When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Many of us have had to consider with pesky neighbors , but for at least one dusty region in the constellation Orion , the problem ’s existential .
Observations by theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) show that a compact disk of gas pedal and dust around a young star in the Orion Nebula is losing monumental amount of atomic number 1 each year . The disk , known as a protoplanetary magnetic disk , is the region in which newfangled planet can form , so the personnel casualty of important amounts of material could determine this operation .

A 3-D visualization of the chaotic Orion Nebula based on observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.
This H loss is being driven by intense ultraviolet ( UV ) radiation pouring in from a group of massive neighboring stars . The UV irradiation is so strong that it may be forbid tumid major planet from ever form in the neighborhood , a new study suggests . The findings could shed Christ Within on the sway massive stars hold on fledgling wandering systems .
" Over the timescale of a million years , all the mass should be gone from this disk , " saidOlivier Berné , a research scientist at the French National Centre for Scientific Research ( CNRS ) and the lead author of the new study . Current good example of major planet formation indicate an orb the size of Jupiter would take at least that long to coalesce , so the rapidly escape material is " in competition with geological formation of planets , " Berné told Live Science .
The team ’s findings were published Thursday ( Feb. 29 ) in the journalScience .

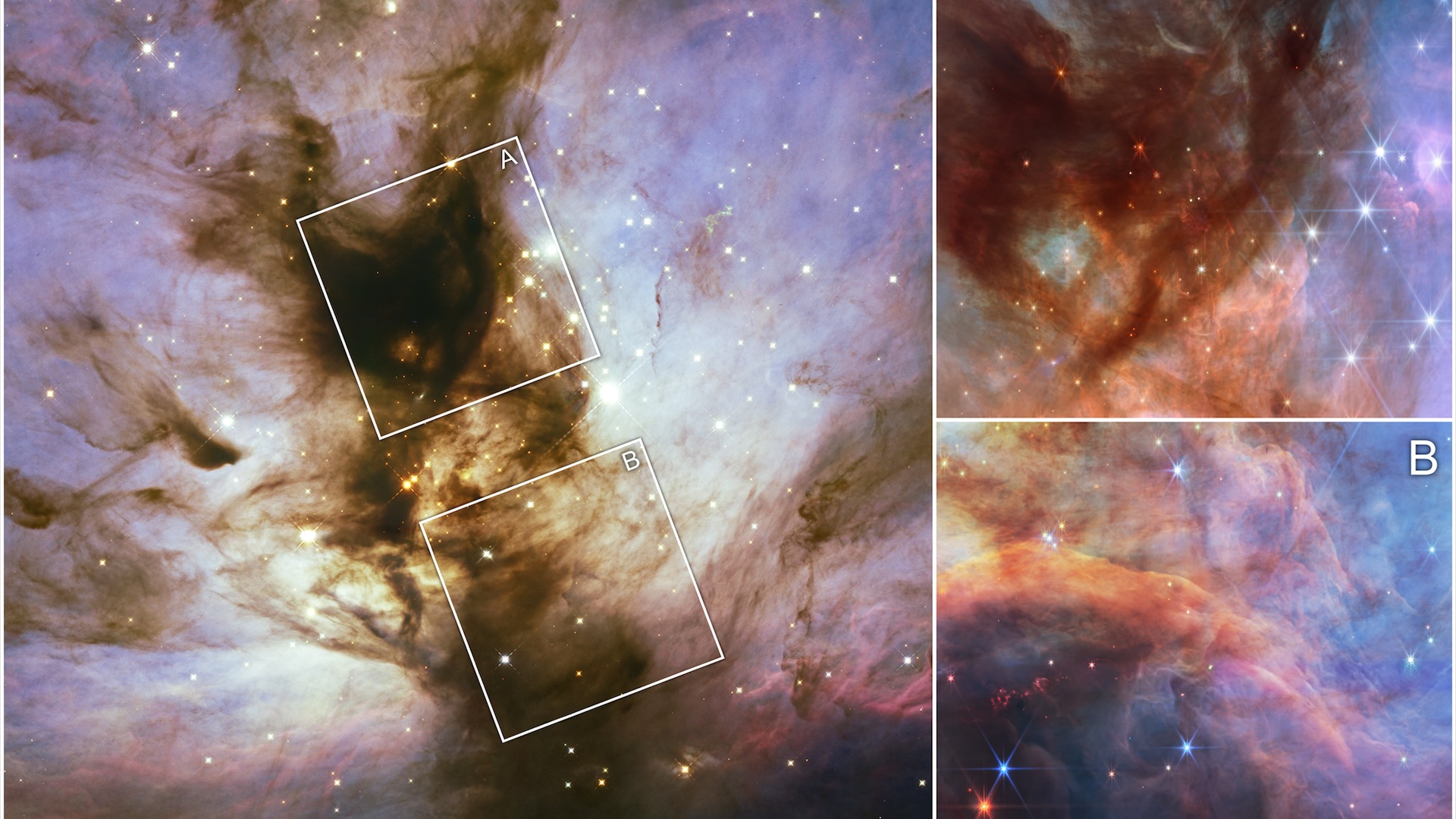
Hubble image of the Orion Nebula, and a zoom in on the protoplanetary disc d203-506 taken with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
Ultraviolent stars
wizard in the Trapezium cluster — a crowded house of many vernal stars , including the well - know group at Orion ’s heart — are each about 10 time more massive than our sun and 100,000 time brighter . The squad ’s raw JWST reflection show that ultraviolet radiation radiation from these ultra - bright stars is importantly heating up gas in the nearby protoplanetary disk , formally named d203 - 506 , induce load of worthful planet - forming material to break free and blow off into blank space .
The disk d203 - 506 is at most a few million years erstwhile , although it ’s difficult to hold a precise age , Berné said . The Orion Nebula itself is believe to be just about 3 million age onetime , " which for us astronomers is very untried , " he said .
Related:35 jaw - dropping James Webb Space Telescope images
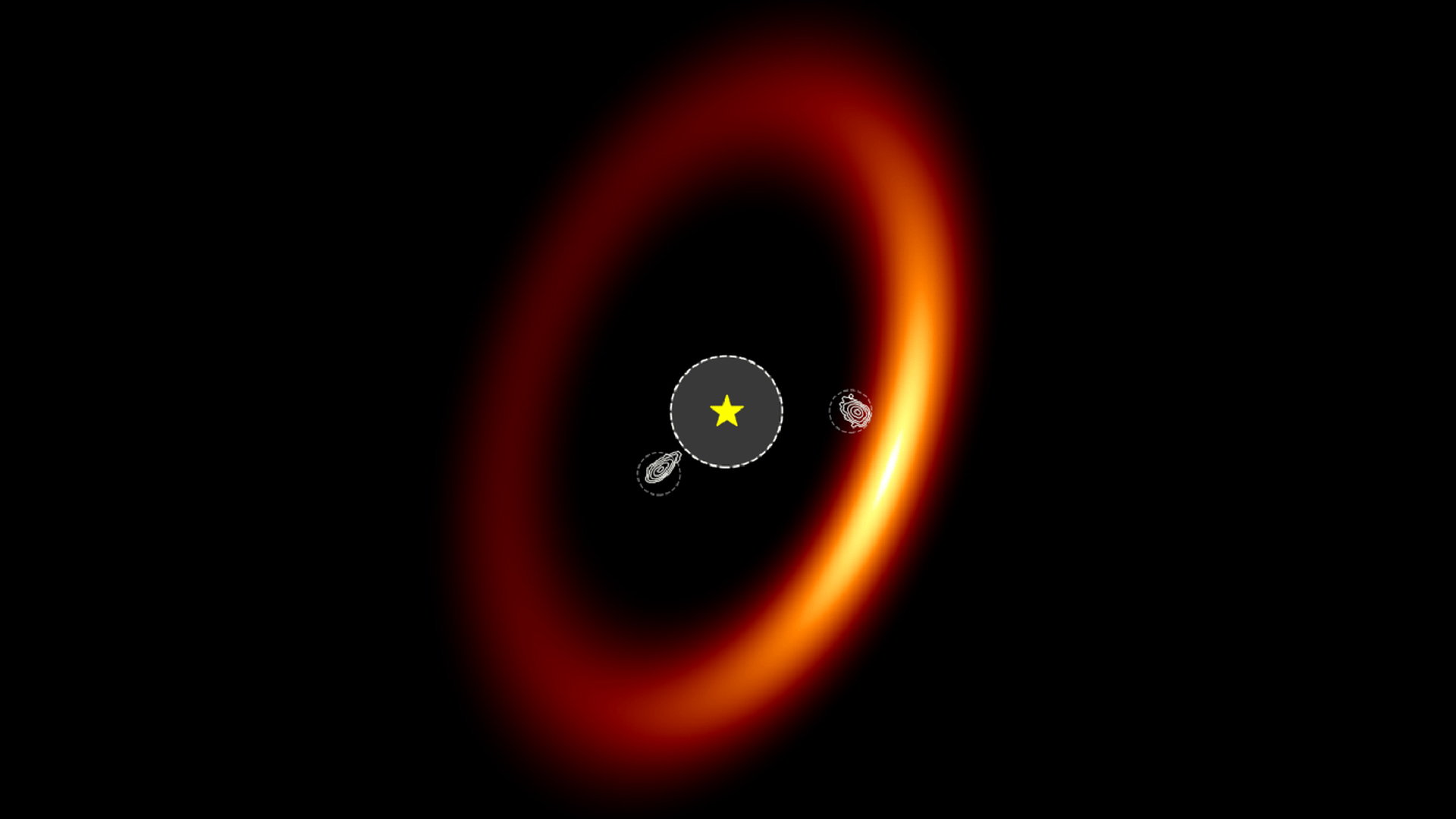
The nascent nebula is about 30 to 40 light - years in diameter , so there is a good luck that the gasoline being squeeze out from the protoplanetary disc stay on within it — although it ’s always lost for any future planet that would sprout in the platter itself . It come out this system is also losing intact oceans ' worth of piss every month from the ultraviolet assault , consort to a relatedpaperfrom the same squad print Feb. 23 in the diary Nature Astronomy .
