When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
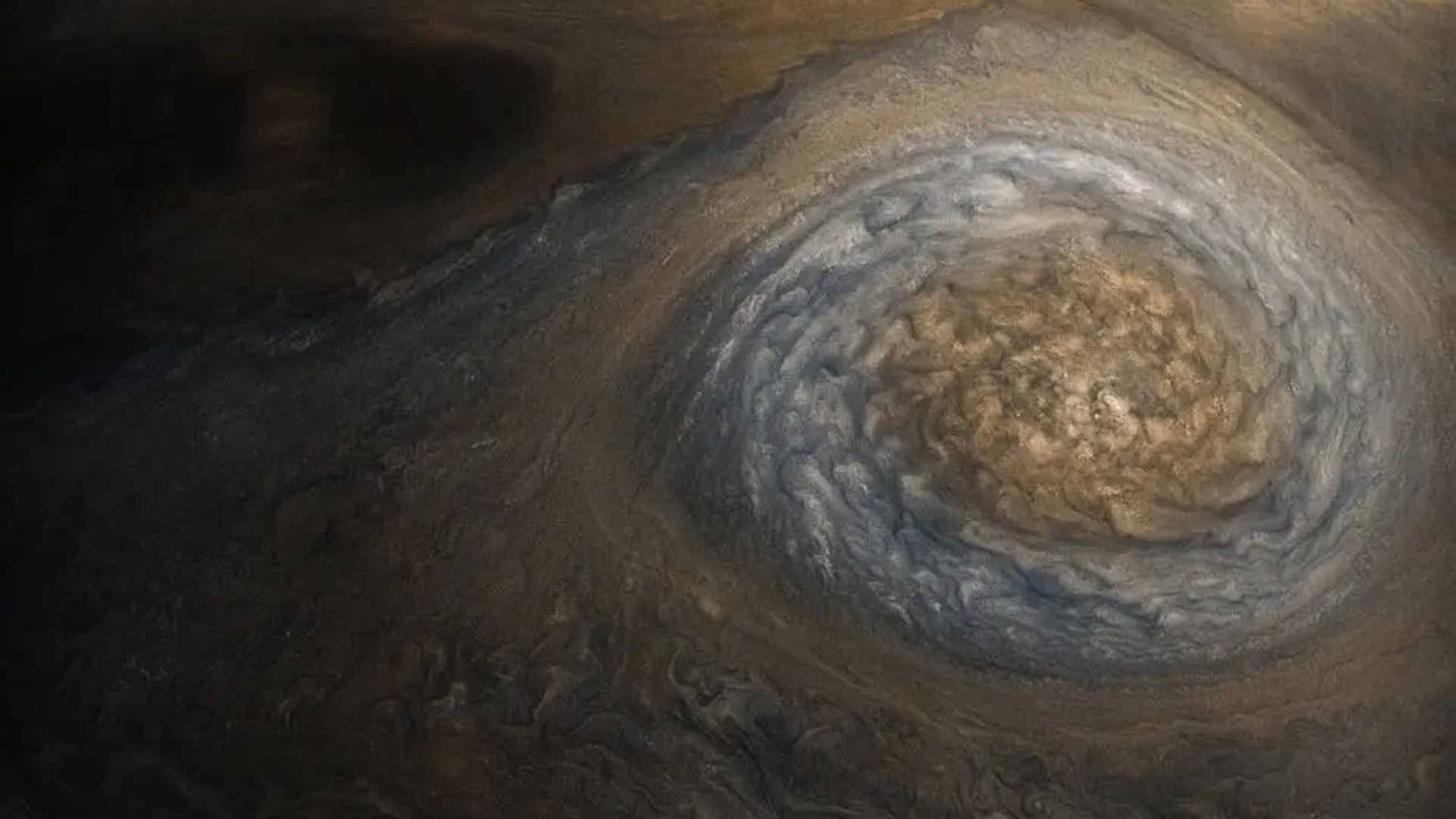
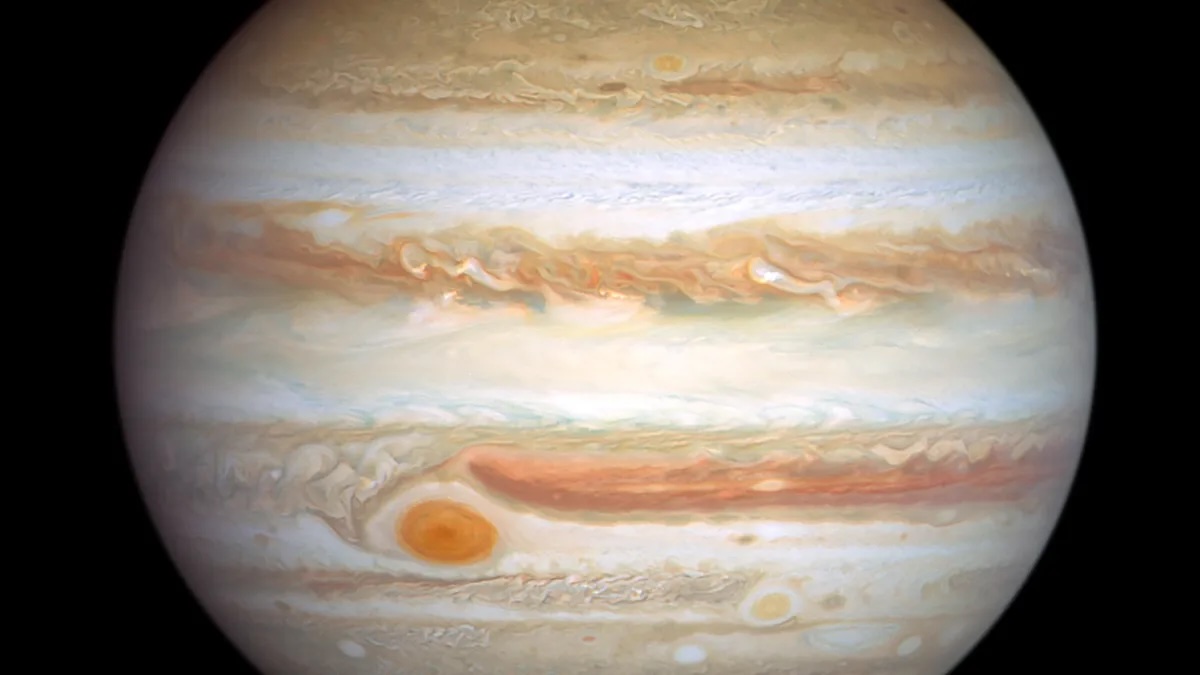
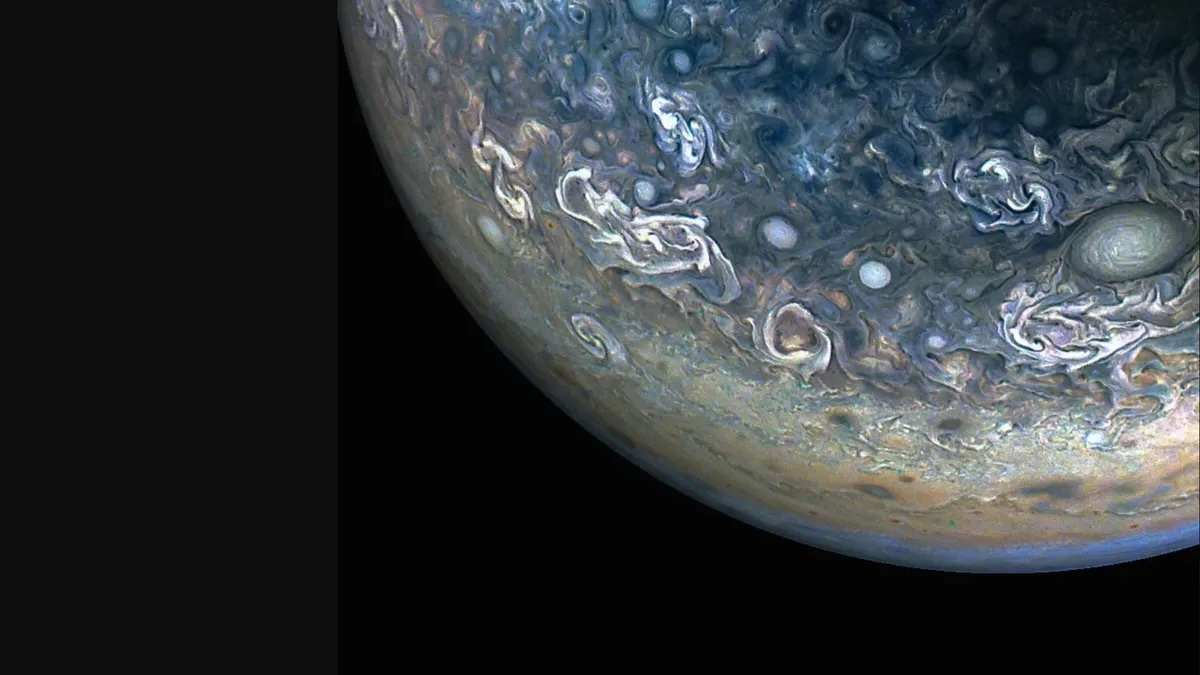
On Christmas Day in 2023 , scientist trained theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) on Jupiter ’s auroras and captured a glary light show .
The researcher observed apace - changing feature article in Jupiter ’s vast cockcrow using JWST ’s infrared cameras . The finding could help excuse how Jupiter ’s air is inflame and chill , according to a study published May 12 inNature Communications .

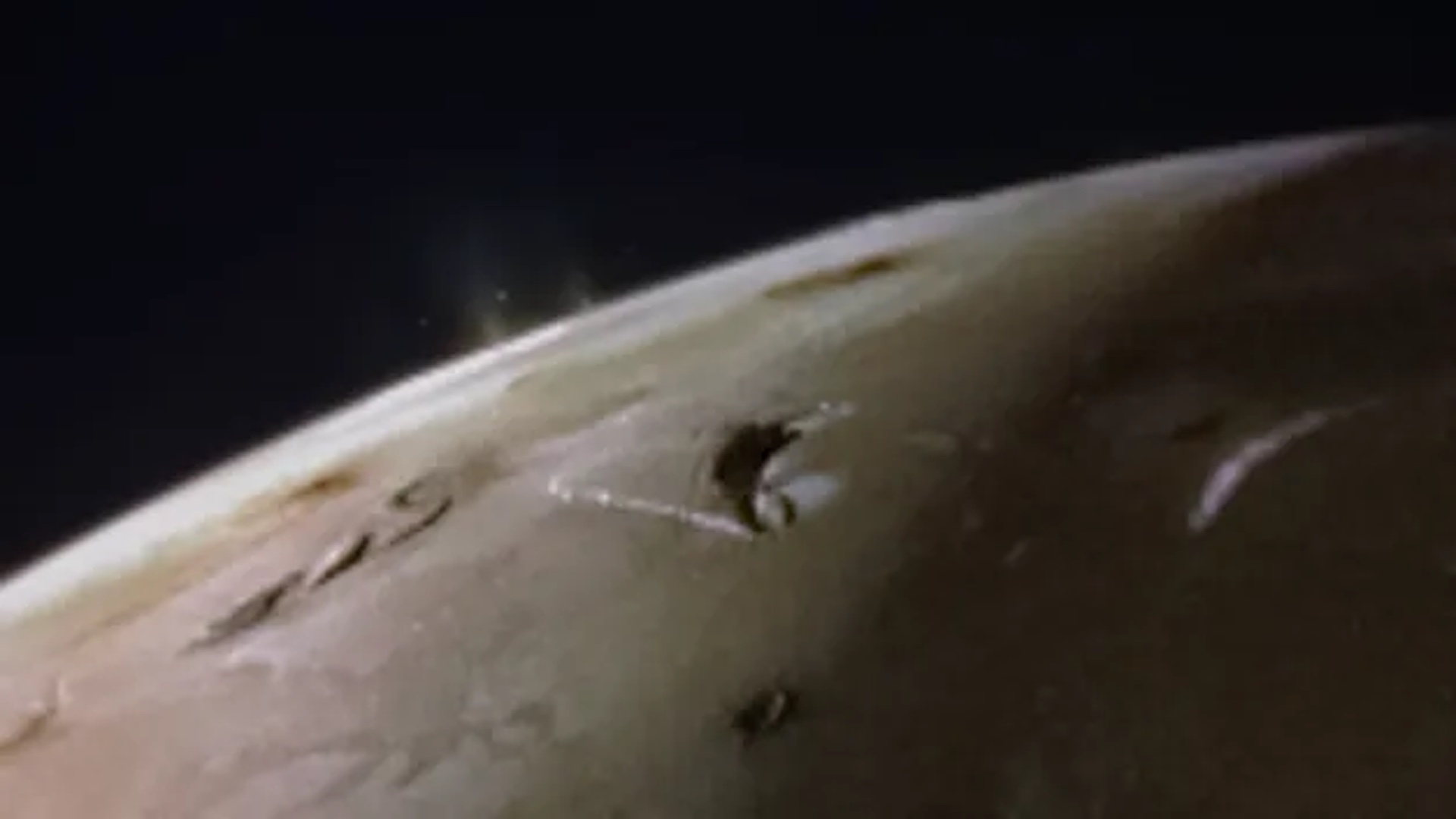
