When you buy through link on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
For the first clock time , researchers have used data from theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) to expose an example of a previously hypothetical phenomenon known as an " Einstein zig - zigzag " — where luminosity from an object in the aloof cosmos hap through two dissimilar region of warped distance - sentence . The newly confirmed result , which was discover among six identical copy of a luminous quasar , could shed light on an publication that is begin to plaguecosmology , experts say .
In 2018 , astronomers discover a quaternion of identical undimmed points billions of light - years from Earth , later named J1721 + 8842 . ab initio , the scientists assumed that the four ignitor were mirror image of asingle quasar — a lambent galactic core powered by a feeding black hole — that had been duplicated through a phenomenon bang as " gravitational lensing . "
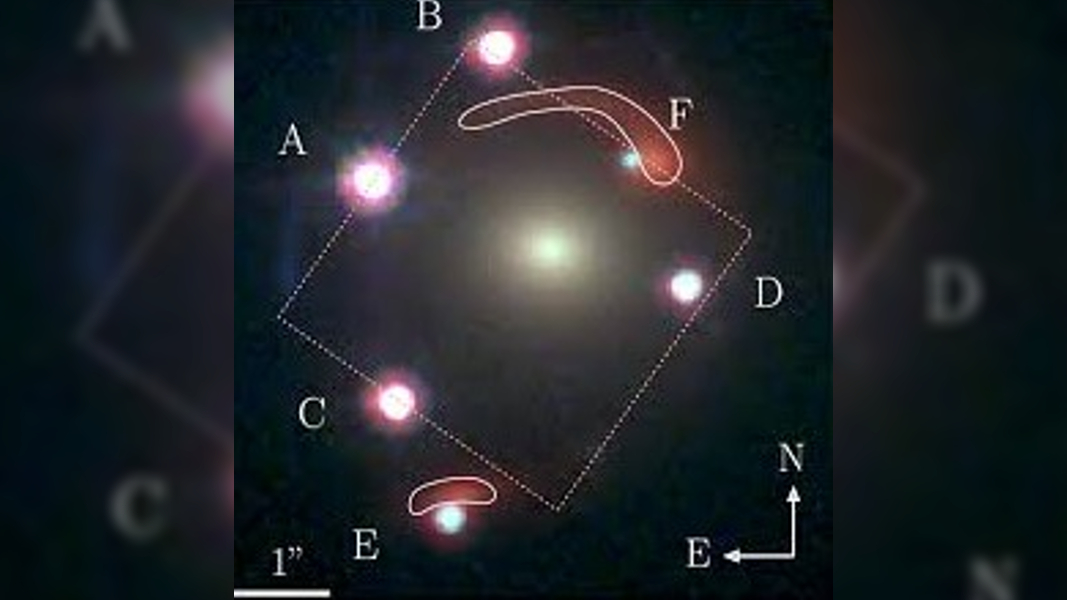
Researchers discovered the “Einstein zig-zag” phenomenon while analyzing six mirror images of a single gravitationally lensed quasar in the distant cosmos.
Gravitational lensing happens when light from a distant objective look to get crumpled as it decease through warpedspace - timethat has been overstretch out of shape by the immensegravityof a lensing object — usually a massive galaxy or cluster of galax — located between the aloof object and the percipient . This warping upshot can either duplicate the initial lite beginning , as the light take different routes around the lensing physical object , or stretch out out the light into lucent ring , eff as Einstein ringsafterAlbert Einstein , who first auspicate gravitational lensing with histheory of universal relativityin 1915 .
But in a2022 study , research worker discovered that J1721 + 8842 had two additional point of illumination alongside the original quartet , as well as a faint red Einstein mob . The newly discovered points were slightly fainter than the other four point , which led researchers to mistrust that the light show prove a pair of conterminous quasars , know as abinary quasar , that had been duplicated three times ( rather than a single quasar that had been copied six time ) .
Related : Researchers solve whodunit of inexplicably dense galax at the core of perfect ' Einstein ringing ' snapped by James Webb scope

Light from Einstein rings and other gravitationally lensed objects appears to bend around their lensing objects. But in reality, the light is travelling in a straight line through warped space-time.
However , in a fresh study , uploaded Nov. 8 to the preprint serverarXiv , researchers reanalyzed J1721 + 8842 using new datum from JWST and found that all six full stop of light are actually from a single quasi-stellar radio source after all . The squad also found that newly uncover bright spot have been lensed around a 2nd massive object farther away from the first , which is also responsible for the faint Einstein ring seen in more recent images . ( The field has not yet been peer - reviewed but has been submit for publication in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics . )
After observing the scant curved shape of each bright spot over two year , researchers showed that there is a slight delay in the metre it demand the two faintest matching image to reach us , which suggests that the sparkle in these copies has to travel further than the other four bright smear . This is likely because the lightness in these look-alike passes around the diametrical side of each lensing object ( i.e. around the left side of the first lens and right side of the 2d lens ) .
The cogitation squad has knight this " extremely rare lensing configuration " an Einstein zig - zag because luminance from some of the forked - lensed smart spots has swerved back and forth as it passed around both lensing galaxy , the researcher wrote .

In 2023, JWST spotted an Einstein ring 21 billion light-years from Earth — the most distant gravitationally lensed object ever seen.
Saving cosmology
Gravitationally lensed objects , such as Einstein gang , are treasured by astronomer and cosmologists because the warped light can facilitate bring out the mass of the extragalactic nebula that lensed them . This , in turn , can help reveal enigma of the universe such asthe secret identity of dark matterandhow dark energy drive cosmic expansion .
JWST has been exceptionally honest at finding these objectsin parts of the universe where we have never been capable to see them before . But alas , the state - of - the - graphics scope has also highlighted discrepancies we can not presently explain .
For object lesson , mensuration from the telescope have confirmed thatdifferent parts of the macrocosm are expanding at different rates , whichthreatens to " break " our understanding of cosmogeny . Researchers refer to this problem as the Hubble stress .

— arresting ' Einstein conflict ring ' from the former universe is one of the former ever discovered
— James Webb scope spies jewel ' Einstein doughnut ' made of warped quasar light
— Rare ' Einstein crabbed ' warp light from one of the universe ’s brightest target

However , researcher trust that the newly confirmed Einstein zig - zag could help to smooth out this tautness because its unique constellation will allow uranologist to incisively measure both the Hubble constant quantity — the rate at which cosmic elaboration is accelerating — and the amount ofdark vigor — the invisible force driving the creation ’s enlargement — in this neighborhood of outer space . Normally , scientist can only define precise trope for one or the other but elaborated knowledge of both is needed to truly understand cosmic expansion , the researchers write .
Thomas Collett , an astrophysicist at the University of Portsmouth in the U.K. who was not involved in the study , toldScience magazinethat studying the zig - zag will " gleam a light on whether the expansion rate of the universe is coherent with the cosmologic model or not . " However , it could take researchers more than a year to correct the shape they demand from the dishevel images , he summate . " So we might have to hold back a while [ for an answer ] . "
Gamma - ray bursts break largest structure in the existence is bigger and close to Earth than we bed : ' The panel is still out on what it all means . '

Universe may revolve once every 500 billion years — and that could work out a problem that threatened to break cosmology
The constant surveillance of modern life could worsen our brain function in way we do n’t fully understand , disturbing studies suggest






