When you buy through inter-group communication on our site , we may clear an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Every beetleweed , including our ownMilky Way , has a ogre lurking in its ticker — asupermassive black-market hole . Despite how unwashed these giant target are , astronomers are still sample to figure out how the universe ’s supermassive black hollow were pay , and how they grew to their walloping size .
Now , new observations fromNASA’sJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) have unveil a primal brainwave into the grow hurting of supermassive fateful holes , also get laid as SMBHs : there are actuallyfewerrapidly maturate mordant holes than previously predicted . This work was of late submitted to the Astrophysical Journal and made usable to read before peer review on the preprint databasearXiv .
Illustration of active galactic nucleus.
Teenage SMBHs grow rapidly , eating up stuff around them , and appear to us as a bright blob live as an dynamic galactic lens nucleus ( AGN ) . astronomer broadly speaking consort our galaxy ’s SMBH has long since quieted , leave its dynamic days in its past tense . Most ofthe monsters ' growth spurtsactually happen around 7 to 11 billion years ago .
Related : A black hole ' assassin ' rip a wiz to shreds and left its guts straw about the galax
In their new research , the study authors used the ultra - powerfulJWSTto hunting for more active disastrous holes in the midst of their prize outgrowth class , surveying a patch of sky for remote galaxies with unprecedented sensitivity . They observe around 400 galaxies that are 1000000000 of light - years away , mean we ’re seeing them as they were billions of years ago — correctly during their astronomical growth spirt .
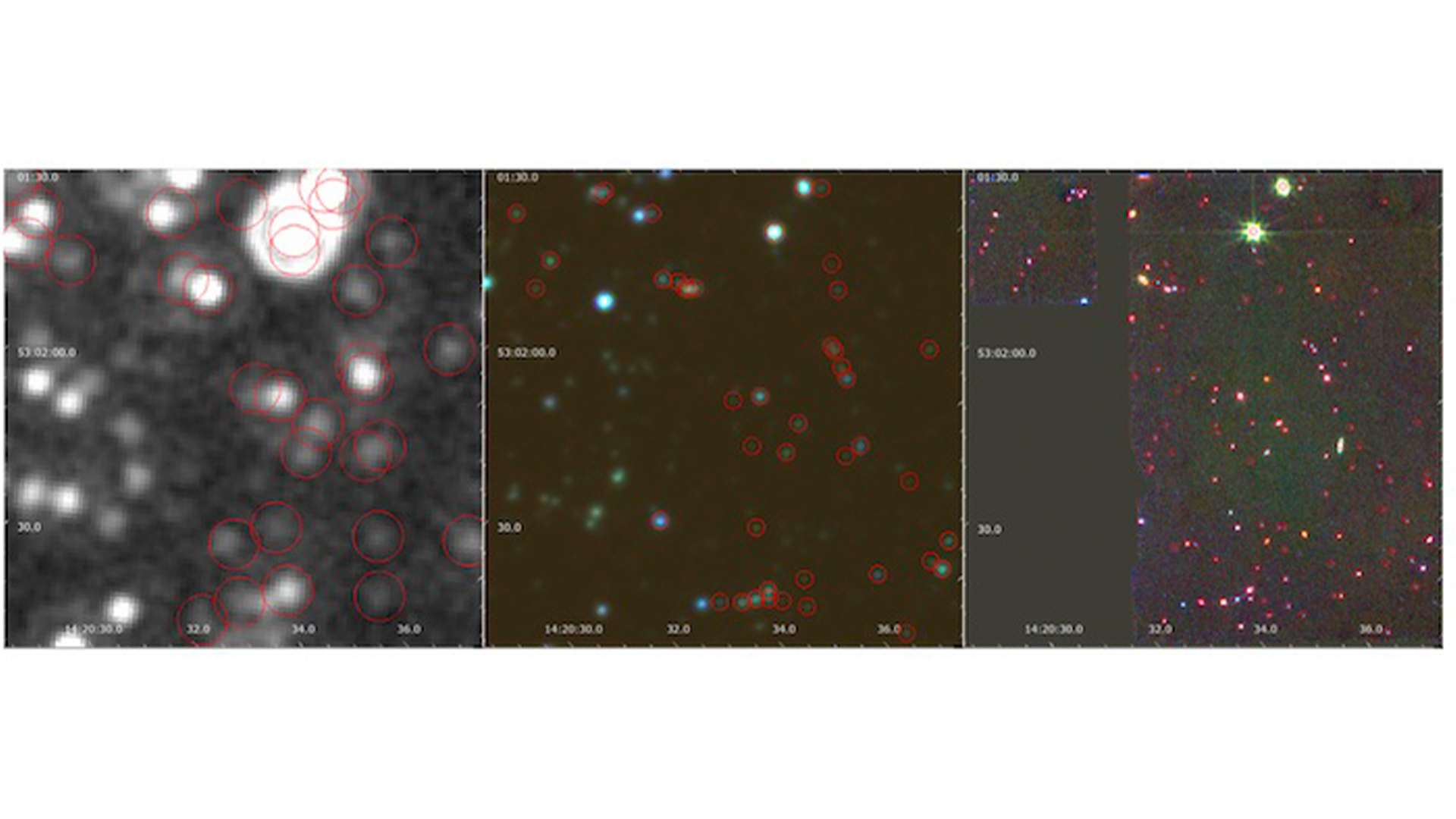
MIRI Pointing 1 (right panel) alongside the Spizter/IRAC (middle) and MIPS (left) observations of the same region.
" Until now , we were only able-bodied to see the most actively growing and biggest supermassive black holes , " star cogitation authorAllison Kirkpatrick , an astronomer at the University of Kansas , told Live Science . " It would be likealienstrying to put together together what the medium human can do but only study Olympian athletes . Now , with JWST , we have our first look at the population of ‘ normal ’ galaxies in the distant past . "
Astronomers previously thought that even " average"-sized black holes like the one in the milklike Way would show signs of their rapid growth , since the large AGN observed antecedently were clearlygrowing up fast . Even with the massive increment in sensitivity from JWST ’s instruments to peer down to smaller galaxies , though , they could n’t find more really combat-ready teenage AGN . In fact , the population of active black muddle was far few than premature estimate have suggested .
— James Webb Space Telescope discovers oldest black hole in the macrocosm — a cosmic monster 10 million times heavier than the sun
Installation of MIRI into the instrument module of the James Webb Space Telescope.
— 1st image of our Galax urceolata ’s ' black hole affection ' unveiled
— mordant holes may be swallowing invisible issue that slows the drift of champion
By looking at these average galaxies , astronomers even gleaned brainwave into our Milky Way ’s past . " If most galaxies , like ours , deficiency perceptible AGN , it could entail that our black hole was never more alive in the yesteryear , " Kirkpatrick said in astatement .

The team ’s next step are to look at even more galaxies ; after all , 400 beetleweed out of million in the universe is only a dip in the pail . With her next survey , Kirkpatrick plans to abide by thousand of galaxies instead of 100 , hopefully clearing up the picture of how modest galaxy get their contraband jam , and acquire into something like the galaxy we know and live in today .