The gasoline puffing away from the magnetic disk is conduct with it at least some rubble food grain , so it ’s an open question whether jumpy planets like Earth can ever birth in this organization , Berné said .
study of meteorites show that our ownsolar system , which is 4,000 times older than d203 - 506 , was also influenced by one or more nearby massive stars during its formation . Evidence for this includes the presence of radioactive elements in comets and asteroid — such asaluminum-26 , which is get it on to take shape in very raging condition like those seen in explode stars — that may have wafted into our solar system thanks to a closeby supernova .

— Are they exomoons or not ? scientist contend existence of 1st moons take care beyond our solar system
— Physics - breaking ' rogue ' objects spotted by James Webb scope are emitting tuner signals that scientists ca n’t explain
— ' creative thinker - blowing ' James Webb telescope images reveal 19 spiral galaxies in the greatest particular ever seen

" Looking at this organization [ d203 - 506 ] is really like looking into the past of our solar arrangement in a elbow room , " Berné said .
Compared with our own Sunday , d203 - 506 ’s star is five to 10 times smaller , so it also has a weak grip on its organization , which may excuse why the planet - form material is elude so easily .
Berné suppose his squad has lend oneself for more time on telescopes to keep this disk and others within the Orion Nebula . As the current finding are based on only one system , the research worker state future notice could paint a more complete depiction of how massive principal touch young planetary systems like d203 - 506 .
