When you purchase through links on our site , we may take in an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it form .
TheJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) has found evidence of two giant asteroids slamming into each other in a nearby mavin scheme . The colossal collision ejected 100,000 time more dust than the impact thatkilled the dinosaurs .
The vehement impact occur recently in Beta Pictoris , a star arrangement locate 63 light - age forth in the constellation Pictoris .
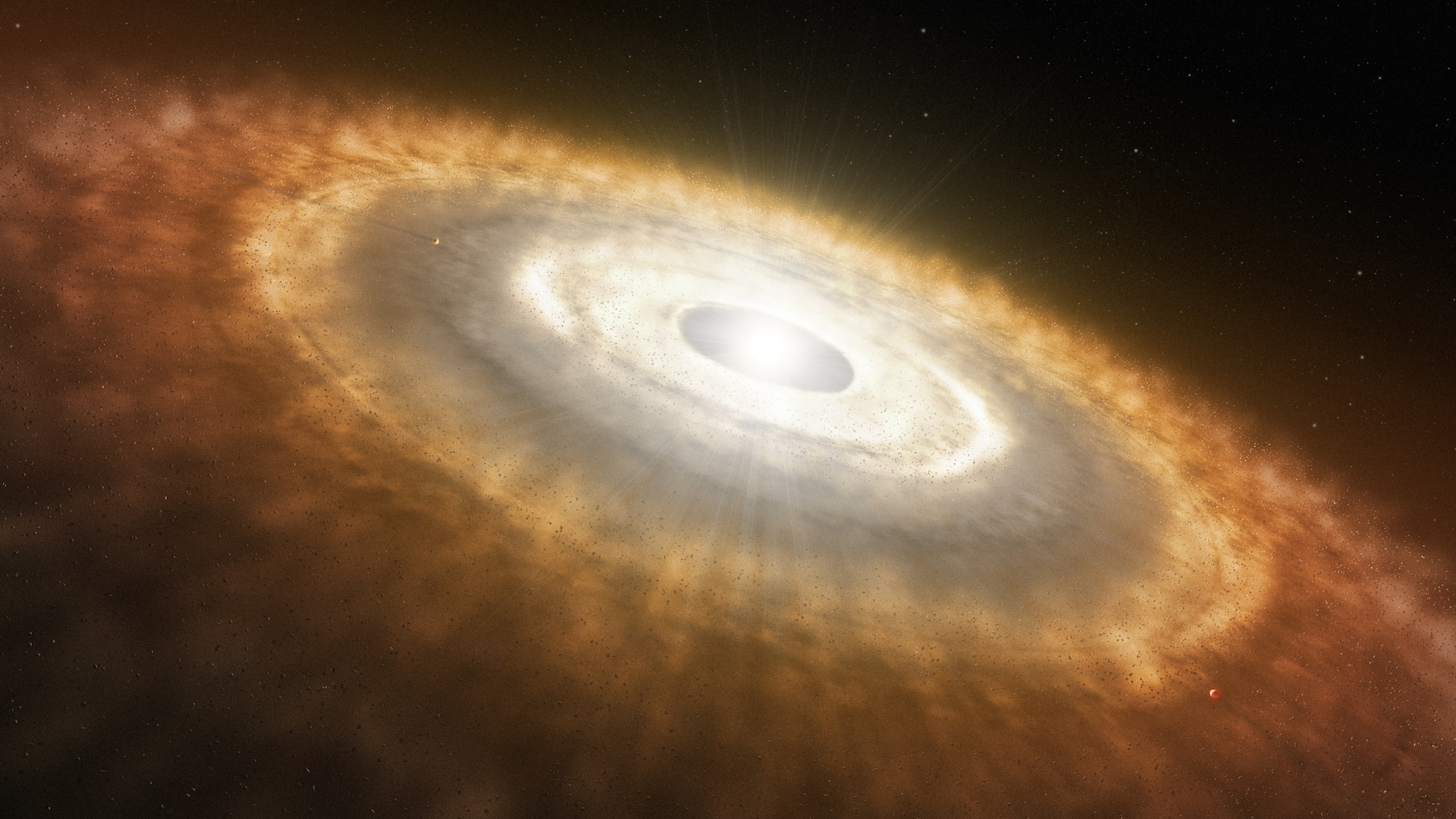
An illustration of a protoplanetary disk, similar to the one studied by the James Webb Space Telescope in new observations of the Beta Pictoris star system.
Beta Pictoris is a babe compare to our ownsolar scheme — having subsist for only 20 million years compared with our system ’s venerable 4.5 billion years . It was first discover in 1983 byNASA ’s Infrared Astronomical Satellite ( IRAS ) ballistic capsule and is thought to have formed from the shockwave of a nearby supernova .
While the young star scheme currently hold at least two gas giant planet it has no have it off rocky worlds like our own . But bumpy inner planets may be in the procedure of forming , thanks to large detritus - producing collision like the one spotted by JWST , the researchers behind the new findings enunciate in a June 10 intro at the244th Meeting of the American Astronomical Societyin Madison , Wisconsin .
Because it is still very untested , the star system ’s circumstellar junk disk — the vast ring of flatulency and dust surrounding the whiz — is a significantly more violent situation than our own , make it the sodding property for astronomers to examine thetumultuous former yearsof planet - constitute arrangement . The team sum that their findings could offer a rare sixth sense into the history of our own solar system .
