When you buy through links on our web site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
A remote asterisk first spotted X ago is actually a distich of sister stars that are each spewing herculean energy jets parallel to one another , scientists have discovered .
The unlikely twins were at last identified thanks to theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) , which peer through a dumb swarm of cosmic debris to espy the adjacent jets take out of the juvenile wiz , researchers said .
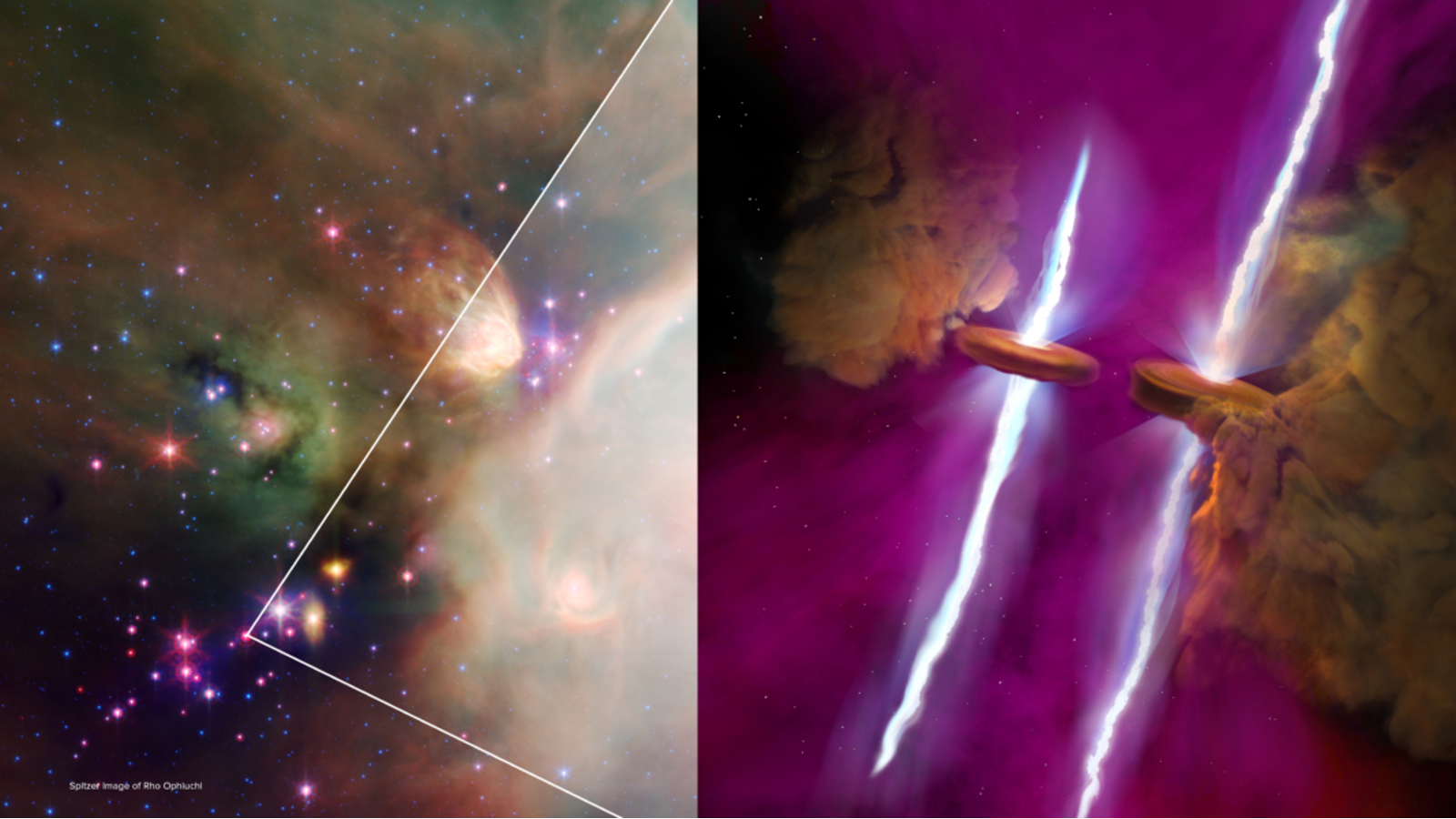