JWST captured auroras on Jupiter “fizzing and popping with light” on Christmas Day 2023.
" What a Christmas present it was — it just blew me away ! " study coauthorJonathan Nichols , a researcher studying break of day at the University of Leicester in the UK , say in astatement . " We want to see how quickly the auroras modification , expecting them to fade in and out ponderously , perhaps over a after part of an hour or so . Instead , we observe the whole aurorean realm fizzing and popping with scant , sometimes vary by the second . "
Auroras form when high - energy file molecule , often released from the sun , shot into throttle in a planet ’s atmosphere , causing the gas to beam . Jupiter ’s substantial magnetic field scoops up charged speck such as electrons from the solar wind — and from eruption on itshighly volcanic moon Io — and sends them hurtling toward the planet ’s poles , where they put on a spectacle hundreds of clock time brighter than Earth’sNorthern Lights .
associate : NASA unveil ' chicken feed - smooth lake of cooling lava ' on surface of Jupiter ’s moon Io
In the new cogitation , the team looked closely at infrared brightness level give out by the trihydrogen cation , H3 + . This molecule shape in Jupiter ’s auroras when gumptious electrons suffer hydrogen in the major planet ’s standard atmosphere . Its infrared expelling send heat out of Jupiter ’s atmosphere , but the molecule can also be destroy by fast - moving electron . To day of the month , no ground - ground scope have been sensitive enough to determine exactly how long H3+sticks around .
But by using JWST ’s Near Infrared Camera , the team observed H3+emissions that varied more than they expected . They bump that H3+lasts about two and a half minute in Jupiter ’s ambiance before being destroyed . That could help scientist tease out how much of an effect H3+has on cooling Jupiter ’s ambience .