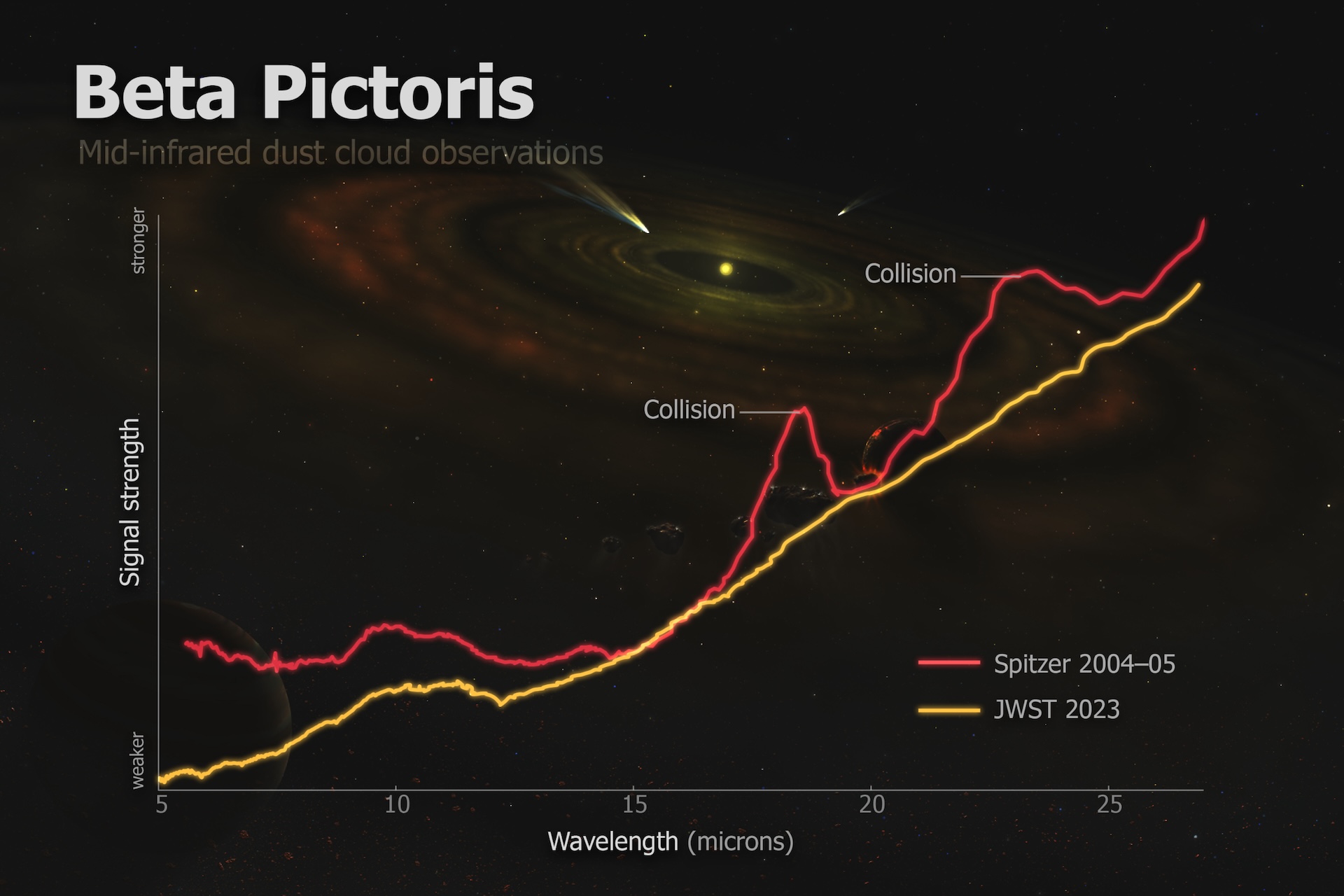
Two different space telescopes took snapshots 20 years apart of the same area around the star called Beta Pictoris. Scientists theorize that the massive amount of dust seen in the 2004–05 image from the Spitzer Space Telescope indicates a collision of asteroids that had largely cleared by the time the James Webb Space Telescope captured its images in 2023.
" Beta Pictoris is at an age when satellite constitution in the terrene planet zone is still ongoing through giant asteroid collisions , so what we could be find out here is basically how bouldered major planet and other bodies are forming in veridical time , " lead study authorChristine Chen , an uranologist at Johns Hopkins University , said in a statement .
have-to doe with : James Webb telescope spots wind spoil faster than a hummer on ' 2 - faced major planet ' with interminable night
To capture a snap of the distant asteroid crash , the astronomers trained JWST ’s sinewy middle on the organization and found that elephantine mickle of clumped silicate dust fleck by the Spitzer Space Telescope between 2004 and 2005 had completely disappeared .

This intend that , sometime 20 years ago , a mammoth collision between two asteroid in all likelihood fall out , pounding the body into vast quantities of dust with subatomic particle smaller than pollen or powdered scratch , Chen said .
" With Webb ’s new information , the best account we have is that , in fact , we witnessed the aftermath of an infrequent , cataclysmic event between large asteroid - sizing bodies , marking a complete change in our intellect of this star topology system , " Chen say .
— James Webb scope finds origins of the large explosion since the Big Bang — revealing a new cosmological whodunit
— ' It could be profound ' : How astronomer Wendy Freedman is test to repair the universe
— James Webb telescope discovers old ignominious cakehole in the universe
The investigator suggest their findings will help astronomers to better understand how the architecture of genius system is fabricate , and how often habitable systems like our own come up into being .

" The question we are attempt to contextualize is whether this whole process of terrestrial and giant planet establishment is common or rare , and the even more basic question : Are planetal systems like the solar organisation that uncommon ? " study co - author Kadin Worthen , a doctorial student in astrophysics at Johns Hopkins University , said in the financial statement . " We ’re basically trying to understand how weird or average we are . "














