humanity exceeds 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit ( 2 degrees Celsius ) of global warming ( in line with current projections ) , the circulation could be 33 % weak by 2040 .

" This newspaper is of import in that it sustain what many have suspected but what has n’t been shown explicitly before,“Stefan Rahmstorf , an oceanographer who runs the Earth system analysis department at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany , narrate Live Science . " For the future , the results suggest that we must await a faster AMOC descent than IPCC has foretell . "