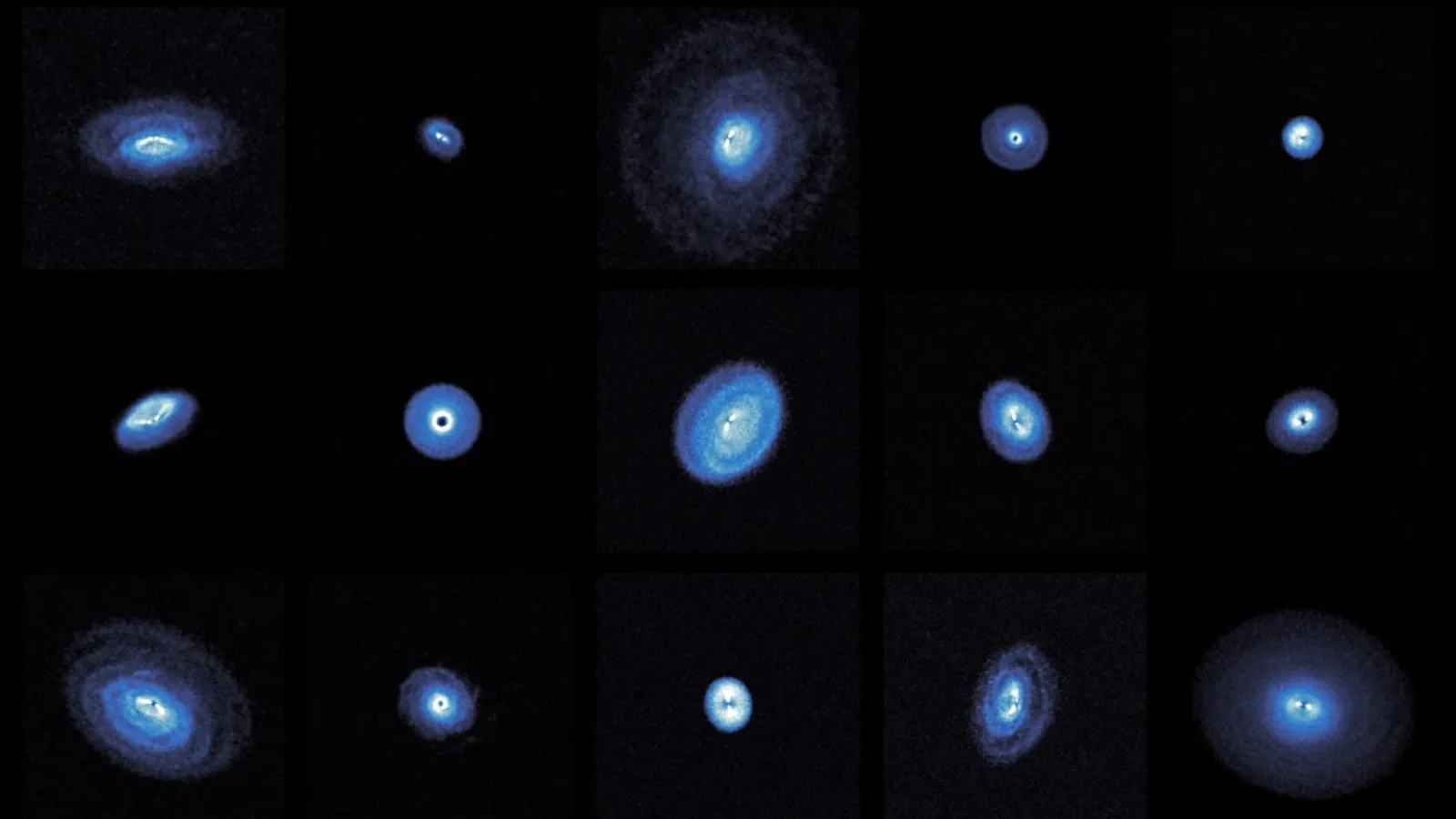
" It ’s just the crown of the iceberg that we ’ve been expect at so far , " Berné say .