Left: An image of WL20 in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex taken by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope. Right: An artist’s impression of the two new stars and their stellar jets based of JWST data.
The freshly key out stars are situate in the WL 20 organisation — a little stellar cluster in theRho Ophiuchi cloud coordination compound , about 400 light - yr from Earth . Researchers have been studying this system for around 50 age and have list a number of star topology there , include a babe star , or protostar , designated WL 20S , which was hem in by a large ring of gas and dust , known as a protoplanetary disk .
" What we discovered was absolutely wild,“Mary Barsony , an astronomer with the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence ( SETI ) Institute , said in astatement . " We actually saw that this ONE star was TWO whizz mighty next to each other . "
Researcherspresented the new findingsJune 12 at the 244th meeting of the American Astronomy Society .
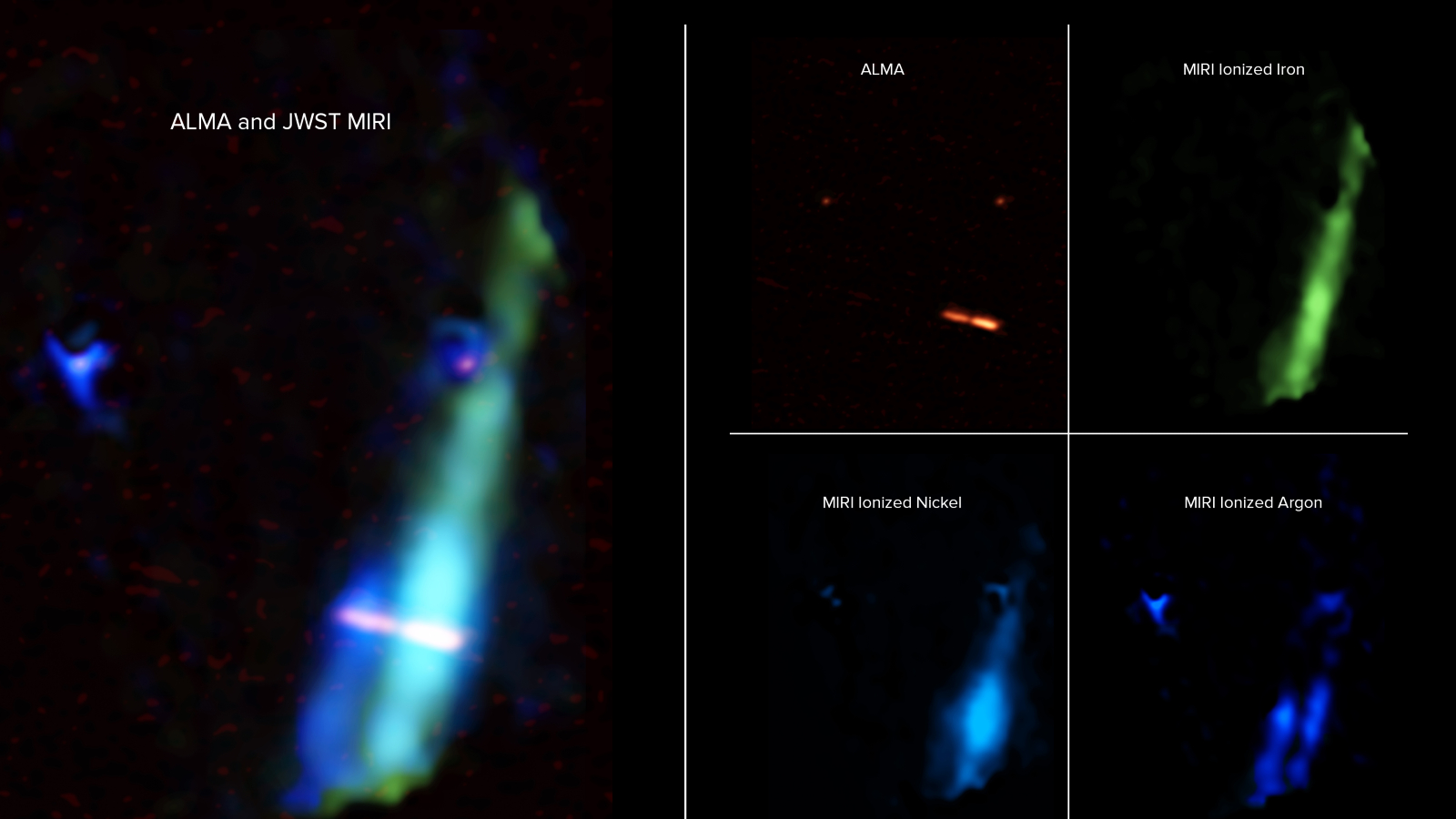

JWST captured the infrared radiation given off by the new stars and their stellar jets.
Related:8 stunning James Webb Space Telescope discoveries made in 2023
The two principal , which are yet to be individually describe , arebinary stars , intend that they orbit one another . They in all probability form from a undivided protoplanetary disk that fragmented ahead of time on in the maven formation process , the researchers said .
Based on the size of their respective disks , which are both around 100 time wider than the space between the sun and Earth , researchers guess that they are between 2 million and 4 million days old , which is a tiny fraction of our family ace ’s roughly 4.6 billion days in space .

JWST’s superior infrared instrument allowed it to see the new stars in unprecedented detail.
The researchers believe there is a decent prospect thatexoplanetswill eventually shape from what ’s left of the protoplanetary disks when the stars have fully formed .
Despite being studied for decades , astronomer have only pull in circumscribed information from the WL 20 bunch due to a enceinte cloud of dust that is located between the far - off part and Earth . This swarm blocks almost all seeable luminance , mean investigator have to rely on infrared radiation from the principal and their surrounding objects .
— James Webb scope get wind most upstage supernova ever seen
— James Webb telescope sees ' birthing ' of 3 of the world ’s earlier galaxies in world-1st observations
— James Webb scope reveals ' cataclysmic ' asteroid hit in nearby hotshot organization
Until now , telescopes have not been knock-down enough to properly distinguish infrared lighter at mellow resolution . But JWST ’s nation - of - the - art Mid - Infrared Instrument ( MIRI ) activate the infinite telescope to see more wavelengths of this invisible radiation in greater point than ever before .

" Without Mirish we would not have bed this was two star or that these jet survive , " Barsony said in aNASA statement . The power of MIRI is stupefying , she added . " It ’s like have mark new eyes . "