— secret of Jupiter ’s powerful X - ray break of day last solved

— Powerful solar winds squish Jupiter ’s magnetic field ' like a elephantine squash ball '
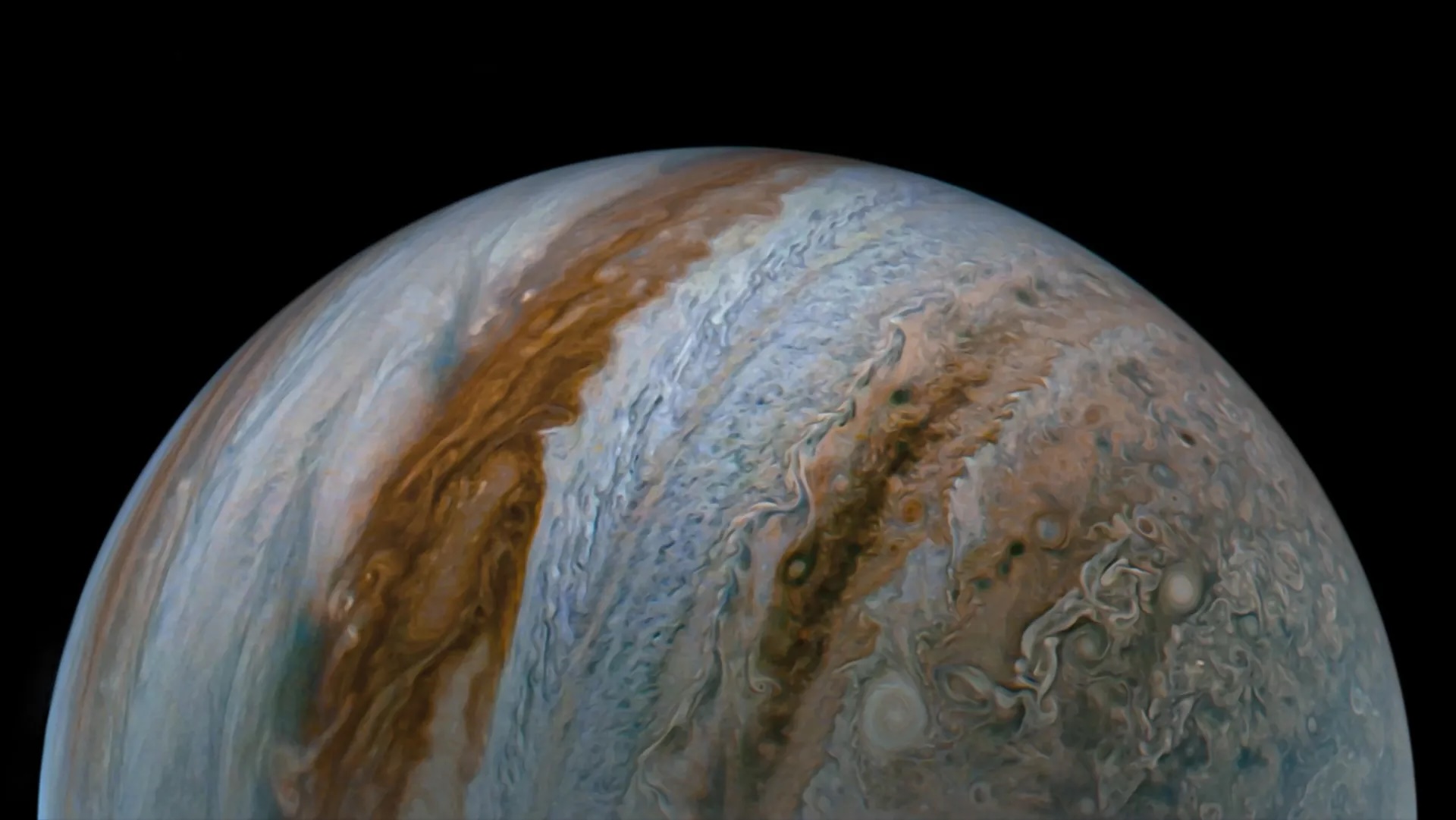
— Jupiter glows in stunning novel James Webb telescope persona
But the scientists do n’t have the full picture yet . They also found some puzzling data when they turn theHubble Space Telescopetoward Jupiter at the same time . Hubble captured the ultraviolet light coming from the auroras , while JWST capture infrared Inner Light .

" Bizarrely , the brightest light observed by Webb had no veridical opposite number in Hubble ’s pictures , " Nichols say in the statement . " This has leave behind us scrape our heads . In social club to cause the combining of brightness seen by both Webb and Hubble , we need to have a combination of gamey amount of very low - energy particles hitting the aura , which was antecedently thought to be unacceptable . We still do n’t understand how this happens . "
In future piece of work , the research worker design to study the source of this unexpected design using additional JWST data as well as observations fromNASA’sJuno spacecraft , which has been observing Jupiter from orbit since 2016 .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be instigate to move into your display name .














